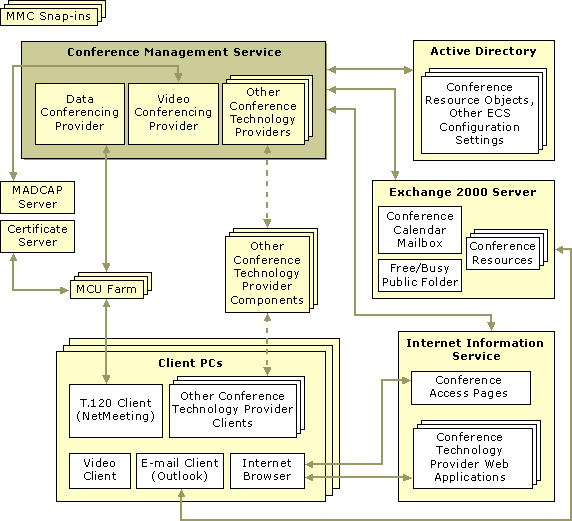
Exchange Conferencing Server contains a group of interrelated components and services that work together to provide real-time conferencing. In addition to these internal features, external components and services from other products are necessary for Exchange Conferencing Server to work. This section discusses these internal and external components and services and the recommended client configuration.
The following figure illustrates how these components and services relate to one another. A description of each component follows.

Figure 2.1 Exchange 2000 Conferencing Server interrelated components and services
The following components and services are included with Exchange 2000 Conferencing Server.
Conference Management Service manages conference technology providers and allows for the management of conference resources, scheduled conference profiles, conference duration, and verification of attendee access rights. Conference Management Service controls the client’s access to all online conferences. Clients access conference access pages from a Web site hosted by IIS.
Data Conferencing Provider is a conference technology provider consisting of a controller —which must be installed on the same server as Conference Management Service — and one or more T.120 MCUs. You can install MCUs on a separate server that does not have other Exchange Conferencing Server or Exchange components.
Video Conferencing Provider is always installed with Conference Management Service. In addition, MADCAP must be installed on a server on the network for video conferencing to function.
Conference participants use these HTML pages to join and participate in conferences. Exchange Conferencing Server uses IIS to host the conference access pages. A portion of the access control for these pages is based on IIS settings for public or private conferences.
The T.120 MCU service runs as a component of Data Conferencing Provider and is used to interconnect network connections between participants in a data conference. The MCU communicates with the Data Conferencing Provider controller through a distributed Component Object Model (COM) session and with conference participants through the T.120 protocol. You must install an MCU to have online data conferences. You can install MCUs on Windows 2000 sites with Conference Management Service, or without it. If you install an MCU on a Windows 2000 site without Conference Management Service, you must be able to connect to another site running Conference Management Service.
The H.323 video conference bridge service runs as a component of the T.120 MCU. It permits clients with NetMeeting that are unable to connect directly to Video Conferencing Provider multicast conferences to connect through a H.323 unicast session.
In addition to the two conference technology providers that Exchange Conferencing Server includes, Conference Management Service can accommodate third-party conference technology providers that are specifically designed for it.
The following are additional components and services that are required for Exchange Conferencing Server. These are required components and services that must be present on your Windows 2000 site or on your client’s computers in order to use all of the features of Exchange Conferencing Server.
Exchange Conferencing Server uses Exchange 2000 Server to store the conference schedule and reserve conference resources. This makes it easy to apply Exchange policies to elements of Exchange Conferencing Server.
Exchange Conferencing Server uses two types of Exchange mailboxes: a conference calendar mailbox and a conference resource mailbox. The conference calendar mailbox stores the definitions and structure of all conferences. The conference resource mailbox is invited to a conference to reserve the virtual conference room of the conference technology providers hosting the conference.
MADCAP servers must exist on the network and routers must be multicast-aware for multicast video conferences to work. Servers running DHCP can assign multicast and unicast addresses. You configure multicast scopes and corresponding multicast IP ranges with Administrative Tools on Windows 2000. This is required before users can successfully schedule and conduct video conferences.
The T.120 MCU uses Certificate Services to enroll in the X509v3 public certificate authentication. The MCU uses these certificates to authenticate conference participants and connections with other MCUs during secure data conferences.
Conference participants can obtain client certificates from Certificate Services. To join private conferences, participants using NetMeeting 3.01 must have client certificates.
Exchange Conferencing Server stores all configuration information in Active Directory. This facilitates multimaster, remote, and offline administration. Exchange Conferencing Server also uses information in Active Directory to access the network topology.
Exchange Conferencing Server and conference technology providers use Microsoft Management Console (MMC) for system administration.
Clients running Windows 2000 can participate in multicast video conferences because Windows 2000 is multicast-enabled. Windows 2000 includes Telephony Application Programming Interface (TAPI) 3.0 telephony libraries. Exchange Conferencing Server uses these libraries support multicast video conferencing.
Internet Explorer 4.01 or higher is recommended, but a browser that supports frames and JavaScript will also work. Conference participants use an Internet browser to participate in conferences through conference access pages.
Conference organizers use an e-mail client to schedule conferences and reserve conference resources. Outlook 2000 is the preferred e-mail client for Exchange Conferencing Server. You can also use previous versions of Outlook or Outlook Web Access.
NetMeeting 3.01 is the preferred T.120 client. This application allows conference participants to connect to an MCU and send and receive data during a data conference. You can also use other T.120-compliant applications.