Applies to: Exchange Server 2010 SP2
Topic Last Modified: 2012-07-23
When you configure a hybrid deployment between an on-premises Exchange organization and a cloud-based organization, you need to decide how to route mail and also understand how your existence organization will be impacted.
The route taken by inbound messages sent to recipients in the on-premises organization or cloud-based organization depends on whether you've chosen to use a shared or split namespace. The route taken by outbound messages sent from recipients in the on-premises organization or cloud-based organization depends on whether you've configured centralized mail control or decentralized mail control.
Whether you choose shared or split namespaces, or centralized or decentralized mail control, messages sent between the on-premises organization and the cloud-based organization are configured to use Transport Layer Security (TLS) transport to help secure that communication.
 Important: Important: |
|---|
| The cloud-based service must communicate directly with the on-premises hybrid server for secure communication to work correctly. |
The following section discusses what you need to think about as you add the hybrid server to your organization.
Exchange 2010 Hub Transport in an Exchange 2007 organization
You need to consider the impact of introducing an Exchange 2010 Hub Transport server into an existing Exchange 2007 organization when you install the hybrid server. Hub Transport in Exchange 2010 has new features that impact how mail routing and configuration are handled. Here are some of the following things you need to consider:
- Exchange 2007 Service Pack All of the
Exchange 2007 servers in the site where you're installing the
hybrid server must be running, at minimum, Exchange 2007 Service
Pack 3 (SP3)
- Message routing The hybrid server is
added to the routing topology of the existing Exchange 2007
organization. Messages sent to and from Exchange 2007 mailboxes are
handled by the Exchange 2007 Hub Transport servers in the
organization. Messages sent to and from the cloud-based
organization are handled by the hybrid server. Messages can be
routed directly between the hybrid server and the Exchange 2007
Edge Transport server, if one is configured.
- Transport and journal rules Any
existing Exchange 2007 transport and journal rules are copied to
the hybrid server when it's added to the Exchange 2007
organization. Transport and journal rules on Exchange 2007 and
Exchange 2010 servers are stored differently and must be maintained
separately.
- DSN messages Delivery status
notification (DSN) messages are stored differently and must be
maintained separately, similar to transport and journal rules.
- Message tracking The tracking tool you
use to track messages depends on the originating and destination
mailboxes.
New additional functionality, such as moderated recipients and shadow redundancy, are only available on Exchange 2010 servers. This new functionality doesn't extend to Exchange 2007 servers.
Learn more at: Upgrade from Exchange 2007 Transport
The following sections talk about shared and split namespaces, centralized and decentralized mail control, and trusted communication between the on-premises and cloud-based organizations.
Shared and Split Namespaces
When you choose to use a shared namespace, all recipients in the on-premises and cloud-based organizations share the same SMTP domain in their e-mail addresses. The mail exchanger (MX) record for this SMTP domain sends mail to the on-premises Exchange organization.
When a message arrives at the on-premises Exchange organization for a recipient that resides in the cloud, the Edge Transport server determines whether the message is spam or is malicious and if not, forwards it to a Hub Transport server in your organization. The Hub Transport server it sends the message to can be either an existing Exchange 2007 Hub Transport server, or it could be the hybrid server.
The Hub Transport server determines whether a mailbox is located on an on-premises Exchange server or in the cloud-based organization by checking the recipient type. If the recipient type is a mailbox, the Hub Transport server routes the message to the on-premises Exchange server that contains that mailbox.
 Note: Note: |
|---|
| If the Hub Transport server that performed the lookup is the hybrid server, the message is first routed to the Exchange 2007 Hub Transport server before delivery to the mailbox |
If the recipient type is a remote mailbox, which is a special type of mail user, the Hub Transport retrieves the remote routing address for that remote mailbox. The remote routing address for the mail user is the SMTP address of its associated mailbox in the cloud-based organization. The Hub Transport server readdresses the message with the SMTP address of the cloud-based mailbox. If the server that performed the lookup is an Exchange 2007 server, it sends the message to the hybrid server. The hybrid server then sends the message to the cloud-based organization. The examples in this checklist use service.contoso.com as the SMTP address of the cloud-based organization.
 Important: Important: |
|---|
| You must not use the service tenant FQDN, for example, contoso.onmicrosoft.com, as the SMTP address of the cloud-based organization. |
 Note: Note: |
|---|
| For the best hybrid deployment experience, we strongly recommend that you use a shared namespace. |
When you choose to use a split namespace, the e-mail addresses of recipients in the cloud-based organization are configured with an SMTP domain that's different from e-mail addresses of recipients in the on-premises organization. Messages sent to recipients in one organization are delivered directly to that organization.
Learn more about shared and split namespaces at: Understanding Shared and Split SMTP Namespaces
Centralized and Decentralized Mail Control
In addition to choosing how inbound messages addressed to recipients to your organizations are routed, you can also choose how outbound messages sent from cloud-based recipients are routed. The following describes the available options:
- Centralized mail control This option
routes outbound messages sent from the cloud-based organization
through your on-premises organization. Except for messages sent to
other recipients in the same cloud-based organization, all messages
sent from recipients in the cloud-based organization are sent
through the on-premises organization. This enables you to apply
compliance rules to these messages and any other processes or
requirements that must be applied to all of your recipients,
regardless of whether they're located in the cloud-based
organization or the on-premises organization.
 Important:
Important:Your on-premises hybrid server must be accessible from the Internet for recipients in the cloud-based organization to send messages to the Internet. If your on-premises hybrid server is unavailable, messages sent from the cloud-based organization will queue until it's available again. - Decentralized mail control This option
routes outbound messages sent from the cloud-based organization
directly to the Internet. Use this option if you don't need to
apply any on-premises policies or other processing to messages that
are sent from recipients in the cloud-based organization.
Trusted Communication
Regardless of whether you've selected shared or split namespaces, or centralized or decentralized mail control, all messages that are sent between recipients in your on-premises organization and the cloud-based organization are sent directly to and from either organization. As part of the configuration provided in the procedures in this checklist, each organization is configured to treat messages sent from the other organization as internal. This allows messages to bypass anti-spam settings and other services.
To help protect recipients in both organizations, and to help ensure that messages sent between the organizations aren't intercepted and read, transport between both organizations is configured to use forced TLS transport using Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificates provided by a trusted third-party Certificate Authority (CA).
When using forced TLS transport, the sending and receiving servers examine the certificate configured on the other server. The subject name, or one of the subject alternative names (SANs), configured on the certificates must match the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) that an administrator has explicitly specified on the other server. For example, if the cloud-based organization is configured to accept and secure messages sent from the mail2.contoso.com FQDN, the sending on-premises hybrid server must have an SSL certificate with mail2.contoso.com in either the subject name or SAN. If this requirement isn't met, the connection is refused.
 Note: Note: |
|---|
| The FQDN used doesn't need to match the e-mail domain name of the recipients. The only requirement is that the FQDN in the certificate subject name or SAN must match the FQDN that the receiving or sending servers are configured to accept. |
Trusted communication between your on-premises organization and cloud-based organization requires that the on-premises server accepting the connection, called the TLS endpoint, be an Exchange 2010 server. In your on-premises organization, this is the hybrid server. If the TLS endpoint is a non-Exchange 2010 server, the connection will fail. For this reason, you must configure the cloud-based organization to send mail directly to the hybrid server. Your existing Exchange 2007 Hub Transport or Edge Transport servers can't be the TLS endpoint for connections from the cloud-based organization. This requires that you provide an external IP address to the hybrid server and open port 25 on your firewall to the hybrid server.
Learn more about SSL certificates and domain security at: Understanding Certificate Requirements, Understanding TLS Certificates
Each of the following sections shows how mail flows, depending on the choices you've made. Select the section to see how mail flows for your choice.
Shared namespace with centralized mail control
When you configure your on-premises and cloud-based organization to use a shared namespace and to also use centralized mail control, all messages sent to and from recipients in both the on-premises organization and the cloud-based organization are sent through the on-premises organization.
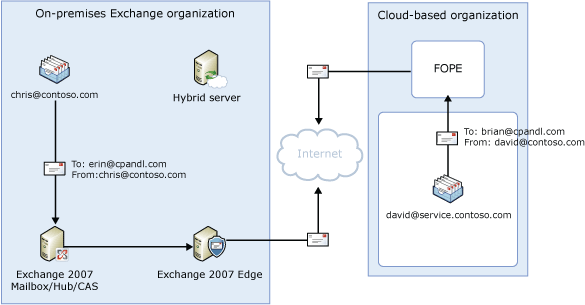
In the diagram below, which shows inbound messages sent to recipients in your organization, the following occurs:
- An inbound message is sent from an Internet sender to the
recipients chris@contoso.com and david@contoso.com. Chris's mailbox
is located on an Exchange 2007 server in the on-premises
organization. David's mailbox is located in the cloud-based
organization.
- Because the recipients both have contoso.com e-mail addresses,
and the MX record for contoso.com points to the on-premises Edge
transport server, the message is delivered to the on-premises Edge
Transport server.
- The Edge Transport server selects a Hub Transport server in the
on-premises organization to transfer the message to. The Edge
Transport server can select either an Exchange 2007 Hub Transport
server or it can select the hybrid server.
- The message is delivered to a Hub Transport server which
performs a lookup for each recipient using an on-premises global
catalog server. Through the global catalog lookup, it determines
that Chris's mailbox is located on the Exchange 2007 server while
David's mailbox is located in the cloud and has a routing address
of david@service.contoso.com
- The Hub Transport server splits the message into two copies.
One copy of the message is sent to the Exchange 2007 mailbox. If
the hybrid server received the message and performed the lookup,
Chris's message is first delivered to the Exchange 2007 Hub
Transport before final delivery to her mailbox on the Exchange 2007
server.
- The second copy is sent to the cloud-based organization. If the
Exchange 2007 Hub Transport server received the message and
performed the lookup, David's message is first delivered to the
hybrid server. Then, the message is sent, over the Internet,
through the send connector that's configured between the hybrid
server and the Forefront Online Protection for Exchange (FOPE)
service, which receives message sent to the cloud-based
organization.
- FOPE scans the message for viruses and then sends the message
to the cloud-based organization where the message is delivered to
David's mailbox.
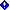
In the diagram below, which shows outbound messages sent to the Internet, the following occurs:
- Chris, who has a mailbox on the on-premises Exchange 2007
server, sends a message to an external Internet recipient,
erin@cpandl.com. David, who has a mailbox in the cloud-based
organization, sends a message to the external recipient
brian@cpandl.com. Both Chris and David have a contoso.com reply
address.
- The Exchange 2007 mailbox server sends Chris's message to the
Exchange 2007 Hub Transport server. The Hub Transport server sends
the message to the Exchange 2007 Edge Transport server.
- The cloud-based organization sends David's message to FOPE.
- FOPE is configured to send all Internet-bound messages to the
on-premises hybrid server, so the message is routed to the hybrid
server. FOPE is configured to bypass the on-premises Exchange 2007
Edge Transport server.
- The hybrid server sends the message to the Exchange 2007 Hub
Transport server.
- The Edge Transport server performs compliance, anti-virus, and
any other processes configured by the administrator, on both Chris
and David's messages.
- The Edge Transport server looks up the MX record for cpandl.com
and sends the messages to the cpandl.com mail servers located on
the Internet.
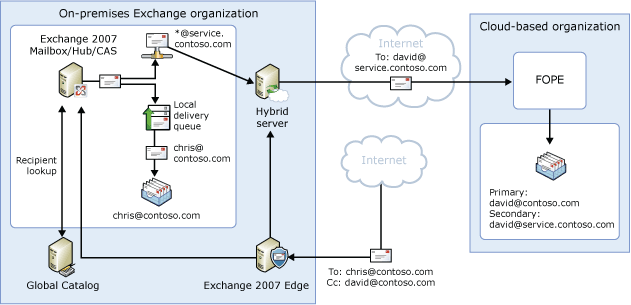
Shared namespace with decentralized mail control
When you configure your on-premises and cloud-based organizations to use a shared namespace, but choose to use decentralized mail control, all inbound messages sent to recipients in either organization are sent through the on-premises organization. However, outbound messages sent from recipients in either organization are sent directly to the Internet. The cloud-based organization doesn't send messages to the Internet through the on-premises organization.
In the diagram below, which shows inbound messages sent to recipients in your organization, the following occurs:
- An inbound message is sent from an Internet sender to the
recipients chris@contoso.com and david@contoso.com. Chris's mailbox
is located on an Exchange 2007 server in the on-premises
organization. David's mailbox is located in the cloud-based
organization.
- Because the recipients both have contoso.com e-mail addresses,
and the MX record for contoso.com points to the on-premises Edge
transport server, the message is delivered to the on-premises Edge
Transport server.
- The Edge Transport server selects a Hub Transport server in the
on-premises organization to transfer the message to. The Edge
Transport server can select either an Exchange 2007 Hub Transport
server or it can select the hybrid server.
- The message is delivered to a Hub Transport server which
performs a lookup for each recipient using an on-premises global
catalog server. Through the global catalog lookup, it determines
that Chris's mailbox is located on the Exchange 2007 server while
David's mailbox is located in the cloud and has a routing address
of david@service.contoso.com.
- The Hub Transport server splits the message into two copies.
One copy of the message is sent to the Exchange 2007 mailbox. If
the hybrid server received the message and performed the lookup,
Chris's message is first delivered to the Exchange 2007 Hub
Transport before final delivery to her mailbox on the Exchange 2007
server.
- The second copy is sent to the cloud-based organization. If the
Exchange 2007 Hub Transport server received the message and
performed the lookup, David's message is first delivered to the
hybrid server. Then, the message is sent, over the Internet,
through the send connector that's configured between the hybrid
server and the Forefront Online Protection for Exchange (FOPE)
service, which receives message sent to the cloud-based
organization.
- FOPE scans the message for viruses and then sends the message
to the cloud-based organization where the message is delivered to
David's mailbox.

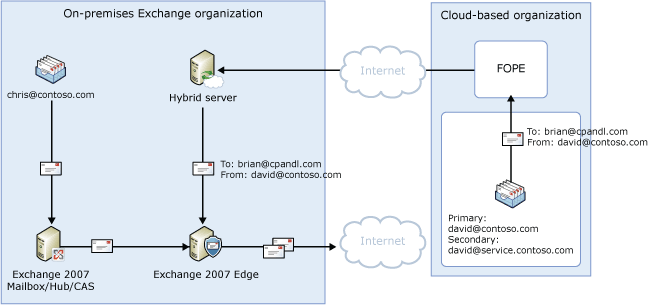
In the diagram below, which shows outbound messages sent to the Internet, the following occurs:
- Chris, who has a mailbox on the on-premises Exchange 2007
server, sends a message to an external Internet recipient,
erin@cpandl.com. David, who has a mailbox in the cloud-based
organization, sends a message to the external recipient
brian@cpandl.com. Both Chris and David have a contoso.com reply
address.
- The Exchange 2007 mailbox server sends Chris's message to the
Exchange 2007 Hub Transport server. The Hub Transport server sends
the message to the Exchange 2007 Edge Transport server.
- The Edge Transport server performs compliance, anti-virus, and
any other processes configured by the administrator, on Chris's
message.
- The Edge Transport server looks up the MX record for cpandl.com
and sends the message to the cpandl.com mail servers located on the
Internet.
- The cloud-based organization sends David's message to FOPE.
- FOPE is configured to send all Internet-bound messages directly
to the Internet. FOPE looks up the MX record for cpandl.com.
- FOPE delivers the message directly to the cpandl.com mail
servers located on the Internet. Because the message never transits
through the hybrid server, no on-premises processes are applied to
it.

Split namespace with centralized mail control
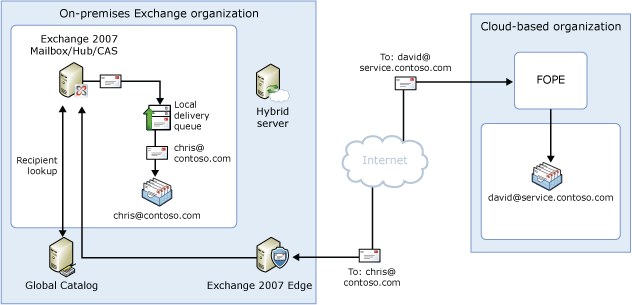
In the diagram below, which shows inbound messages sent to recipients in your organization, the following occurs:
- An inbound message is sent from an Internet sender to the
chris@contoso.com and another message is sent to
david@service.contoso.com. Chris's mailbox is located on an
Exchange 2007 server in the on-premises organization. David's
mailbox is located in the cloud-based organization.
- Because the recipients have different e-mail address domains,
the sending server sends each message to the organization that
receives messages for each domain. The MX record for contoso.com
points to the on-premises Edge Transport server while the MX record
for service.contoso.com points to FOPE.
- The Edge Transport server selects a Hub Transport server in the
on-premises organization to transfer the message to. The Edge
Transport server can select either an Exchange 2007 Hub Transport
server or it can select the hybrid server.
- The message is delivered to a Hub Transport server which
performs a lookup for each recipient using an on-premises global
catalog server. Through the global catalog lookup, it determines
that Chris's mailbox is located on the Exchange 2007 server.
- If the hybrid server received the message, it sends Chris's
message to the Exchange 2007 Hub Transport server. The Hub
Transport server delivers the message to Chris's mailbox on the
Exchange 2007 server.
- The message for David is sent to FOPE, which receives message
sent to the cloud-based organization.
- FOPE scans the message for viruses and then sends the message
to the cloud-based organization where the message is delivered to
David's mailbox.
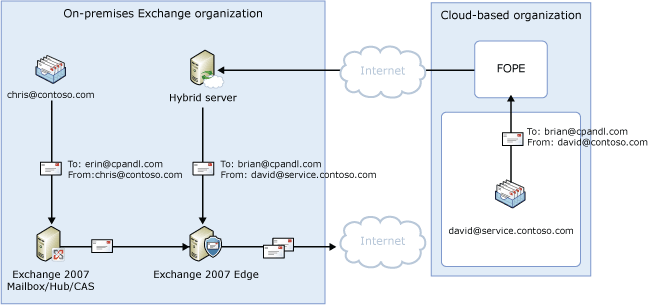
In the diagram below, which shows outbound messages sent to the Internet, the following occurs:
- Chris, who has a mailbox on the on-premises Exchange 2007
server, sends a message to an external Internet recipient,
erin@cpandl.com. David, who has a mailbox in the cloud-based
organization, sends a message to the external recipient
brian@cpandl.com. Chris has a reply address of chris@contoso.com
and David has a reply address of david@service.contoso.com.
- The Exchange 2007 mailbox server sends Chris's message to the
Exchange 2007 Hub Transport server. The Hub Transport server sends
the message to the Exchange 2007 Edge Transport server.
- The cloud-based organization sends David's message to FOPE.
- FOPE is configured to send all Internet-bound messages to the
on-premises hybrid server, so the message is routed to the hybrid
server. FOPE is configured to bypass the on-premises Exchange 2007
Edge Transport server.
- The hybrid server sends the message to the Exchange 2007 Hub
Transport server.
- The Edge Transport server performs compliance, anti-virus, and
any other processes configured by the administrator, on both Chris
and David's messages.
- The Edge Transport server looks up the MX record for cpandl.com
and sends the messages to the cpandl.com mail servers located on
the Internet.
Split namespace with decentralized mail control
In the diagram below, which shows inbound messages sent to recipients in your organization, the following occurs:
- An inbound message is sent from an Internet sender to the
chris@contoso.com and another message is sent to
david@service.contoso.com. Chris's mailbox is located on an
Exchange 2007 server in the on-premises organization. David's
mailbox is located in the cloud-based organization.
- Because the recipients have different e-mail address domains,
the sending server sends each message to the organization that
receives messages for each domain. The MX record for contoso.com
points to the on-premises Edge Transport server while the MX record
for service.contoso.com points to FOPE.
- The Edge Transport server selects a Hub Transport server in the
on-premises organization to transfer the message to. The Edge
Transport server can select either an Exchange 2007 Hub Transport
server or it can select the hybrid server.
- The message is delivered to a Hub Transport server which
performs a lookup for each recipient using an on-premises global
catalog server. Through the global catalog lookup, it determines
that Chris's mailbox is located on the Exchange 2007 server.
- If the hybrid server received the message, it sends Chris's
message to the Exchange 2007 Hub Transport server. The Hub
Transport server delivers the message to Chris's mailbox on the
Exchange 2007 server.
- The message for David is sent to FOPE, which receives message
sent to the cloud-based organization.
- FOPE scans the message for viruses and then sends the message
to the cloud-based organization where the message is delivered to
David's mailbox.

In the diagram below, which shows outbound messages sent to the Internet, the following occurs:
- Chris, who has a mailbox on the on-premises Exchange 2007
server, sends a message to an external Internet recipient,
erin@cpandl.com. David, who has a mailbox in the cloud-based
organization, sends a message to the external recipient
brian@cpandl.com. Chris has a reply address of chris@contoso.com
and David has a reply address of david@service.contoso.com.
- The Exchange 2007 mailbox server sends Chris's message to the
Exchange 2007 Hub Transport server. The Hub Transport server sends
the message to the Exchange 2007 Edge Transport server.
- The Edge Transport server performs compliance, anti-virus, and
any other processes configured by the administrator, on Chris's
message.
- The Edge Transport server looks up the MX record for cpandl.com
and sends the message to the cpandl.com mail servers located on the
Internet.
- The cloud-based organization sends David's message to FOPE.
- FOPE is configured to send all Internet-bound messages directly
to the Internet. FOPE looks up the MX record for cpandl.com.
- FOPE delivers the message directly to the cpandl.com mail
servers located on the Internet. Because the message never transits
through the hybrid server, no on-premises processes are applied to
it.