Applies to: Exchange Server 2013
Topic Last Modified: 2013-02-13
This topic explains how to deploy Exchange 2013 in a cross-forest topology using Microsoft Forefront Identity Manager 2010 R2 SP1. To deploy Exchange 2013 in a cross-forest topology, you must first install Exchange 2013 in each forest, and then connect the forests so that users can see address and availability data across the forests.
The following figure illustrates user synchronization between two Exchange 2013 forests.
Example of Exchange 2013 cross-forest synchronization
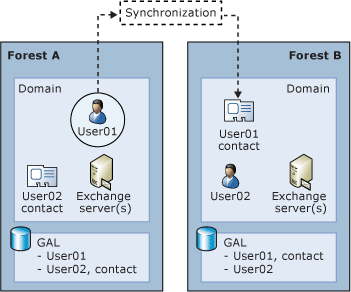
This topic does not describe how to deploy Exchange 2013 in a dedicated Exchange forest (or resource forest) topology. For more information about how to deploy Exchange 2013 in a resource forest topology, see Deploy Exchange 2013 in an Exchange Resource Forest Topology.
What do you need to know before you begin?
To perform the following procedure in Exchange 2013, confirm the following:
- You have correctly configured Domain Name System (DNS) for name
resolution across forests in your organization. To verify that DNS
is configured correctly, use the Ping tool to test connectivity to
each forest from the other forests in your organization and from
the server on which you will run the GALSync agent.
- The GALSync management agent (MA) communicates with the
Exchange 2013 forest using Windows PowerShell V2.0 RTM. Make sure
Windows PowerShell v1.0 isn't installed on this computer by going
to Control Panel, and then clicking Programs and Features.
- Ensure that Windows Remote Management has not been installed by
Windows Update.
- Install Windows PowerShell and Windows Remote Management. For
details, see Microsoft Knowledge Base article 968930, Windows Management Framework Core package
(Windows PowerShell 2.0 and WinRM 2.0).
- Download Forefront Identity Manager 2010 R2 SP1. See Download of Microsoft Forefront Identity Manager 2010 R2
SP1.
- For information about keyboard shortcuts that may apply to the
procedures in this topic, see Keyboard Shortcuts in
the Exchange Admin Center.
 Tip: Tip: |
|---|
| Having problems? Ask for help in the Exchange forums. Visit the forums at: Exchange Server, Exchange Online, or Exchange Online Protection |
Deploy Exchange 2013 in a cross-forest topology with Forefront Identity Manager 2010 R2 SP1
- In each forest, install Exchange 2013 separately. To install
Exchange 2013, perform the same steps that you would if you were
installing Exchange 2013 in a single forest topology. For detailed
steps, see one of the following topics:
- Deploy a New
Installation of Exchange 2013
- Install
Exchange 2013 Using the Setup Wizard
 Note:
Note:This topic assumes that you don't have an existing Exchange 2007 or Exchange 2010 topology. If you do have an existing Exchange topology and you want to upgrade, see Upgrade from Exchange 2010 to Exchange 2013 or Upgrade from Exchange 2007 to Exchange 2013.
- Deploy a New
Installation of Exchange 2013
- In each forest, use Active Directory Users and Computers to
create a container in which FIM 2010 R2 SP1 will create contacts
for each mailbox from the other forest. We recommend that you name
this container FromFIM. To create the container, select the
domain in which you want to create the container, right-click the
domain, select New > Organizational Unit. In
New Object - Organizational Unit, type FromFIM, and
then click OK.
- Create a GALSync management agent for each forest by using
Forefront Identify Manager. This allows you to synchronize the
users in each forest and create a common GAL. For detailed steps,
see the following resources:
- Configuring Global Address List (GAL)
Synchronization with Forefront Identity Manager (FIM) 2010
- Work with Management Agents
- Forefront Identity Manager 2010 R2 Documentation
Roadmap
 Important:
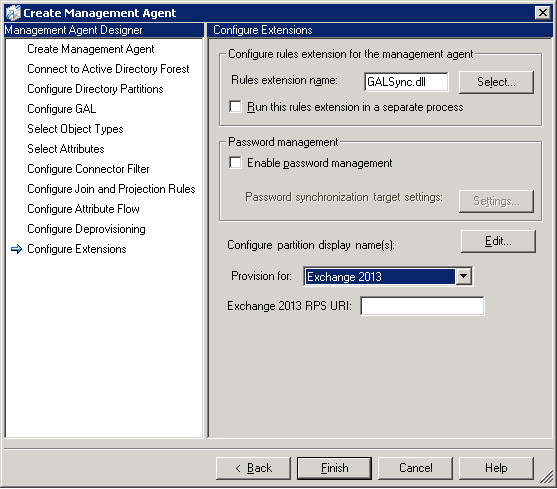
Important:While the resources discuss Exchange 2010, Exchange 2013 is supported for FIM 2010 R2 SP1. Make sure that you configure Extensions in FIM 2010 R2 SP1 for Exchange 2013. - On the Configure Extensions page, under Configure
partition display name(s), next to Provision for, select
Exchange 2013. You will see the Exchange 2013 RPS URI
field. Enter the URI of an Exchange 2013 Client Access server to
make sure the remote PowerShell connection is functioning. The
Exchange 2013 RPS URI should be in the following format:
http://CAS_Server_FQDN/Powershell. Click OK.
Provision GalSync Management Agent for Exchange 2013 Note:
Note:Make sure that the administrator credentials used to connect to the Exchange 2013 forest can also make remote PowerShell connections to that forest.
The following figure shows how to select provisioning for Exchange 2013.
- Configuring Global Address List (GAL)
Synchronization with Forefront Identity Manager (FIM) 2010
- Create an SMTP Send connector in each of the forests. For
detailed steps, see Configure a Cross-Forest
Send Connector.
- In each forest, enable the Availability service so that users
in each forest can view free/busy data about users in the other
forest. For more information, see Availability Service in
Exchange 2013.
- If you want mail relayed through any forest in your
organization, you must configure a domain in that forest as an
authoritative domain. For detailed steps, see Configure Exchange to
Accept Mail for Multiple Authoritative Domains.

