Applies to: Exchange Server 2010 SP3, Exchange Server 2010 SP2
Topic Last Modified: 2012-07-23
The instructions in this topic will walk you through the steps required to migrate from Exchange 2007 ACL-based global address list (GAL) segmentation (also known as GAL segregation) to Exchange 2010 Service Pack 2 (SP2) address book policies (ABPs).
 Important: Important: |
|---|
| Several procedures in this topic will impact users. As a result, scheduled downtime is often required. |
Prerequisites
- Although not a specific prerequisite, it’s highly recommended
that you review the considerations and best practices in Understanding Address
Book Policies before performing the procedures in this
topic.
- The procedures in this topic assume that you followed the steps
in the white paper Configuring Virtual Organizations and
Address List Segregation in Exchange 2007 to configure your
Exchange 2007 organization.
- If you followed the steps in the white paper listed above to
implement GAL segmentation in your Exchange 2010 organization, you
are officially in an unsupported state. To successfully perform the
procedures in this topic, you must first return your organization
to a supported state.
- Most of the code and Shell examples in this document use
Contoso as the Active Directory domain name and the Exchange
organization name, and Fabrikam, and Tailspin Toys as
the sub-organization names. Be sure to change the name of the
Exchange organization, domain, and sub-organizations to match your
configuration.
- You will need the scripts that you used to segment the virtual
organizations in Exchange 2007.
Setting Up the Scenario
In this scenario, Tailspin Toys and Fabrikam are subsidiaries of the parent company Contoso.
Step1: Prepare to install Exchange 2010 SP2 in an existing Exchange 2007 organization that has configured GAL segmentation (downtime required)
If your organization is using Exchange 2007 GAL segmentation, installing Exchange 2010 will fail because using GAL segmentation required you to remove all the default settings and permissions from the default GAL.
- On a domain controller in the Exchange 2007 organization, run
the following command at the command prompt to allow access to the
default GAL.
 Copy Code
Copy CodeDSACLS "CN=Default Global Address List,CN=All Global Address Lists,CN=Address Lists Container,CN=CONTOSO,CN=Microsoft Exchange,CN=Services,CN=Configuration,DC=contoso,DC=com" /N /G contoso\administrator:RP
- On a domain controller that has Windows PowerShell installed or
on an Exchange server using the Exchange Management Shell, run the
following commands to reconfigure the default settings on the
GAL.
 Note:
Note:After you complete this step, Outlook 2007 users will be able to see the default GAL. However, Outlook Web App users won’t be able to see the default GAL because Outlook Web App uses the QueryBaseDNattribute to query the GAL.You will receive the following warning and output: Copy Code
Copy Code$container = "CN=Default Global Address List,CN=All Global Address Lists,CN=Address Lists Container,CN=CONTOSO,CN=Microsoft Exchange,CN=Services, CN=Configuration,DC=contoso,DC=com"Add-ADPermission $container -User "Authenticated Users" -AccessRights GenericRead, ListChildren -ExtendedRights Open-Address-Book
 Copy Code
Copy CodeWARNING: Appropriate ACE is already present on object "CN=Default Global Address List,CN=All Global Address Lists,CN=Address Lists Container,CN=CONTOSO,CN=Microsoft Exchange,CN=Services,CN=Configuration,DC=CONTOSO,DC=COM" for account "NT AUTHORITY\Authenticated Users" Identity User Deny Inherited Rights -------- ---- ---- --------- ------ \Default Global A... NT AUTHORITY\Auth... False False Open-Address-Book \Default Global A... NT AUTHORITY\Auth... False False ReadProperty \Default Global A... NT AUTHORITY\Auth... False False ListObject, Generi... \Default Global A... NT AUTHORITY\Auth... False False ListChildren
Step 2: Install the first Exchange 2010 server
For detailed instructions, see Upgrade from Exchange 2007 Client Access
Step 3: Secure the default GAL
After you install Exchange 2010 SP2, you can remove the address lists that are created during installation and then secure the default GAL again. After you complete this step, you can continue to install additional Exchange 2010 SP2 servers in your organization. For more information, see Understanding Upgrade from Exchange 2007 to Exchange 2010.
- (Optional) On an Exchange 2010 server, use the Shell to remove
the newly created address lists.
For more detail, see Remove an Address List. Copy Code
Copy CodeRemove-AddressList "All Contacts" Remove-AddressList "All Groups" Remove-AddressList "All Users" Remove-AddressList "Public Folders"
- On an Exchange 2010 server, use the Shell to secure the GAL
based on the instructions in the white paper Configuring Virtual Organizations and
Address List Segregation in Exchange 2007.
 Copy Code
Copy CodeGet-GlobalAddressList "Default Global Address List" | Add-ADPermission -User "Authenticated Users" -AccessRights GenericRead -ExtendedRights Open-Address-Book -Deny:$True
- To verify that the commands were successful, run the following
commands.
The output of this command should resemble the following: Copy Code
Copy Code$galContainer = "CN=All Global Address Lists,CN=Address Lists Container,CN=CONTOSO,CN=Microsoft Exchange,CN=Services,CN=Configuration,DC=contoso,DC=com" Get-ADPermission $galContainer -user "authenticated users"
 Copy Code
Copy CodeIdentity User Deny Inherited Rights -------- ---- ---- --------- ------ All Global Addres... NT AUTHORITY\Auth... False False GenericRead All Global Addres... NT AUTHORITY\Auth... False False Open-Address-Book All Global Addres... NT AUTHORITY\Auth... False True ListChildren All Global Addres... NT AUTHORITY\Auth... True True ReadProperty
Step 4: Switchover to Exchange 2010 servers (downtime required)
Before moving any mailboxes to Exchange 2010 SP2 servers, you must switchover external URL names. This requires configuring Outlook Anywhere, Outlook Web App, Exchange Web Services (EWS), Exchange Control Panel (ECP), AutoDiscover, and offline address books (OABs) to use Exchange 2010 servers instead of Exchange 2007 servers. There are many steps in this process, and you should refer to the information in Exchange 2007 - Planning Roadmap for Upgrade and Coexistence for more detail.
 Note: Note: |
|---|
| The following steps outline only the key procedures in the overall process and explain what each of them accomplishes. You may need to run some of these commands on each server in your organization (some only once), and most will result in some period of downtime. Therefore, it’s strongly recommended that you spend adequate time testing your entire switchover process to ensure minimal impact to your clients. |
- Use the Shell to move all OAB generation to an Exchange 2010
Mailbox server. Moving the OAB generation to Exchange 2010 SP2
servers allows OABs to use GALs and not just address lists as
sources for the OAB content.
For more detail, see Move the Offline Address Book Generation to Another Server. Copy Code
Copy CodeGet-OfflineAddressBook | Move-OfflineAddressBook -Server "MBX01_Ex2010SP2"
- Set the virtual directory for the OAB to include an Exchange
2010 virtual organization. This will distribute copies of the OABs
to the Exchange 2010 servers.
This example ensures both the Exchange 2007 and Exchange 2010 servers have copies of all OABs.
For more detail, see Configure Offline Address Book Distribution Properties. Copy Code
Copy CodeGet-OfflineAddressBook | Set-OfflineAddressBook -virtualdirectories "CAS1_Ex2007\OAB (Default Web Site)","CAS1_Ex2010SP2\OAB (Default Web Site)"
- Before any mailboxes can be moved to Exchange 2010, you must
route all incoming Outlook Anywhere traffic through Exchange
2010.
This example enables Outlook Anywhere on an Exchange 2010 server and disables it on an Exchange 2007 server.
For more detail, see the following topics: Copy Code
Copy CodeEnable-OutlookAnywhere -Server:CAS1_Ex2010SP2 -ExternalHostname:mail.contoso.com -ClientAuthenticationMethod:Basic Disable-OutlookAnywhere -Server:CAS1_Ex2007
- To allow AutoDiscover to properly return URLs from Exchange
2010 servers, you must configure Outlook Web App, Exchange
ActiveSync, EWS, and ECP on all Exchange 2010 servers to have valid
external URL properties for the virtual directories.
The following examples assume that mail.contoso.com is the external name used to access the Exchange 2010 servers.
For more detail about how to configure the above settings, see the following topics: Copy Code
Copy CodeSet-ActiveSyncVirtualDirectory -Identity 'CAS1_Ex2010SP2\Microsoft-Server-ActiveSync*' -ExternalURL https://mail.contoso.com/Microsoft-Server-ActiveSync Set-WebServicesVirtualDirectory -Identity 'CAS1_Ex2010SP2\EWS*' -ExternalUrl https://mail.contoso.com/EWS/exchange.asmx Set-OWAVirtualDirectory -Identity 'CAS1_Ex2010SP2\OWA*' -ExternalURL https://mail.contoso.com/OWA Set-EcpVirtualDirectory -Identity 'CAS1_Ex2010SP2\ECP*' -ExternalURL https://mail.contoso.com/ECP
- To allow Exchange 2010 to redirect Outlook Web App and EWS
requests back to Exchange 2007 for those users with mailboxes on
Exchange 2007 servers, you need to configure the Outlook Web App
and EWS external URL for 2007 to use legacy.contoso.com. This
namespace is the external name used to access the Exchange 2007
servers.
 Copy Code
Copy CodeSet-WebServicesVirtualDirectory -Identity 'CAS1_Ex2007\EWS*' -ExternalUrl https://legacy.contoso.com/EWS/exchange.asmx Set-OWAVirtualDirectory -Identity 'CAS1_Ex2007\OWA*' -ExternalURL https://legacy.contoso.com/OWA
- To allow Exchange 2010 to proxy all incoming Exchange
ActiveSync connections to Exchange 2007, clear the 2007 external
URL for Exchange ActiveSync.
 Copy Code
Copy CodeSet-ActiveSyncVirtualDirectory -Identity 'CAS1_Ex2007\Microsoft-Server-ActiveSync*' -ExternalURL:$null
- The final step in the process is to change the public DNS so
that mail.contoso.com (in the example we provided) and
autodiscover.contoso.com resolve to Exchange 2010, and the
legacy.contoso.com DNS record resolves to Exchange 2007. All client
connections will go through Exchange 2010, and then Exchange 2010
will either redirect (in the case of Outlook Web App), proxy (in
the case of Exchange ActiveSync), or provide version-specific URLs
(in the case of EWS) to clients via AutoDiscover.
Step 5: Create ABPs that mirror the Exchange 2007 address list segmentation ACLs
The next step is to figure out what address lists, GALs, and OABs the virtual organizations have access to using GAL segmentation, and then create an ABP for each virtual organization that mirrors them.
- If you used the steps in Configuring Virtual Organizations and
Address List Segregation in Exchange 2007 to set up your
Exchange 2007 organization, you created scripts that segmented your
virtual organizations. View those scripts that you used to create
the virtual organizations in Exchange 2007 to determine the GAL,
address lists, and OAB for each virtual organization. For each
virtual organization, you should find one GAL, at least one address
list, and one OAB.
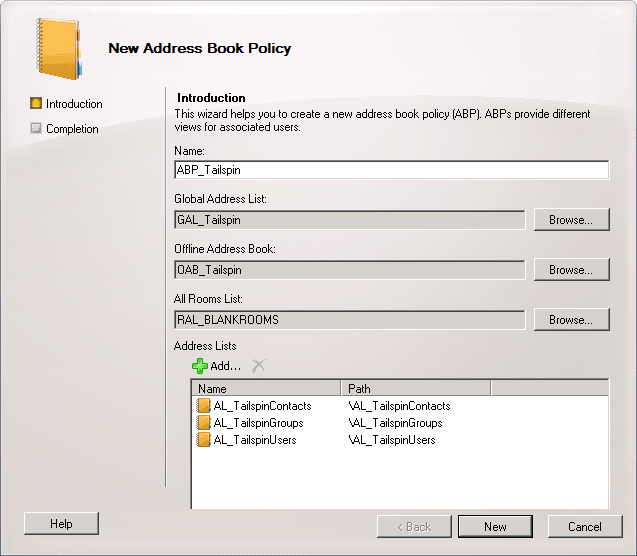
For example, when viewing the script used to segment the child company Tailspin Toys, the following information is located: Note:
Note:ABPs must have a room list. If you don’t use room lists in your organization, create a blank room address list and then use that address list when configuring the ABP or set the room list property in the ABP to use the same address list you specify for the GAL.
- Tailspin Toys users are all contained in a security group
called Tailspin_SG.
- The security group Tailspin_SG grants users read/open access to
the following:
Address Lists
GAL
OAB
AL_TailspinUsers
AL_TailspinGroups
AL_TailspingContacts
GAL_Tailspin
OAB_Tailspin
- Tailspin Toys doesn’t have a room address list.
- Tailspin Toys users are all contained in a security group
called Tailspin_SG.
- Create an ABP that matches the Tailspin Toys organization.
- For example, if you use the Exchange Management Console to
create the ABP in, input the following information in the New
Address Book Policy wizard:
If you use the Shell to create the ABP, run the following command.
For more detail, see Create an Address Book Policy. Copy Code
Copy CodeNew-AddressBookPolicy -Name 'ABP_Tailspin' -GlobalAddressList '\GAL_Tailspin' -OfflineAddressBook '\OAB_Tailspin' -AllRoomList '\RAL_BLANKROOMS' -AddressLists '\AL_TailspinContacts','\AL_TailspinGroups','\AL_TailspinUsers'
- Follow the above instructions for each of your virtual
organizations. For example, Fabrikam.
Step 6: Move mailboxes from Exchange 2007 servers to Exchange 2010 servers (downtime required)
In moving mailboxes to the Exchange 2010 servers, you will be switching over from using the ACLs to using ABPs.
 Note: Note: |
|---|
| We recommend that you create a script that performs this procedure in one step. |
- Move the mailboxes using the MoveRequest cmdlets. For
more information, see Create a Local Move Request.
- Assign the ABP to moved mailboxes. For more information, see
Assign an Address Book Policy to a Mailbox
User (EPW).
- Clear the QueryBaseDN from the user object. This can be done
directly via the Adsiedit.msc console or by using a multi-step
process from the Shell. This example shows how to clear the
QueryBaseDN by using the Shell.
 Copy Code
Copy Code$user = ([ADSI]"LDAP://CN=Bob,CN=Users,DC=Contoso,DC=com").psbase $user.Properties["msExchQueryBaseDN"].Value=$null $user.CommitChanges()
- Remove the OAB setting from the mailbox.
This example removes the OAB from John’s mailbox:
 Copy Code
Copy CodeSet-Mailbox -Identity John -OfflineAddressBook $null
After the mailboxes are moved and all of the other settings have been configured, users using Outlook will get the following error and they will be required to close and restart Outlook: “The Microsoft Exchange Administrator has made a change that requires you to quit and restart Outlook.”
Step 7: What’s next?
So, after you’ve moved all of your mailboxes to Exchange 2010 SP2 and all of the mailboxes are running on ABPs with your ACLs decommissioned, you can start following the standard Exchange guidance for removing the Exchange 2007 organization.
Removing and Modifying Exchange 2007
How to Remove an Exchange 2007 Organization
If you get stuck, this Microsoft Knowledge Base article may help:

