Applies to: Exchange Server 2007 SP3, Exchange Server
2007 SP2, Exchange Server 2007 SP1, Exchange Server 2007
Topic Last Modified: 2007-07-03
The property configuration of a Microsoft Exchange Server 2007 transport server determines how that server processes messages. You can configure the transport server properties by using the Exchange Management Console or the Exchange Management Shell on a computer that has the Hub Transport server role or the Edge Transport server role installed. This topic provides information about the settings that you can configure for a transport server. The transport server settings that you configure on a Hub Transport server or Edge Transport server apply only to the specific server. The transport server settings aren't shared across other transport servers in the Exchange organization.
In the Exchange Management Console, view and modify the transport server configuration from the transport server property pages. In the Exchange Management Shell, use the Get-TransportServer cmdlet to view the transport server configuration and the Set-TransportServer cmdlet to modify the transport server configuration.
 Before You Begin
Before You Begin
To perform the following procedures, the account you use must be delegated the following:
- Exchange Server Administrator role
To perform the following procedures on a computer that has the Edge Transport server role installed, you must log on by using an account that is a member of the local Administrators group on that computer.
For more information about permissions, delegating roles, and the rights that are required to administer Exchange 2007, see Permission Considerations.
 How to View Transport Server
Configuration
How to View Transport Server
Configuration
You can use the Exchange Management Console to view a limited set of transport server properties. You can view all the transport server settings by using the Exchange Management Shell.
To use the Exchange Management Console to view transport server configuration-
Open the Exchange Management Console. Perform one of the following steps:
- On a computer that has the Edge Transport server role
installed, in the console tree, select Edge Transport, and
then click the Properties link that is directly under the
server name.
- On a computer that has the Hub Transport server role installed,
in the console tree, expand Server Configuration, and then
select Hub Transport. In the result pane, select a server.
In the action pane, click the Properties link that is under
the server name.
- On a computer that has the Edge Transport server role
installed, in the console tree, select Edge Transport, and
then click the Properties link that is directly under the
server name.
-
The transport server properties are displayed.
In the release to manufacturing (RTM) version of Exchange 2007, the following tabs are displayed in the properties of Edge Transport servers and Hub Transport servers:
- General
- External DNS Lookups
- Internal DNS Lookups
- Limits
In Exchange 2007 Service Pack 1 (SP1), the following tabs are displayed in the properties of Hub Transport servers and Edge Transport servers:
- General
- System Settings
- External DNS Lookups
- Internal DNS Lookups
- Limits
- Log Settings
- General
-
To display the transport server name, whether the message tracking log is enabled, and the external postmaster address for the specified server, run the following command:
 Copy Code
Copy CodeGet-TransportServer <Transport Server Name>
 Note:
Note:The external postmaster address is only used on Edge Transport servers as the sender of system-generated messages. On Hub Transport servers, the Microsoft Exchange Recipient is used as the sender of system-generated messages. For more information, about the external postmaster address, see Managing the External Postmaster Address. For more information about the Microsoft Exchange Recipient, see Managing the Microsoft Exchange Recipient. -
To display a list of all properties configured for a specified transport server, run the following command:
 Copy Code
Copy CodeGet-TransportServer <Transport Server Name> | format-list
-
To display a table of selected properties for a specified transport server, run the following command:
 Copy Code
Copy CodeGet-TransportServer <Transport Server Name> | format-table Name,ExternalDNSAdapterEnabled,ExternalDNSServer
-
To view all properties related to a similar area, such as Domain Name System (DNS), you can use wildcard characters with the Format-Table command. For example, to view all DNS-related properties, run the following command:
 Copy Code
Copy CodeGet-TransportServer <Transport Server Name> | format-table Name,*DNS*
-
To view all properties related to a similar area, such as Domain Name System (DNS), you can use wildcard characters with the Format-Table command. For example, to view all DNS-related properties, run the following command:
 Copy Code
Copy CodeGet-TransportServer <Transport Server Name> | format-table Name,*DNS*
-
To view other information that isn't specific to the Hub Transport server role or the Edge Transport server role, such as the Exchange server version, run the following command:
 Copy Code
Copy CodeGet-ExchangeServer | format-list
 General Properties of Transport
Servers
General Properties of Transport
Servers
You may use the following methods to view general information about the transport server:
- In the Exchange Management Console, use the General
tab of the transport server properties. In
Exchange 2007 SP1, some of the information that is
displayed for a Hub Transport server has been moved to the
new System Settings tab. The System Settings tab
doesn't exist in Exchange 2007 RTM. In
Exchange 2007 RTM, the same information is displayed on
the General tab.
- Use the Get-ExchangeServer cmdlet in the Exchange
Management Shell. For any modifiable properties, use the
Set-ExchangeServer cmdlet. For more information,
see Set-ExchangeServer.
General Tab of the Transport Server Properties in the Exchange Management Console in Exchange 2007 RTM
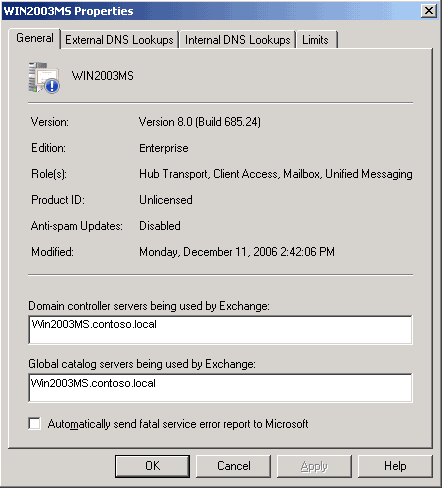
In Exchange 2007 RTM, the General tab of the transport server properties in the Exchange Management Console displays the following information about the server:
- The Exchange product version
- The Exchange edition
- The server roles that are installed on the server
- The Exchange server product ID
- The status of anti-spam updates. Typically, anti-spam features
are only installed on an Edge Transport server. For more
information, see Anti-Spam and Antivirus
Functionality.
- The last modification date
- On a Hub Transport server, the domain controller servers and
global catalog servers that are used by the Exchange server
are displayed. This information doesn't apply to Edge Transport
servers.
You can't modify any of these properties. These properties are automatically updated when you modify the computer that is running Exchange Server.
On the General tab, you can also enable or disable the automatic sending of fatal service error reports to Microsoft. The corresponding parameter in the Set-ExchangeServer cmdlet is ErrorReportingEnabled.
Figure 1 shows the General tab for the Hub Transport server properties in Exchange 2007 RTM.
General Tab of the Transport Server Properties in the Exchange Management Console in Exchange 2007 SP1
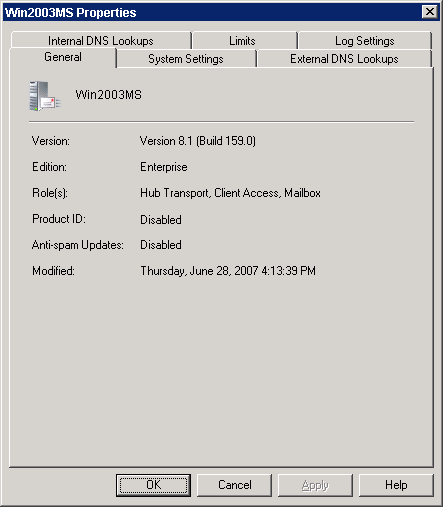
In Exchange 2007 SP1, the General tab of the transport server properties in the Exchange Management Console displays the following information about the server:
- The Exchange product version
- The Exchange edition
- The server roles that are installed on the server
- The Exchange product ID
- The status of anti-spam updates
- The last modification date
- On a Hub Transport server, the domain controller servers and
global catalog servers that are used by the Exchange server are
displayed. This information doesn't apply to Edge Transport
servers.
You can't modify any of these properties. These properties are automatically updated when you modify the computer that is running Exchange Server.
Figure 2 shows the General tab for the Hub Transport server properties in Exchange 2007 SP1.
System Settings Tab of the Transport Server Properties in the Exchange Management Console in Exchange 2007 SP1
 Note: Note: |
|---|
| In Exchange 2007 RTM, there is no System Settings tab in the transport server properties. This information is located on the General tab. |
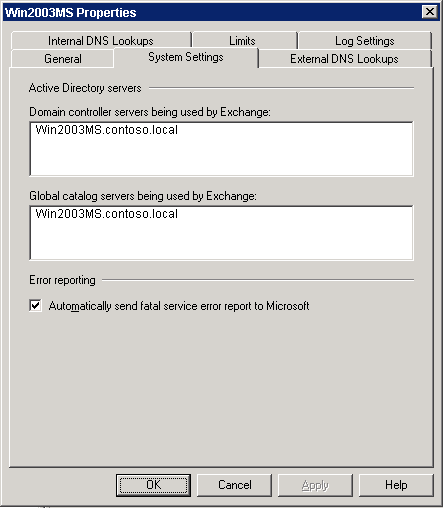
In Exchange 2007 SP1, the System Settings tab of the transport server properties in the Exchange Management Console displays Active Directory directory service connection information and error report settings for the server.
If you view the System Settings properties for a Hub Transport server, the domain controller servers and global catalog servers that are used by Exchange are displayed. This information doesn't apply to Edge Transport servers.
On the System Settings tab, you can set the option to automatically send fatal service error reports to Microsoft. The corresponding parameter in the Set-ExchangeServer cmdlet is ErrorReportingEnabled.
Figure 3 shows the System Settings tab for the Hub Transport server properties in Exchange 2007 SP1.
 DNS Lookups
DNS Lookups
DNS lookups are used by Exchange 2007 transport servers to resolve a host name to an IP address. Make sure that the server is configured to enable DNS resolution for hosts inside the Active Directory directory service forest and hosts that are outside the Exchange organization. The configuration of the transport server controls the DNS server that is queried to resolve an individual lookup. The transport server properties can be configured to use the DNS server configuration of a local network adapter. The transport server properties can also be configured to query a specific DNS server for host name resolution. If the transport server has more than one network adapter, you can configure DNS lookup to use the configuration of a specific network adapter for external and internal DNS lookups.
DNS lookups are directed to a particular DNS server as follows:
- By default, the DNS configuration of a network adapter is
selected. To override use of the network adapter configuration, by
using the Set-TransportServer cmdlet in the Exchange
Management Shell, you must set the
InternalDNSAdapterEnabled and
ExternalDNSAdapterEnabled parameters to
$Falseand configure a list of DNS servers to query. You can also use the Exchange Management Console to modify this configuration.
- The configuration of internal DNS Lookups is used by
default.
- The configuration of external DNS lookups is used only when a
Send connector is configured to use these settings. This setting is
enabled on a per-connector basis.
- If you configure more than one DNS server address, the first
DNS server listed is considered the primary DNS server. Additional
entries are considered secondary DNS servers. Secondary DNS servers
are queried only when the primary DNS server can't be reached.
- If you configure DNS lookups to use the DNS server
configuration of a specific network adapter, you must specify the
adapter by its GUID. Never apply the network adapter GUID of one
server to the transport settings of another server. If you do this,
the server can't send mail because it can't locate the network
adapter that is referenced by the GUID.
- To retrieve the GUID for a network adapter, run the
Get-NetworkConnectionInfo cmdlet in the Exchange Management
Shell. This cmdlet must be run locally on the computer for which
you want to retrieve the network adapter GUID. The following
example shows the output of the Get-NetworkConnectionInfo
cmdlet.
 Copy Code Copy Code |
|
|---|---|
[PS] D:\Documents and Settings\Administrator>Get-NetworkConnectionInfo
Name : Intel(R) PRO/1000 MT Network Connection
DnsServers : {10.197.12.19, 10.197.12.20}
IPAddresses : {10.197.21.53}
AdapterGuid : 0d372140-eae6-4350-9ef8-14d9d10061f2
MacAddress : 00:0B:DB:4E:8C:A6
|
|
 Note: Note: |
|---|
| If Exchange 2007 SP1 is deployed on a computer that is running Windows Server 2008, you can enter IP addresses and IP address ranges in the Internet Protocol Version 4 (IPv4) format, Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6) format, or both formats. A default installation of Windows Server 2008 enables support for IPv4 and IPv6. For more information about Exchange 2007 SP1 support for IPv6 addresses, see IPv6 Support in Exchange 2007 SP1 and SP2. |
External DNS Lookups
When a Send connector is configured to use the external DNS lookup settings on a transport server, it uses the external DNS settings that you configure to resolve host or MX records to IP addresses. The external DNS settings also apply to Receive connectors for the anti-spam agents, such as the Sender ID agent and Connection Filter agent. You can select the DNS configuration of a specific network adapter. Alternatively, you can manually create DNS server entries. You can configure external DNS lookups in the Exchange Management Console and in the Exchange Management Shell.
To use the Exchange Management Console to configure external DNS lookups-
Open the Exchange Management Console. Take one of the following steps:
- On a computer that has the Edge Transport server role
installed, in the console tree, select Edge Transport. Click
the Properties link that is directly under the server
name.
- On a computer that has the Hub Transport server role installed,
in the console tree, expand Server Configuration, and then
select Hub Transport. In the result pane, select a server.
In the action pane, click the Properties link that is
directly under the server name.
- On a computer that has the Edge Transport server role
installed, in the console tree, select Edge Transport. Click
the Properties link that is directly under the server
name.
-
Click the External DNS Lookups tab. By default, external DNS lookups are configured to use network adapter DNS settings. The network adapter that should be used is set to (All available). Take one of the following steps to configure the external DNS lookups.
- To configure the external DNS lookups to use the DNS
configuration of a specific network adapter, select Use network
card DNS settings as shown in Figure 4, and then click
OK. Select an adapter from the list that appears. The DNS
settings for that adapter are now displayed on the External DNS
Lookups properties.
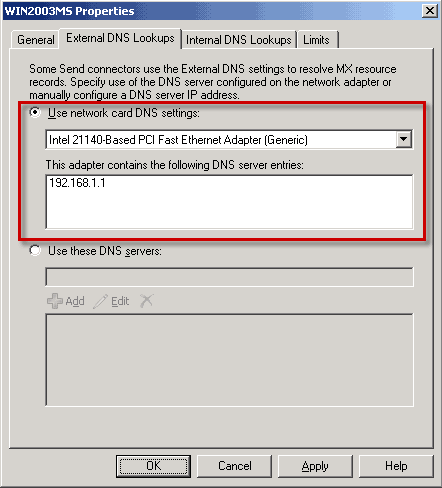
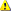 Caution:
Caution:Do not select a specific network adapter unless you are logged on locally to the server that you are configuring. If you are configuring a remote server, you must select the (All Available) option. Figure 4 External DNS Lookups tab on a transport server configured to use a specific network adapter - To configure the external DNS lookups to use a specific DNS
server, select Use these DNS servers. Enter the IP address
of the DNS server and then click Add as shown in
Figure 5, and then click OK.
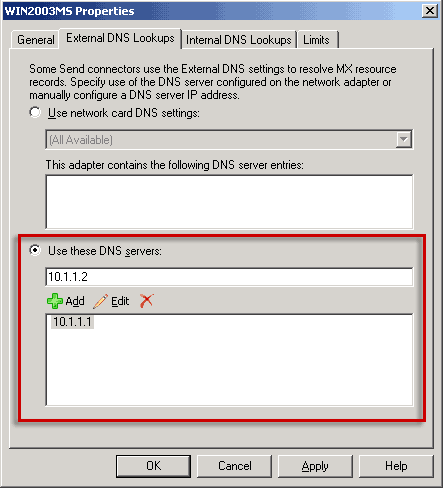
 Note:
Note:Figure 4 and Figure 5 show the External DNS Lookups tab in Exchange 2007 RTM. The External DNS Lookups tab is the same in Exchange 2007 RTM and in Exchange 2007 SP1. Figure 5 External DNS Lookups tab on a transport server that is configured to use a manually configured list of DNS servers
- To configure the external DNS lookups to use the DNS
configuration of a specific network adapter, select Use network
card DNS settings as shown in Figure 4, and then click
OK. Select an adapter from the list that appears. The DNS
settings for that adapter are now displayed on the External DNS
Lookups properties.
-
To configure the transport server to use a specific network adapter for external DNS lookups, run the following command:
 Copy Code
Copy CodeSet-TransportServer <Transport Server Name> -ExternalDNSAdapterEnabled $true - ExternalDNSAdapterGUID 64fb8dba-0d5c-49eb-9ae3-93071551e4d9
-
To configure the transport server to use a list of DNS servers for external DNS lookups, run the following command:
 Copy Code
Copy CodeSet-TransportServer <Transport Server Name> -ExternalDNSAdapterEnabled $false -ExternalDNSServers {192.168.1.1, 192.168.1.2}
Internal DNS Lookups
The internal DNS lookups configuration settings are used to resolve DNS queries for all communications that do not route through a Send connector that is set to use the external DNS lookup settings on a transport server. For example, all messages that are sent between Hub Transport servers in the organization by using the implicit intra-organization Send connector use the internal DNS lookups configuration.
You can configure internal DNS lookups in the Exchange Management Console and in the Exchange Management Shell.
To use the Exchange Management Console to configure internal DNS lookups-
Open the Exchange Management Console. Perform one of the following steps:
- On a computer that has the Edge Transport server role
installed, in the console tree, select Edge Transport. Click
the Properties link that is directly under the server
name.
- On a computer that has the Hub Transport server role installed,
in the console tree, expand Server Configuration, and then
select Hub Transport. In the result pane, select a server.
In the action pane, click the Properties link that is
directly under the server name.
- On a computer that has the Edge Transport server role
installed, in the console tree, select Edge Transport. Click
the Properties link that is directly under the server
name.
-
Click the Internal DNS Lookups tab. By default, internal DNS lookups are configured to use network adapter DNS settings. The network adapter to use is set to (All available). Take one of the following steps to configure the internal DNS lookups.
- To configure the internal DNS lookups to use the DNS
configuration of a specific network adapter, select Use network
card DNS settings as shown in Figure 6, and then click
OK. Select an adapter from the list that appears. The DNS
settings for that adapter are now displayed on the Internal DNS
Lookups properties.

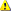 Caution:
Caution:Do not select a specific network adapter unless you are logged on locally to the server that you are configuring. If you are configuring a remote server, only select the (All Available) option. Figure 6 Internal DNS Lookups tab on a transport server configured to use a specific network adapter - To configure the internal DNS lookups to use a specific DNS
server, select Use these DNS servers. Enter the IP address
of the DNS server, click Add as shown in Figure 7, and
then click OK.
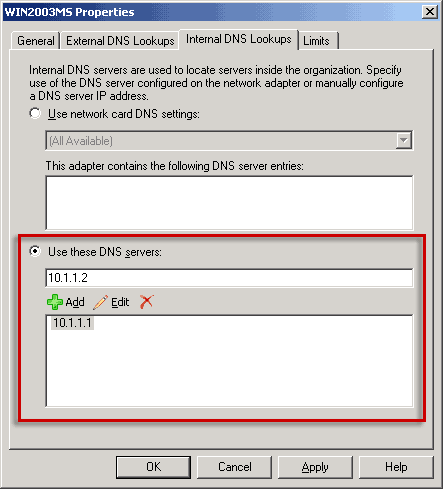
 Note:
Note:Figure 6 and Figure 7 show the Internal DNS Lookups tab in Exchange 2007 RTM. The Internal DNS Lookups tab is the same in Exchange 2007 RTM and in Exchange 2007 SP1. Figure 7 Internal DNS Lookups tab on a transport server that is configured to use a manually configured list of DNS servers
- To configure the internal DNS lookups to use the DNS
configuration of a specific network adapter, select Use network
card DNS settings as shown in Figure 6, and then click
OK. Select an adapter from the list that appears. The DNS
settings for that adapter are now displayed on the Internal DNS
Lookups properties.
-
To configure the transport server to use a specific network adapter for internal DNS lookups, run the following command:
 Copy Code
Copy CodeSet-TransportServer <Transport Server Name> -InternalDNSAdapterEnabled $true - InternalDNSAdapterGUID 64fb8dba-0d5c-49eb-9ae3-93071551e4d9
-
To configure the transport server to use a list of DNS servers for internal DNS lookups, run the following command:
 Copy Code
Copy CodeSet-TransportServer <Transport Server Name> -InternalDNSAdapterEnabled $false -InternalDNSServers {192.168.1.1, 192.168.1.2}
 Transport Server Limits
Transport Server Limits
The Limits tab of the transport server properties or the Set-TransportServer cmdlet is used to configure the following settings:
- Retries These settings determine the
interval at which an Exchange 2007 transport server will retry
message delivery when a connection failure occurs. The available
settings are as follows:
- Outbound connection failure retry interval
(minutes) Use this field to specify the retry
interval for subsequent connection attempts to a remote server
where earlier connections have failed. The previously failed
connection attempts are controlled by the value of Transient
failure retry attempts and the Transient failure retry
interval. On a Hub Transport server, the default value is
10 minutes. On an Edge Transport server, the default value is
30 minutes. The valid input range is 1 minute to
28,800 minutes (20 days). The corresponding parameter in
the Set-TransportServer cmdlet is
OutboundConnectionFailureRetryInterval.
- Transient failure retry interval
(seconds) Use this field to specify the
connection interval between each connection attempt that is
specified by the value of Transient failure retry attempts.
On a Hub Transport server, the default value is 5 minutes. On
an Edge Transport server, the default value is 10 minutes. The
valid input range is 1 second to 43,200 seconds
(12 hours). The corresponding parameter in the
Set-TransportServer cmdlet is
TransientFailureRetryInterval.
- Transient failure retry attempts Use
this field to specify the maximum number of times that a server
immediately retries when it encounters a connection failure with a
remote server. The default value is 6. The valid input range
is 0 to 6. When this parameter is set to 0, the
server doesn't immediately try to reconnect. The corresponding
parameter in the Set-TransportServer cmdlet is
TransientFailureRetryCount.
- Outbound connection failure retry interval
(minutes) Use this field to specify the retry
interval for subsequent connection attempts to a remote server
where earlier connections have failed. The previously failed
connection attempts are controlled by the value of Transient
failure retry attempts and the Transient failure retry
interval. On a Hub Transport server, the default value is
10 minutes. On an Edge Transport server, the default value is
30 minutes. The valid input range is 1 minute to
28,800 minutes (20 days). The corresponding parameter in
the Set-TransportServer cmdlet is
OutboundConnectionFailureRetryInterval.
- Message expiration This setting
determines how long an Exchange 2007 transport server tries to
deliver a message before the server removes the message from the
queue. If a message remains in the queue for more time, the
message is returned to the sender as a hard failure. The default
value is 2 days. The valid input range is 1 day to
90 days. The corresponding parameter in the
Set-TransportServer cmdlet is
MessageExpirationTimeout.
- Notifications This setting is used to
determine how long the server waits before it generates a delivery
status notification (DSN) to the sender about a delivery delay. The
default value is 4 hours. The valid input range is 1 hour
to 720 hours (30 days). The value of Notifications
should always be greater than the value of the Transient failure
retry interval multiplied by the value of Transient failure
retry attempts. The corresponding parameter in the
Set-TransportServer cmdlet is
DelayNotificationTimeout.
- Connection restrictions These settings
limit the maximum number of concurrent connections that can exist
on an Exchange 2007 transport server. You can configure an
overall limit. You can also configure a per domain limit. The
available settings are as follows:
- Maximum concurrent outbound
connections Select this option to specify the
maximum number of outbound connections that can be open at a time.
If the connection limit is reached, the server does not initiate
new connections until the number of current connections decreases.
The default value is 1000. The valid input range
is
1to 2147483647. If you clear the checkbox next to Maximum concurrent outbound connections, no limit is imposed on the number of concurrent outbound connections. The value of Maximum concurrent outbound connections must be greater than or equal to the value of Maximum concurrent outbound connections per domain. The corresponding parameter in the Set-TransportServer cmdlet is MaxOutboundConnections.
- Maximum concurrent outbound connections per
domain Select this option to specify the
maximum number of concurrent connections to any single domain. The
default value is 20. The valid input range is
1to 2147483647. If you clear the checkbox next to Maximum concurrent outbound connections per domain, no limit is imposed on the number of concurrent outbound connections per domain. The value of Maximum concurrent outbound connections per domain must be less than or equal to the value of Maximum concurrent outbound connections. The corresponding parameter in the Set-TransportServer cmdlet is MaxPerDomainOutboundConnections.
Figure 8 shows the default configuration of the Limits tab for a Hub Transport server. The Limits tab is the same in Exchange 2007 RTM and in Exchange 2007 SP1.
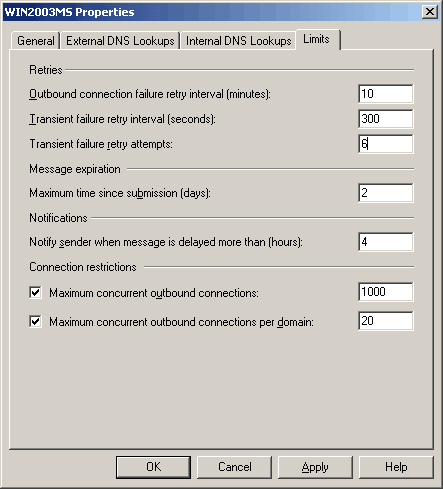
For more information about how to configure these properties, see Managing Message Retry, Resubmit, and Expiration Intervals.
 Transport Server Log
Settings
Transport Server Log
Settings
The Log Settings tab of the transport server properties or the Set-TransportServer cmdlet is used to configure the following transport log settings:
 Note: Note: |
|---|
| In Exchange 2007 RTM, there is no Log Settings tab in the transport server properties. You must use the Set-TransportServer cmdlet in the Exchange Management Shell to configure the transport server log settings. |
- Message tracking log These settings
control the state of message tracking and the location of the
message tracking logs. The message tracking log is a detailed log
of all message activity as messages are transferred to and from a
computer that is running Exchange. Message tracking is available on
Hub Transport servers, Edge Transport servers, and Mailbox servers.
The message tracking settings that are available in the Exchange
Management Console are as follows:
- Enable message tracking log By default,
message tracking is enabled on a Hub Transport servers and Edge
Transport servers. To disable message tracking, clear the checkbox
next to Enable message tracking log. To enable message
tracking, select the checkbox next to Enable message tracking
log. The corresponding parameter in the
Set-TransportServer cmdlet is
MessageTrackingLogEnabled.
- Message tracking log path This field
displays the current location of the message tracking logs. To
change the location of the message tracking logs, message tracking
must be enabled. Click Browse next to Message tracking
log path. In the Browse for folder window, browse to the
new location where you want to store the message tracking log
files. If you want to create a new folder, select a parent folder,
click Make New Folder, and then type the name of the new
folder. After you make your folder selection, click OK to
close the Browse for folder window. The corresponding
parameter in the Set-TransportServer cmdlet is
MessageTrackingLogPath.
- Enable message tracking log By default,
message tracking is enabled on a Hub Transport servers and Edge
Transport servers. To disable message tracking, clear the checkbox
next to Enable message tracking log. To enable message
tracking, select the checkbox next to Enable message tracking
log. The corresponding parameter in the
Set-TransportServer cmdlet is
MessageTrackingLogEnabled.
- Connectivity log These settings control
the state of connectivity logging and the location of the
connectivity logs. The connectivity log is a record of the Simple
Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) connection activity of the outbound
message delivery queues to the destination Mailbox server, smart
host, or domain. The available connectivity log settings in the
Exchange Management Console are as follows:
- Enable connectivity log By default,
connectivity logging is disabled on Hub Transport servers and Edge
Transport servers. To enable connectivity logging, clear the
checkbox next to Enable connectivity log. To enable
connectivity logging, select the checkbox next to Enable
connectivity log. The corresponding parameter in the
Set-TransportServer cmdlet is
ConnectivityLogEnabled.
- Connectivity log path This field
displays the current location of the connectivity logs. To change
the location of the connectivity logs, connectivity logging must be
enabled. Click Browse next to Connectivity log path.
In the Browse for folder window, browse to the new location
where you want to store the connectivity log files. If you want to
create a new folder, select a parent folder, click Make New
Folder, and then type the name of the new folder. After you
make your folder selection, click OK to close the Browse
for folder window. The corresponding parameter in the
Set-TransportServer cmdlet is
ConnectivityLogPath.
- Enable connectivity log By default,
connectivity logging is disabled on Hub Transport servers and Edge
Transport servers. To enable connectivity logging, clear the
checkbox next to Enable connectivity log. To enable
connectivity logging, select the checkbox next to Enable
connectivity log. The corresponding parameter in the
Set-TransportServer cmdlet is
ConnectivityLogEnabled.
- Protocol log These settings control the
location of the protocol logs. A protocol log is a record of the
SMTP activity between messaging servers as part of message
delivery. This SMTP activity occurs on Send connectors and Receive
connectors that are configured on Hub Transport servers and Edge
Transport servers. By default, protocol logging is disabled. The
protocol log settings in the Exchange Management Console are as
follows:
- Send connector protocol log path This
field displays the current location of the Send connector protocol
logs. All of the Send connectors that are configured on the Hub
Transport server or Edge Transport server share the same protocol
logs. By default, protocol logging is disabled on all Send
connectors. You can enable or disable protocol logging on each Send
connector by using the Set-SendConnector cmdlet in the
Exchange Management Shell, or in the properties of the Send
connector in the Exchange Management Console.
To change the location of the Send connector protocol logs, click Browse next to Send connector protocol log path. In the Browse for folder window, browse to the new location where you want to store the Send connector protocol log files. If you want to create a new folder, select a parent folder, click Make New Folder, and then type the name of the new folder. After you make your folder selection, click OK to close the Browse for folder window. The corresponding parameter in the Set-TransportServer cmdlet is SendProtocolLogPath.
- Receive connector protocol log
path This field displays the current location
of the Receive connector protocol logs. All of the Receive
connectors that are configured on the Hub Transport server or Edge
Transport server share the same protocol logs. By default, protocol
logging is disabled on all Receive connectors. You can enable or
disable protocol logging on each Receive connector by using the
Set-ReceiveConnector cmdlet in the Exchange Management
Shell, or in the properties of the Receive connector in the
Exchange Management Console.
To change the location of the Receive connector protocol logs, click Browse next to Receive connector protocol log path. In the Browse for folder window, browse to the new location where you want to store the Receive connector protocol log files. If you want to create a new folder, select a parent folder, click Make New Folder, and then type the name of the new folder. After you make your folder selection, click OK to close the Browse for folder window. The corresponding parameter in the Set-TransportServer cmdlet is ReceiveProtocolLogPath.
- Send connector protocol log path This
field displays the current location of the Send connector protocol
logs. All of the Send connectors that are configured on the Hub
Transport server or Edge Transport server share the same protocol
logs. By default, protocol logging is disabled on all Send
connectors. You can enable or disable protocol logging on each Send
connector by using the Set-SendConnector cmdlet in the
Exchange Management Shell, or in the properties of the Send
connector in the Exchange Management Console.
Figure 9 shows the Log Settings tab for the Hub Transport server properties in Exchange 2007 SP1.

When you change the location of the message tracking log directory, the connectivity log directory, the Send connector protocol log directory, or the Receive connector protocol log directory, this change does not copy any existing log files from the old directory to the new directory. The new log directory is active almost immediately after the configuration change, but any existing log files are left in the old directory.
The following permissions are required on the log directory:
- Administrator: Full Control
- System: Full Control
- Network Service: Read, Write, and Delete Subfolders and
Files
By default, the Exchange Transport service uses the security credentials of the Network Service user account to create the log directory and apply the correct permissions. If the new log directory does not already exist, and the Network Service account has the rights that are required to create folders and apply permissions at the new location, the new log directory is created and the correct permissions are applied to the new directory. If the log directory already exists, the existing folder permissions are not checked. Whenever you move the log directory, it is always a good idea to verify the log directory and to verify that the new directory has the correct permissions applied to it.
 Additional Transport Server
Settings
Additional Transport Server
Settings
When you use the Exchange Management Shell to configure the transport server, you can modify additional properties that are unavailable in the Exchange Management Console. These properties control settings that relate to the following transport features:
- Delivery status notifications
- External Postmaster address
- Connection rates
- Pickup directory
- Pipeline tracing
- Poison messages
- Replay directory
- Routing table logging
For more information about how to modify these properties by using cmdlets in the Exchange Management Shell, see the following topics:
 For More Information
For More Information
For more information, see the following topics:
- Get-ExchangeServer
- Configuring
DNS Settings for Exchange 2007 Servers
- Managing
Message Retry, Resubmit, and Expiration Intervals
- Managing
Connectors
- Managing the
Pickup Directory
- Managing the
Replay Directory
- Managing
Delivery Status Notifications
- Managing
Message Tracking
- Managing
Protocol Logging
- Managing
Connectivity Logging
- Managing
Routing Table Logging

