Applies to: Exchange Server 2010 SP3, Exchange Server 2010 SP2
Topic Last Modified: 2011-03-19
Microsoft Exchange Server 2010 Unified Messaging (UM) provides an efficient and simple deployment model that's highly scalable but doesn't increase the complexity of the deployment. There are many deployment models for Unified Messaging in your organization. The recommended deployment model for Unified Messaging centralizes your Unified Messaging servers. Microsoft Exchange Server 2007 and or later versions contain Unified Messaging features. Versions that are earlier than Exchange 2007 can't be upgraded and require you to deploy an Exchange 2010 organization with all the Exchange server roles, including Unified Messaging, and then move the Microsoft Exchange Server 2003 (or earlier) mailboxes to an Exchange 2010 Mailbox server. For details, see Move Mailboxes from Exchange 2003 Servers to Exchange 2010 Servers.
The following illustration shows the steps that are required to successfully deploy a new Unified Messaging environment.
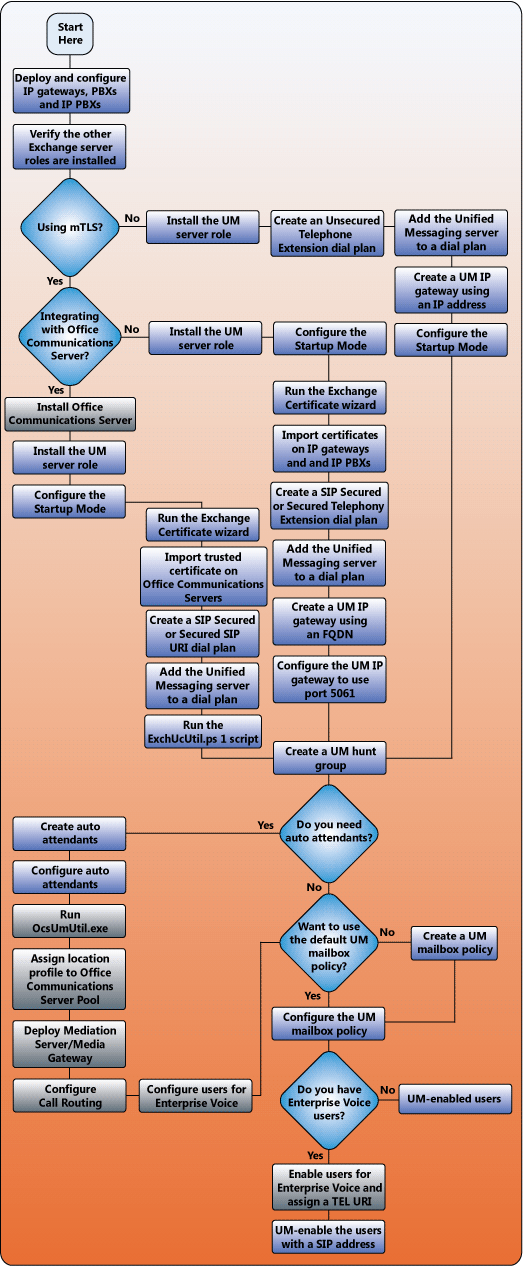
Contents
Before You Deploy
Before you deploy Exchange 2010 Unified Messaging, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with the concepts in the following topics:
- Overview of
Unified Messaging
- Understanding Unified
Messaging Dial Plans
- Understanding Unified
Messaging Mailbox Policies
- Understanding Unified
Messaging IP Gateways
- Understanding Unified
Messaging Hunt Groups
- Understanding Unified
Messaging Auto Attendants
- Understanding Unified
Messaging Servers
- Understanding Unified
Messaging Users
Deploying Unified Messaging
All the available deployment options for Unified Messaging have several steps in common. These steps are required to create a scalable and highly available system to support large numbers of Unified Messaging users. These steps are as follows:
- Deploy and configure your telephony components for Unified
Messaging.
- Verify that you've correctly installed the Exchange 2010 server
roles that are required by Unified Messaging.
- Install the Unified Messaging server role.
- Create and configure the required Unified Messaging Active
Directory components.
- Perform post deployment tasks for Unified Messaging.
- If you're looking for a checklist of tasks that must be
performed to deploy a new UM environment, see Checklist: Deploy a New
Exchange 2010 RTM UM Environment.
Deploy and Configure Telephony Components
To successfully deploy an Exchange 2010 Unified Messaging server in an Exchange organization, the Exchange administrator must become knowledgeable about data networking concepts and telephony terminology and concepts and be able to correctly configure the telephony components that are required by Unified Messaging. Performing a new deployment or upgrading a legacy voice mail system requires significant knowledge about PBXs and Exchange 2010 Unified Messaging. For more information, see the Microsoft Exchange Server 2007 Unified Messaging (UM) Specialists Web site.
Generally, there are three tasks that must be completed to successfully configure the telephony components that are required by Unified Messaging:
- Provision PBX lines The first step in
deploying a scalable UM solution is to provision PBX lines.
- Organize channels After you provision
PBX-based voice channels, you can organize the channels as hunt
groups.
- Deploy IP gateways After you organize
your voice channels as hunt groups, you must end these channels at
IP gateways. IP gateways are used with a legacy PBX to convert the
circuit-switched protocols found on a telephony network to IP-based
packet-switched protocols.
When you integrate your organization's telephony and data networks during the deployment of Exchange 2010 Unified Messaging, you must configure the telephony and data networking components correctly. You must also configure the following components or interfaces to successfully deploy Unified Messaging:
- Configure the connection from the PBXs in your organization
to communicate with your IP gateways. For details, see Configure an IP Gateway
to Communicate with a PBX.
- Configure the connection from the IP gateway interface to
the PBX. For more information about how to configure your PBX
interface to communicate with your supported IP gateway, see the
product documentation that's specific to your PBX. For details, see
Configure an IP
Gateway to Communicate with a PBX.
- Configure the connection from the IP gateway interface to
the Exchange Server 2010 Unified Messaging
server. For details, see Configure an IP Gateway
or IP PBX for Use with a Unified Messaging Server.
- Configure the connection from the Unified Messaging server
to the IP gateway interface. For details, see Connect a Unified
Messaging Server to a Supported IP Gateway.
For more information about telephony components, see Understanding Telephony Concepts and Components.
Verify Installation of the Mailbox, Hub Transport, and Client Access Server Roles
Different deployment paths are available for organizations that plan to deploy Exchange 2010. Although these paths all lead to the same end—a successful deployment of Exchange 2010—each path is slightly different because each customer's needs and starting points are different. However, generally there are common starting points and paths that cover all supported deployment scenarios, including new installations and upgrades. Because Unified Messaging relies on the functionality of other server roles found in Exchange 2010, the Unified Messaging server role will most likely be the last server role that you install in your Exchange 2010 organization. You must follow these steps to install the server roles other than Unified Messaging before you can install the Unified Messaging server role:
- Verify that your existing infrastructure meets certain
prerequisites before you install Exchange 2010. For details, see
Exchange 2010
Prerequisites.
- Verify that you've correctly installed the Exchange 2010 server
roles required by Unified Messaging. After you install Exchange
2010, we recommend that you verify the installation and review the
server setup logs. For details, see Verify an Exchange 2010
Installation.
Install the Unified Messaging Server Role
After you've completed the deployment of your IP gateways or IP PBXs on your network, you must install the Unified Messaging server role on one or more computers in your Exchange environment. Depending on the needs of your business, to provide a highly scalable and available Unified Messaging system, consider installing the Unified Messaging server role on more than one computer. For more information about how to plan and deploy a highly available and scalable Unified Messaging system, see Understanding Unified Messaging Availability or Understanding Unified Messaging Performance and Scalability.
Follow these steps to install the Unified Messaging server role:
- Review the Exchange 2010 system requirements before
installation.
Before you install the Unified Messaging server role, we recommend that you make sure that your network, hardware, software, clients, and other elements meet the requirements for Exchange 2010. For details, see Exchange 2010 System Requirements.
- Install the Unified Messaging server role.
There's more than one way to install the Unified Messaging server role on a computer that's running Exchange 2010. The Unified Messaging server role can be installed on a single computer that has no other Exchange 2010 server roles installed, or on a computer that's running another Exchange 2010 server role. Before you install the Unified Messaging server role, you must install the Mailbox, Hub Transport, and the Client Access server roles. However, you can install the Mailbox, Hub Transport, Client Access and the Unified Messaging server roles on the same physical computer. For details, see Install the Exchange 2010 Unified Messaging Server Role.
- Verify your Exchange 2010 Unified Messaging
installation.
After you install Exchange 2010, we recommend that you verify the installation and review the server setup logs. If the Setup process fails or errors occur during installation, you can use the setup logs to track down the source of the problem. For details, see Verify an Exchange 2010 Installation.
- Download and Install the Unified Messaging Language
Packs.
After you install Exchange 2010, you may have to download and install the required Unified Messaging Service Pack 1 (SP1) language packs you need on the UM servers in your organization. Make sure to install each UM language pack on each UM server and to set the default language on all dial plans that the UM server is associated with.
Exchange Unified Messaging language packs are version-specific and platform-specific. Since Exchange 2007, there have been separate releases for UM language packs, including Exchange 2007 RTM, Exchange 2007 SP1, Exchange 2010 RTM, and Exchange 2010 SP1. For some of these versions, both 32-bit and 64-bit downloads are available, but for other releases only 64-bit downloads are available. It's very important that you install the correct version and platform of the UM language packs on a UM server.
For more information about how to install a UM language pack, see Install a Unified Messaging Language Pack on a UM Server. To download Unified Messaging language packs, see Exchange Server 2010 UM Language Packs.
Create and Configure UM Components
There are several UM components in Active Directory that are required for the deployment and operation of Exchange 2010 Unified Messaging. Unified Messaging components in Active Directory connect the telephony infrastructure with the Unified Messaging Active Directory environment. After you've successfully installed the Unified Messaging server role on at least one computer, follow these steps.
Step 1: Create and configure UM dial plans
UM dial plans are integral to the operation of Exchange 2010 Unified Messaging and are required to successfully deploy Unified Messaging on your network. After you've successfully installed the Unified Messaging server role, a UM dial plan will be the first Active Directory component that you'll create.
By default, UM dial plans and the Unified Messaging servers that are associated with the dial plan send and receive data without using encryption. In Unsecured mode, the VoIP and SIP traffic won't be encrypted. When you create the dial plan or after you've created the dial plan, you can configure the dial plan to encrypt the VoIP and SIP traffic by using Mutual Transport Layer Security (mutual TLS). After you configure the VoIP security setting, you'll then have to configure the startup mode for the UM server. For details, see Configure the Startup Mode on a UM Server.
Perform one of the following procedures to create a new UM dial plan.
Use the EMC to create a UM dial plan
You need to be assigned permissions before you can perform this procedure. To see what permissions you need, see the "UM dial plans" entry in the Unified Messaging Permissions topic.
- In the console tree, navigate to Organization
Configuration > Unified Messaging.
- In the action pane, click New UM Dial Plan.
- In the New UM Dial Plan wizard, complete the following
fields:
- Name Type the name of the dial plan. A
UM dial plan name is required and must be unique. However, the name
you type is used only for display purposes in the EMC and the
Shell. If you have to change the display name of the dial plan
after it's been created, you must first delete the existing UM dial
plan and then create another dial plan that has the appropriate
name. If your organization uses multiple UM dial plans, we
recommend that you use meaningful names for your UM dial plans. The
maximum length of a UM dial plan name is 64 characters, and it
can include spaces. However, it can't include any of the following
characters: " / \ [ ] : ; | = , + * ? < >.
 Important:
Important:Although the field for the name of the dial plan can accept 64 characters, the name of the dial plan can't be longer than 49 characters. This is because, when you create a dial plan, a default UM mailbox policy is also created that has the name <DialPlanName> Default Policy. The name parameter for both the UM dial plan and UM mailbox policy can be 64 characters long. - Number of digits in extension
numbers Enter the number of digits for
extension numbers in the dial plan. The number of digits for
extension numbers is based on the telephony dial plan created on a
Private Branch eXchange (PBX). For example, if a user associated
with a telephony dial plan dials a four-digit extension to call
another user in the same telephony dial plan, you select 4 as the
number of digits in the extension.
This is a required field that has a value range from 1 through 20. The typical extension length is from 3 through 7. If your existing telephony environment includes extension numbers, you must specify a number of digits that matches the number of digits in those extensions.
When you create a Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) dial plan or an E.164 dial plan and associate a UM-enabled user with the dial plan, you must still enter an extension number to be used by the user. This number is used by Outlook Voice Access users when they access their Exchange 2010 mailbox.
- URI Type Use this drop-down list to
select the URI type for the UM dial plan. A URI is a string of
characters that identifies or names a resource. The main purpose of
this identification is to enable VoIP devices to communicate with
other devices over a network using specific protocols. URIs are
defined in schemes that define a specific syntax, format, and the
protocols for the call.
You can select one of the following URI types for the dial plan:
Telephone extension This is the most common URI type. The calling and called party information from the IP gateway or IP PBX will be listed in one of the following formats: Tel:512345 or 512345@<IP address>. This is the default URI type for dial plans.
SIP URI Use this URI type if you need a SIP URI dial plan when an IP PBX supports SIP routing or if you're integrating Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 and Exchange Unified Messaging. The calling and called party information from the IP gateway or IP PBX will be listed as a SIP address in the following format: sip:<username>@<domain or IP address>:Port.
E.164 E.164 is an international numbering plan for public telephone systems in which each assigned number contains a country/region code, a national destination code, and a subscriber number. The calling and called party information sent from the IP gateway is listed in the following format: Tel:+14255550123.
 Note:
Note:After you create a dial plan, you will be unable to change the URI type without deleting the dial plan, and then re-creating the dial plan to include the correct URI type. - VoIP Security Use this drop-down list
to select the VoIP security setting for the UM dial plan. By
default, when you create a UM dial plan, it communicates in
unsecured mode. A Unified Messaging server can operate in any mode
configured on a dial plan because the Unified Messaging server is
configured to listen on TCP port 5060 for unsecured requests and on
TCP port 5061 for secured requests at the same time.
You can select one of the following security settings for the dial plan:
Unsecured By default, when you create a UM dial plan, it communicates in unsecured mode, and the Unified Messaging servers associated with the UM dial plan send and receive data from IP gateways, IP PBXs, and other Exchange 2010 computers using no encryption. In unsecured mode, both the Realtime Transport Protocol (RTP) media channel and SIP signaling information aren't encrypted.
SIP secured When you select SIP secured, only the SIP signaling traffic is encrypted, and the RTP media channels still use TCP, which isn't encrypted. Mutual Transport Layer Security (TLS) is used to encrypt the SIP signaling traffic.
Secured When you select Secured, both the SIP signaling traffic and the RTP media channels are encrypted. An encrypted signaling media channel that uses Secure Realtime Transport Protocol (SRTP) also uses mutual TLS to encrypt the VoIP data.
- Country/Region code Use this field to
type the country/region code number to be used for outgoing calls.
This number will automatically be prepended to the telephone number
that's dialed. This field accepts from 1 through 4 digits. For
example, in the United States, the country/region code is 1. In the
United Kingdom, it's 44.
- Name Type the name of the dial plan. A
UM dial plan name is required and must be unique. However, the name
you type is used only for display purposes in the EMC and the
Shell. If you have to change the display name of the dial plan
after it's been created, you must first delete the existing UM dial
plan and then create another dial plan that has the appropriate
name. If your organization uses multiple UM dial plans, we
recommend that you use meaningful names for your UM dial plans. The
maximum length of a UM dial plan name is 64 characters, and it
can include spaces. However, it can't include any of the following
characters: " / \ [ ] : ; | = , + * ? < >.
- On the Set UM Servers page, click Add and then on
the Select UM Server page select the UM server that you want
to add to the UM dial plan.
- On the Completion page, confirm whether the dial plan
was successfully created:
- A status of Completed indicates that the wizard
completed the task successfully.
- A status of Failed indicates that the task wasn't
completed. If the task fails, review the summary for an
explanation, and then click Back to make any configuration
changes.
- A status of Completed indicates that the wizard
completed the task successfully.
- Click Finish to complete the New UM Dial Plan
wizard.
Use the Shell to create a UM dial plan
You need to be assigned permissions before you can perform this procedure. To see what permissions you need, see the "UM dial plans" entry in the Unified Messaging Permissions topic.
This example creates a new UM dial plan named
MyUMDialPlan that uses four-digit extension
numbers.
 Copy Code Copy Code |
|
|---|---|
New-UMDialplan -Name MyUMDialPlan -NumberofDigits 4 |
|
This example creates a new UM dial plan named
MyUMDialPlan that uses five-digit extension numbers
and supports SIP URIs:
 Copy Code Copy Code |
|
|---|---|
New-UMDialplan -Name MyUMDialPlan -UriType SIPName -NumberofDigits 5 |
|
For more information about syntax and parameters, see Set-UMDialplan.
Step 2: Create and configure your UM IP gateways
A UM IP gateway represents either an IP gateway hardware device or an IP PBX hardware device. The combination of the UM IP gateway object and a UM hunt group object establishes a logical link between an IP gateway or IP PBX and a UM dial plan.
If you've created or enabled VoIP security on a dial plan, the UM IP gateway that you will create by using one of the following procedures in this section will be associated with a UM dial plan that uses VoIP security. In that case, you must use a fully qualified domain name (FQDN) to create the UM IP gateway, and not an IP address. You must also configure the UM IP gateway to listen on TCP port 5061. To configure a UM IP gateway to listen on TCP port 5061, run the following command: Set-UMIPGateway -identity MyUMIPGateway -Port 5061. You must also verify that any IP gateways or IP PBXs have also been configured to listen on port 5061 for mutual TLS.
Perform one of the following procedures to create a new UM IP gateway.
Use the EMC to create a UM IP gateway
- In the console tree, navigate to Organization
Configuration > Unified Messaging.
- In the result pane, click the UM IP Gateways tab.
- In the action pane, click New UM IP Gateway.
- In the New UM IP Gateway wizard, in the Name
section, type the name of the UM IP gateway. This is the display
name for the UM IP gateway.
- In the IP Address section, type the IP address for the
UM IP gateway, and then click New.
 Note:
Note:Alternatively, you can enter an FQDN for the UM IP gateway. If you choose to use an FQDN, you must add the appropriate host records with the correct IP addresses to the DNS zone. If you're configuring a UM IP gateway that will be associated with a dial plan that's operating in Secured mode, you must create the UM IP gateway with an FQDN. - On the New UM IP Gateway page, click New.
- On the Completion page, click Finish.
Use the Shell to create a UM IP gateway
You need to be assigned permissions before you can perform this procedure. To see what permissions you need, see the "UM IP gateways" entry in the Unified Messaging Permissions topic.
This example creates a UM IP gateway named
MyUMIPGateway that enables a Unified Messaging server
to start accepting calls from an IP gateway that has an IP address
of 10.10.10.1.
 Copy Code Copy Code |
|
|---|---|
New-UMIPGateway -Name MyUMIPGateway -Address 10.10.10.1 |
|
This example creates a UM IP gateway named
MyUMIPGateway that enables a Unified Messaging server
to start accepting calls from an IP gateway that has an FQDN of
MyUMIPGateway.contoso.com and listens on port 5061.
 Copy Code Copy Code |
|
|---|---|
New-UMIPGateway -Name MyUMIPGateway -Address "MyUMIPGateway.contoso.com" -Port 5061 |
|
For more information about syntax and parameters, see New-UMIPGateway.
Step 3: Create and configure your UM hunt groups (optional)
Hunt group is a term that's used to describe a group of PBX or IP PBX resources or extension numbers that are shared by users. Hunt groups are used to efficiently distribute calls into or out of a given business unit.
If you've created a UM IP gateway and associated the UM IP gateway with a UM dial plan, a default UM hunt group is created. You can associate another UM hunt group with the same or a different UM IP gateway, depending on the number of UM IP gateways that you've created.
When you create a UM hunt group, you enable all Unified Messaging servers that are specified within the UM dial plan to communicate with an IP gateway. To learn more about UM hunt groups, see Understanding Unified Messaging Hunt Groups. To create a new UM hunt group, perform one of the following procedures.
Use the EMC to create a UM hunt group
You need to be assigned permissions before you can perform this procedure. To see what permissions you need, see the "UM hunt groups" entry in the Unified Messaging Permissions topic.
- In the console tree, navigate to Organization
Configuration > Unified Messaging.
- In the work pane, click the UM IP Gateways tab.
- In the result pane, select a UM IP gateway.
- In the action pane, click New UM Hunt Group.
- In the New UM Hunt Group wizard, view or complete the following
fields:
- Associated UM IP gateway This
display-only field shows the name of the UM IP gateway that will be
associated with the UM hunt group.
- Name Use this text box to create the
display name for the UM hunt group. A UM hunt group name is
required and must be unique, but it's used only for display
purposes in the EMC and the Shell. If you have to change the
display name of the hunt group after it's been created, you must
first delete the existing hunt group and then create another hunt
group that has the appropriate name.
If your organization uses multiple hunt groups, we recommend that you use meaningful names for your hunt groups. The maximum length of a UM hunt group name is 64 characters, and it can include spaces. However, it can't include any of the following characters: " / \ [ ] : ; | = , + * ? < >.
- Dial plan Click the Browse
button to select the dial plan that will be associated with the UM
hunt group. Associating a hunt group with a dial plan is required.
A UM hunt group can be associated with only one UM IP gateway and
one UM dial plan.
- Pilot identifier Use this text box to
specify a string that uniquely identifies the pilot identifier or
pilot ID configured on the PBX or IP PBX.
An extension number or a SIP URI can be used in this field. Alphanumeric characters are accepted in this field. For legacy PBXs, a numeric value is used as a pilot identifier. However, some IP PBXs can use SIP URIs.
- Associated UM IP gateway This
display-only field shows the name of the UM IP gateway that will be
associated with the UM hunt group.
- On the Completion page, confirm whether the UM hunt
group was successfully created:
- A status of Completed indicates that the wizard
completed the task successfully.
- A status of Failed indicates that the task wasn't
completed. If the task fails, review the summary for an
explanation, and then click Back to make any configuration
changes.
- A status of Completed indicates that the wizard
completed the task successfully.
- Click Finish to complete the New UM Hunt Group
wizard.
Use the Shell to create a UM hunt group
You need to be assigned permissions before you can perform this procedure. To see what permissions you need, see the "UM hunt groups" entry in the Unified Messaging Permissions topic.
This example creates a UM hunt group named
MyUMHuntGroup that has a pilot identifier of
12345.
 Copy Code Copy Code |
|
|---|---|
New-UMHuntGroup -Name MyUMHuntGroup -PilotIdentifier 12345 -UMDialplan MyUMDialPlan -UMIPGateway MyUMIPGateway |
|
This example creates a UM hunt group named
MyUMHuntGroup that has multiple pilot identifiers.
 Copy Code Copy Code |
|
|---|---|
New-UMHuntGroup -Name MyUMHuntGroup -PilotIdentifier 5551234,55555 -UMDialplan MyUMDialPlan -UMIPGateway MyUMIPGateway |
|
For more information about syntax and parameters, see New-UMHuntGroup.
Step 4: Create and configure a UM mailbox policy
UM mailbox policies are required when you enable users for Exchange 2010 Unified Messaging. The mailbox of each UM-enabled user must be linked to a single UM mailbox policy. After you create a UM mailbox policy, you link one or more UM-enabled mailboxes to the UM mailbox policy. This lets you control PIN security settings such as the minimum number of digits in a PIN or the maximum number of failed sign-in attempts for the UM-enabled users who are associated with the UM mailbox policy.
Every time that you create a UM dial plan, a UM mailbox policy is also created. The UM mailbox policy will be named <DialPlanName> Default Policy. However, if you have to create a new UM mailbox policy, perform one of the following procedures.
Use the EMC to create a UM mailbox policy
You need to be assigned permissions before you can perform this procedure. To see what permissions you need, see the "UM mailbox policies" entry in the Unified Messaging Permissions topic.
- In the console tree, navigate to Organization
Configuration > Unified Messaging.
- In the work pane, click the UM Mailbox Policies tab.
- In the action pane, click New UM Mailbox Policy.
- In the New UM Mailbox Policy wizard, complete the following
fields:
- Name Use this text box to specify a
unique name for the UM mailbox policy. If you must change the
display name of the UM mailbox policy after it's been created, you
must first delete the existing UM mailbox policy, and then create
another UM mailbox policy that has the appropriate name. To delete
the UM mailbox policy, there must not be any UM-enabled users
associated with the UM mailbox policy.
The UM mailbox policy name is required, but it's used for display purposes only. Because your organization may use multiple UM mailbox policies, we recommend that you use meaningful names for your UM mailbox policies. The maximum length of a UM mailbox policy name is 64 characters, and it can include spaces. However, it cannot include any of the following characters: " / \ [ ] : ; | = , + * ? < >.
- Select associated dial plan Click
Browse to select the UM dial plan that will be associated
with the UM mailbox policy. You must associate a UM mailbox policy
with at least one UM dial plan. However, you can also associate
multiple UM mailbox policies with a single dial plan.
- Name Use this text box to specify a
unique name for the UM mailbox policy. If you must change the
display name of the UM mailbox policy after it's been created, you
must first delete the existing UM mailbox policy, and then create
another UM mailbox policy that has the appropriate name. To delete
the UM mailbox policy, there must not be any UM-enabled users
associated with the UM mailbox policy.
- On the Completion page, confirm whether the UM mailbox
policy was successfully created:
- A status of Completed indicates that the wizard
completed the task successfully.
- A status of Failed indicates that the task wasn't
completed. If the task fails, review the summary for an
explanation, and then click Back to make any configuration
changes.
- A status of Completed indicates that the wizard
completed the task successfully.
- Click Finish to complete the New UM Mailbox Policy
wizard.
Use the Shell to create a UM mailbox policy
You need to be assigned permissions before you can perform this procedure. To see what permissions you need, see the "UM mailbox policies" entry in the Unified Messaging Permissions topic.
This example creates a UM mailbox policy named
MyUMMailboxPolicy associated with a UM dial plan named
MyUMDialPlan.
 Copy Code Copy Code |
|
|---|---|
New-UMMailboxPolicy -Name MyUMMailboxPolicy -UMDialPlan MyUMDialPlan |
|
For more information about syntax and parameters, see New-UMMailboxPolicy.
Step 5: Add a Unified Messaging server to dial plans
After you install the Unified Messaging server role, the UM server can't answer incoming calls until you add it to a UM dial plan. Although the status of the Exchange 2010 Unified Messaging server is set to enabled after installation, there's a parameter that's used to enable or disable the status of the Unified Messaging server.
A Unified Messaging server can be associated with a single or multiple UM dial plans. A single UM server can be added to a multiple dial plans that use mutual TLS (Secured), SIP secured, or TCP (Unsecured). To add a UM server to a dial plan, perform one of the following procedures.
Use the EMC to add a UM server to a dial plan
You need to be assigned permissions before you can perform this procedure. To see what permissions you need, see the "UM dial plans" entry in the Unified Messaging Permissions topic.
- In the console tree, click Server Configuration.
- In the result pane, select the Unified Messaging server you
want to add to a dial plan.
- In the action pane, click Properties.
- On the UM Settings > Associated Dial Plans,
click Add.
- In the Select Dial Plan window, from the list of
available dial plans, select the dial plan you want to add the UM
server to, and then click OK.
Use the Shell to add a UM server to a dial plan
You need to be assigned permissions before you can perform this procedure. To see what permissions you need, see the "UM dial plans" entry in the Unified Messaging Permissions topic.
This example adds a Unified Messaging server to a dial
plan named MyUMDialPlan and prevents the UM server
from accepting new calls. It also sets the startup mode to dual
mode, which enables the UM server to accept TCP and TLS
requests.
 Copy Code Copy Code |
|
|---|---|
Set-UMServer -Identity MyUMServer -DialPlans MyUMDialPlan -Status Disabled -UMStartupMode Dual |
|
This example adds the Unified Messaging server named
MyUMServer to two UM dial plans, named
MyUMDialPlan and MyUMDialPlan2, and also
sets the maximum number of incoming voice and fax calls.
 Copy Code Copy Code |
|
|---|---|
Set-UMServer -Identity MyUMServer -DialPlans MyUMDialPlan, MyUMDialPlan2 -MaxCallsAllowed 50 |
|
For more information about syntax and parameters, see Set-UMServer.
Step 6: Create and configure UM auto attendants (optional)
Exchange 2010 Unified Messaging enables you to create one or more UM auto attendants, depending on the needs of your organization. When you create a UM auto attendant, you create a voice menu system for your organization. Callers from outside or inside your organization can then move through the menu system to locate and place or transfer calls to users or departments in your organization.
Callers can move through the menu system by using dual tone multi-frequency (DTMF), also known as touchtone, or voice inputs. For automatic speech recognition (ASR) to work, so users can use voice inputs, you must speech-enable the UM auto attendant.
Creating and using auto attendants is optional in Exchange 2010 Unified Messaging. However, if you want to create a new UM auto attendant, perform one of the following procedures.
Use EMC to create a UM auto attendant
You need to be assigned permissions before you can perform this procedure. To see what permissions you need, see the "UM auto attendants" entry in the Unified Messaging Permissions topic.
- In the console tree, navigate to Organization
Configuration > Unified Messaging.
- In the work pane, click the UM Auto Attendants tab.
- In the action pane, click New UM Auto Attendant.
- In the New UM Auto Attendant wizard, complete the following
fields:
- Name Use this text box to create the
display name for the UM auto attendant. A UM auto attendant name is
required and must be unique. However, it's used only for display
purposes in the EMC and the Shell.
If you have to change the display name of the auto attendant after it's created, you must first delete the existing UM auto attendant and then create another UM auto attendant that has the appropriate name. If your organization uses multiple UM auto attendants, we recommend that you use meaningful names for your UM auto attendants. The maximum length of a UM auto attendant name is 64 characters, and it can include spaces.
- Select associated dial plan Click
Browse to select the UM dial plan to associate with this UM
auto attendant. Selecting and associating a UM dial plan with the
auto attendant is required. A UM auto attendant can be associated
with only one UM dial plan.
- Extension numbers Use this field to
enter the extension number that callers will use to reach the auto
attendant. Type an extension number in the box, and then click
Add to add the number to the list. The number of digits in
the extension number that you provide doesn't have to match the
number of digits for an extension number configured on the
associated UM dial plan. This is because direct calls are allowed
to UM auto attendants.
You can also create a new auto attendant without adding an extension number, because an extension number isn't required.
You can edit or remove an existing extension number. To edit an existing extension number, click Edit. To remove an existing extension number from the list, click Remove.
- Create auto attendant as enabled Select
this option to enable the auto attendant to answer incoming calls
when you complete the New UM Auto Attendant wizard. By default, a
new auto attendant is created as disabled.
If you decide to create the UM auto attendant as disabled, you can use the EMC or the Shell to enable the auto attendant after you finish the wizard.
- Create auto attendant as
speech-enabled Select this check box to
speech-enable the UM auto attendant. When you speech-enable the
auto attendant, callers will be able to respond to the system or
custom prompts used by the UM auto attendant using touchtone or
voice inputs. By default, the auto attendant won't be
speech-enabled when it's created.
For callers to use a speech-enabled auto attendant, you must install the appropriate Unified Messaging language pack that contains Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) support and configure the properties of the auto attendant to use this language.
- Name Use this text box to create the
display name for the UM auto attendant. A UM auto attendant name is
required and must be unique. However, it's used only for display
purposes in the EMC and the Shell.
- On the Completion page, confirm whether the UM auto
attendant was successfully created:
- A status of Completed indicates that the wizard
completed the task successfully.
- A status of Failed indicates that the task wasn't
completed. If the task fails, review the summary for an
explanation, and then click Back to make any configuration
changes.
- A status of Completed indicates that the wizard
completed the task successfully.
- Click Finish to complete the New UM Auto Attendant
wizard.
Use the Shell to create a new UM auto attendant
You need to be assigned permissions before you can perform this procedure. To see what permissions you need, see the "UM auto attendants" entry in the Unified Messaging Permissions topic.
This example creates a UM auto attendant named
MyUMAutoAttendant that can accept incoming calls but
isn't speech-enabled.
 Copy Code Copy Code |
|
|---|---|
New-UMAutoAttendant -Name MyUMAutoAttendant -UMDialPlan MyUMDialPlan -PilotIdentifierList 55000 -Enabled $true |
|
This example creates a speech-enabled UM auto attendant
named MyUMAutoAttendant.
 Copy Code Copy Code |
|
|---|---|
New-UMAutoAttendant -Name MyUMAutoAttendant -UMDialPlan MyUMDialPlan -PilotIdentifierList 56000,56100 -SpeechEnabled $true |
|
For more information about syntax and parameters, see New-UMAutoAttendant.
After you've created a non-speech-enabled or a speech-enabled auto attendant, you must create and configure key mappings so that the auto attendant can function correctly. If you don't enable key mappings for either business or non-business hours, callers will hear the voice prompts but won't be able to interact with the auto attendant. To create key mappings for an auto attendant, see the following topics:
Post Deployment Tasks for Unified Messaging
After you complete a new installation of the Unified Messaging server role and have successfully deployed Unified Messaging, you should complete the post-installation tasks. The post-deployment tasks will help you enable users for Unified Messaging, secure your UM deployment, and deploy incoming faxing for UM-enabled users.
Enabling Users for Unified Messaging
After you've deployed your IP gateways or IP PBXs, installed the Unified Messaging server role, and created the Active Directory components for Unified Messaging, you must enable your users for Unified Messaging. For details, Enable a User for Unified Messaging.
Secure Your UM Deployment
You can help increase the level of protection for your network if you correctly plan a UM security strategy and then correctly configure the security settings for UM servers and UM-enabled users.
Mutual TLS for UM
To use mutual TLS to encrypt SIP and Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) traffic that's sent and received by your Unified Messaging servers, perform the following tasks:
- Run the Exchange Certificate wizard. For details, see Create a New Exchange
Certificate.
- Associate the certificate with the UM server.
- Import the required certificates on the IP gateways and the IP
PBX and Unified Messaging servers in your organization. To import
an Exchange certificate, see Import an Exchange
Certificate.
- Configure VoIP security on the UM dial plans. For details, see
Configure VoIP
Security on a UM Dial Plan.
- Configure the startup mode on the Unified Messaging server. For
details, see Configure the Startup
Mode on a UM Server.
- Configure the UM IP gateways to listen on port 5061. For
details, see Configure the TCP
Listening Port on a UM IP Gateway.
For more information about VoIP security with Unified Messaging, see Understanding Unified Messaging VoIP Security.
PIN Policies for UM-enabled Users
In Exchange 2010 Unified Messaging, PIN policies are defined and configured on a UM mailbox policy. Multiple UM mailbox policies can be created, depending on your requirements. When you enable a user for Exchange 2010 Unified Messaging, you associate the user with an existing UM mailbox policy. The UM PIN policies that are configured on the UM mailbox policy should be based on the security requirements of your organization. For more information about how to configure PIN settings for UM-enabled users, see Configuring Security for Unified Messaging Users.
Deploying Faxing
Exchange 2010 UM forwards incoming fax calls to a dedicated fax partner solution, which then establishes the fax call with the fax sender and receives the fax on behalf of the UM-enabled user. However, to allow UM-enabled users to receive fax messages in their mailbox, you must first deploy Exchange 2010 Unified Messaging, set up and configure the fax partner server, and then configure the UM dial plans, UM mailbox policies, and UM-enabled users to receive faxes. For details, see Deploy and Configure Incoming Faxing.

