Applies to: Exchange Server 2007 SP3, Exchange Server
2007 SP2, Exchange Server 2007 SP1, Exchange Server 2007
Topic Last Modified: 2009-08-19
Every computer that is on the Internet has a Domain Name System (DNS) name. This is also known as the machine name or host name. Every computer running the Microsoft Windows operating system with networking capabilities also has a NetBIOS name.
A computer running Windows in an Active Directory directory service domain has both a DNS domain name and a NetBIOS domain name. The DNS domain name consists of one or more subdomains separated by a dot (.) and is terminated by a top-level domain name. For example, in the DNS domain name corp.contoso.com, the subdomains are corp and contoso, and the top-level domain name is com. Typically, the NetBIOS domain name is the subdomain of the DNS domain name. For example, if the DNS domain name is contoso.com, the NetBIOS domain name is contoso. If the DNS domain name is corp.contoso.com, the NetBIOS domain name is corp.
A computer in an Active Directory domain also has a primary DNS suffix and can have additional DNS suffixes. By default, the primary DNS suffix is the same as the DNS domain name. For detailed steps about how to change the primary DNS suffix, see the procedures later in this topic.
You define the DNS domain name and NetBIOS domain name of an Active Directory domain when you configure the first domain controller in the domain. For more information about configuring domain controllers, see Domain controller role: Configuring a domain controller.
The following figure illustrates the page in the Windows Server 2003 Active Directory Installation wizard in which you define the DNS domain name of an Active Directory domain.
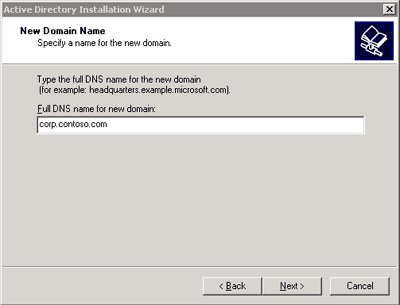
The following figure illustrates the page in the Windows Server 2003 Active Directory Installation wizard in which you define the NetBIOS domain name of an Active Directory domain.

The procedures in this section describe how to view the following items on a computer that is running Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2003:
- DNS host name
- Primary DNS suffix
- DNS domain name
- NetBIOS name
- NetBIOS domain name
-
Click Start, right-click Computer, and then click Properties.
-
In System, the DNS host name and primary DNS suffix are displayed under Computer name, domain, and workgroup settings, next to Full computer name. The DNS domain name is displayed next to Domain.
-
Click Change settings.
-
In System Properties, on the Computer Name tab, click Change.
-
In Computer Name/Domain Changes, click More. The primary DNS suffix is displayed under Primary DNS suffix of this computer. The NetBIOS computer name is displayed under NetBIOS computer name.
To change the primary DNS suffix, type the new primary DNS suffix under Primary DNS suffix of this computer, and then click OK.
-
From a Command Prompt window, type set. The variable USERDNSDOMAIN displays the DNS domain name. The variable USERDOMAIN displays the NetBIOS domain name.
-
Click Start, right-click My Computer, and then click Properties.
-
In System Properties, click the Computer Name tab. The DNS host name and primary DNS suffix are displayed next to Full computer name. The DNS domain name is displayed next to Domain.
-
On the Computer Name tab, click Change.
-
On the Computer Name Changes page, click More. The primary DNS suffix is displayed under Primary DNS suffix of this computer. The NetBIOS computer name is displayed under NetBIOS computer name.
To change the primary DNS suffix, type the new primary DNS suffix under Primary DNS suffix of this computer, and then click OK.
-
From a Command Prompt window, type set. The variable USERDNSDOMAIN displays the DNS domain name. The variable USERDOMAIN displays the NetBIOS domain name.
 Note: Note: |
|---|
| You can also run the command ipconfig /all from a Command Prompt window to view the primary DNS suffix. However, if you have a policy that overrides the primary DNS suffix, this command will not display the correct primary DNS suffix. |
 Disjointed Namespaces
Disjointed Namespaces
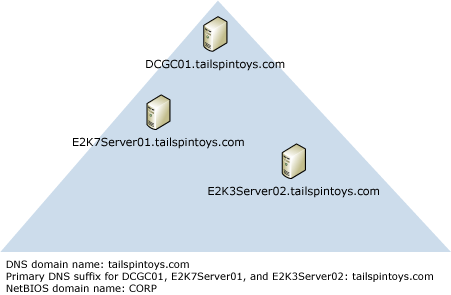
In most domain topologies, the primary DNS suffix of the computers in the domain is the same as the DNS domain name. The following figure illustrates a typical namespace scenario in which the primary DNS suffix, the DNS domain name, and the NetBIOS domain name match.
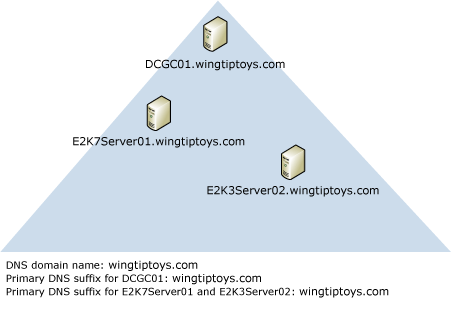
In some cases, you may require these namespaces to be different. This is called a disjointed namespace. For example, a merger or acquisition may cause you to have a topology with a disjointed namespace. In addition, if DNS management in your company is split between administrators who manage Active Directory and administrators who manage networks, you may need to have a topology with a disjointed namespace.
A disjointed namespace scenario is one in which the primary DNS suffix of a computer does not match the DNS domain name where that computer resides. The computer with the primary DNS suffix that does not match is said to be disjointed. Another disjointed namespace scenario occurs if the NetBIOS domain name of a domain controller does not match the DNS domain name.
 Exchange 2007 and Disjointed
Namespaces
Exchange 2007 and Disjointed
Namespaces
In Microsoft Exchange Server 2007, there are three supported scenarios for deploying Exchange in a domain that has a disjointed namespace. The supported scenarios are as follows:
- Scenario 1 The primary DNS suffix of
the domain controller is not the same as the DNS domain name.
Computers that are members of the domain can be either disjointed
or not disjointed.
- Scenario 2 A member computer in an
Active Directory domain is disjointed, even though the
domain controller is not disjointed.
- Scenario 3 The NetBIOS domain name of
the domain controller is not the same as the subdomain of the DNS
domain name of that domain controller.
These scenarios are detailed in the following sections.
Scenario 1
In this scenario, the primary DNS suffix of the domain controller is not the same as the DNS domain name. The domain controller is disjointed in this scenario. Computers that are members of the domain, including Exchange servers and Microsoft Outlook client computers, can have a primary DNS suffix that either matches the primary DNS suffix of the domain controller or matches the DNS domain name.
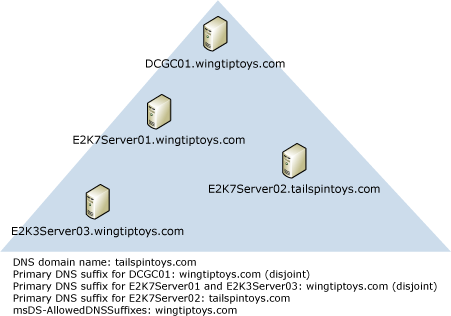
To allow Exchange 2007 servers to access domain controllers that are disjointed, you must modify the msDS-AllowedDNSSuffixes Active Directory attribute on the domain object container. You must add both of the DNS suffixes to the attribute. For detailed steps about how to modify the attribute, see The computer's primary DNS suffix does not match the FQDN of the domain where it resides.
In addition, to make sure that the DNS suffix search list contains all DNS namespaces that are deployed within the organization, you must configure the search list for each computer in the domain that is disjointed. The list of namespaces should include not only the primary DNS suffix of the domain controller and the DNS domain name, but also any additional namespaces for other servers with which Exchange may interoperate (such as monitoring servers or servers for third-party applications). You can do this by setting Group Policy for the domain. For more information about Group Policy, see the following topics:
For detailed steps about how to configure the DNS suffix search list Group Policy, see How to Configure the DNS Suffix Search List for a Disjoint Namespace.
Scenario 2
In this scenario, the primary DNS suffix of a member computer on which Exchange 2007 is installed is not the same as the DNS domain name, even though the primary DNS suffix of the domain controller is the same as the DNS domain name. In this scenario, you have a domain controller that is not disjointed and a member computer that is disjointed. Member computers that are running Outlook can have a primary DNS suffix that either matches the primary DNS suffix of the disjointed Exchange server or matches the DNS domain name.
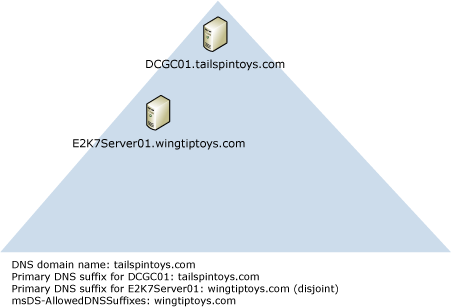
To allow disjointed Exchange 2007 servers to access domain controllers, you must modify the msDS-AllowedDNSSuffixes Active Directory attribute on the domain object container. You must add both of the DNS suffixes to the attribute. For detailed steps about how to modify the attribute, see The computer's primary DNS suffix does not match the FQDN of the domain where it resides.
In addition, to make sure that the DNS suffix search list contains all DNS namespaces that are deployed within the organization, you must configure the search list for each computer in the domain that is disjointed. The list of namespaces should include not only the primary DNS suffix of the disjointed member computer and the DNS domain name, but also any additional namespaces for other servers with which Exchange may interoperate (such as monitoring servers or servers for third-party applications). You can do this by setting Group Policy for the domain. For more information about Group Policy, see the following topics:
For detailed steps about how to configure the DNS suffix search list Group Policy, see How to Configure the DNS Suffix Search List for a Disjoint Namespace.
Scenario 3
In this scenario, the NetBIOS domain name of the domain controller is not the same as the DNS domain name of the same domain controller.
 Getting Additional Help
Getting Additional Help
It is supported to run Exchange 2007 in any of the disjointed namespace scenarios described in this topic. If you have a disjointed namespace scenario that is not one of the three scenarios described in this topic, you must work with Microsoft Services to deploy Exchange 2007. For more information, see Microsoft Services.
In September 2007, the Microsoft Sustained Engineering and Microsoft Product Team created a DNS Disjointed Namespace and Multi-Tree test plan that can be used by customers to test DNS namespace environments that may not supported by Exchange 2007.
For more information, see DNS Disjoint Namespace and Multi Tree Test Plan.
 Important: Important: |
|---|
| We recommend that you test any disjointed DNS name space scenarios in a lab environment before you deploy to a production environment. |

