Applies to: Exchange Server 2010 SP3, Exchange Server 2010 SP2
Topic Last Modified: 2010-08-10
Information workers increasingly use e-mail to exchange sensitive information. To help secure this information, organizations can use Information Rights Management (IRM) to apply persistent protection to messaging content. Prior to Microsoft Exchange Server 2010, effective use of IRM protection was limited to Outlook clients. In Exchange Server 2007, Microsoft Outlook Web Access users were required to download the Rights Management add-in for Microsoft Internet Explorer so they could access IRM-protected content.
In Exchange 2010, IRM in Outlook Web App allows your users to access the rich IRM functionality offered by Exchange to apply persistent IRM-protection to messaging content.
The following IRM functionality is available in Outlook Web App:
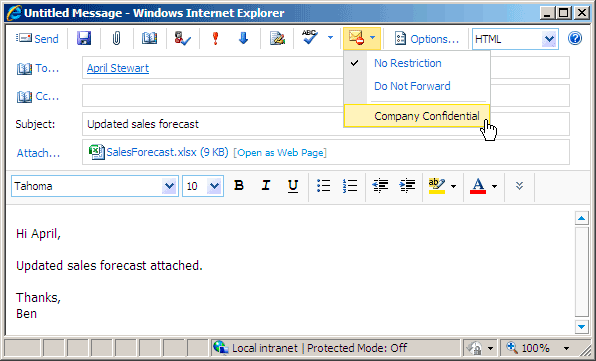
- Send IRM-protected messages As shown in
the following figure, Outlook Web App users can use the permissions
drop-down list and select a rights policy template to apply to the
message. This allows users to send IRM-protected messages from
within Outlook Web App. Messages are IRM-protected by Client Access
servers.
- IRM-protected attachments When users
send an IRM-protected message from Outlook Web App, any files
attached to the message also receive the same IRM protection and
are protected by using the same rights policy template as the
message. In Exchange 2010, IRM protection is applied to files
associated with Microsoft Office Word, Excel, and PowerPoint,
as well as .xps files and e-mail messages. IRM protection is
applied to an attachment only if it's not already IRM-protected. To
learn more about Active Directory Rights Management Services
(AD RMS) rights policy templates, see Understanding
Information Rights Management.
 Note:
Note:IRM in Outlook Web App protects only the supported file attachments mentioned in this section. Attachments that use unsupported file formats aren't protected. When Outlook Web App users protect a message and attach a file of an unsupported type, a notification is displayed informing the users that only supported file types are protected.  Important:
Important:IRM protection can't be applied to a message that's already signed or encrypted by using S/MIME. To apply IRM protection, S/MIME signature and encryption must be removed from the message. The same applies for IRM-protected messages; users can't sign or encrypt them by using S/MIME. - Read IRM-protected messages Messages
protected by senders using your organization's AD RMS cluster
are rendered in the preview pane in Outlook Web App. No add-ins
need to be installed, and the computer doesn't need to be enrolled
in the AD RMS deployment. When a user opens a message or views
it in the preview pane, the message is decrypted by using the use
license added by the Pre-licensing agent. After decryption, the
message is displayed in the preview pane. If a pre-license isn't
available, Outlook Web App requests one from the AD RMS server
and then renders the message. When reading IRM-protected
attachments in Outlook Web App, Web-Ready Document Viewing isn't
available.
 Note:
Note:IRM in Outlook Web App can't prevent users from taking screen captures by using Print Screen functionality in the way Outlook and other Office applications do. This impacts the EXTRACT right, which prevents message content from being copied, if specified in the AD RMS rights policy template. - Cross-browser, multiple platform IRM
support IRM in Outlook Web App offers
cross-browser, multiple platform IRM support. IRM in Outlook Web
App is supported in all browsers supported by Exchange 2010,
including on Apple Macintosh and Linux operating systems. To learn
more about supported browsers and operating systems, see Outlook Web App Supported Browsers.
- WebReady Document Viewing In Exchange
2010 SP1, users can view supported IRM-protected attachments by
using WebReady Document Viewing. This allows users to view
supported attachments without having to download the attachment use
the associated application. To learn more about WebReady Document
Viewing, including the supported file formats, see Understanding File and
Data Access for Outlook Web App.
Looking for management tasks related to managing IRM? See Managing Information Rights Management.
Enabling IRM in Outlook Web App
To enable IRM in Outlook Web App, you must add the Federation mailbox, a system mailbox created by Exchange 2010 Setup, to the super users group in AD RMS. For details, see Add the Federation Mailbox to the AD RMS Super Users Group. This allows Exchange 2010 servers to access IRM-protected messages.
You must also enable IRM in Outlook Web App by using the Set-IRMConfiguration cmdlet in the Exchange Management Shell. This enables IRM in Outlook Web App for your Exchange 2010 organization. You can disable or enable IRM in Outlook Web App for an Outlook Web App virtual directory. You can also control IRM in Outlook Web App at the following levels of granularity:
- Per-Outlook Web App virtual
directory To enable or disable IRM in Outlook
Web App for an Outlook Web App virtual directory, use the
Set-OWAVirtualDirectory cmdlet and set the IRMEnabled
parameter to
$falseor$true(default). This allows you to disable IRM in Outlook Web App for one virtual directory on an Exchange 2010 Client Access server, while keeping it enabled on another virtual directory on a different Client Access server.
- Per-Outlook Web App mailbox policy To
enable or disable IRM in Outlook Web App for an Outlook Web App
mailbox policy, use the Set-OWAMailboxPolicy cmdlet and set
the IRMEnabled parameter to
$falseor$true(default). This allows you to enable IRM in Outlook Web App for one set of users and disable it for another set of users by assigning them a different Outlook Web App mailbox policy.
For more information, see Enable or Disable Information Rights Management on Client Access Servers.

