Applies to: Exchange Server 2007 SP3, Exchange Server
2007 SP2, Exchange Server 2007 SP1, Exchange Server 2007
Topic Last Modified: 2007-04-25
The selection of an outbound anonymous Transport Layer Security (TLS) certificate occurs in the following scenarios:
- Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) sessions between Edge
Transport servers and Hub Transport servers for authentication
- SMTP sessions between Hub Transport servers for encryption only
by using public keys
For communication between Hub Transport servers, anonymous TLS and the public keys from certificates are used to encrypt the session. But the next authentication is Kerberos authentication. When an SMTP session is established, the receiving server initiates a certificate selection process to determine which certificate to use in the TLS negotiation. The receiving server also performs a certificate selection process. For more information about that process, see Selection of Inbound Anonymous TLS Certificates.
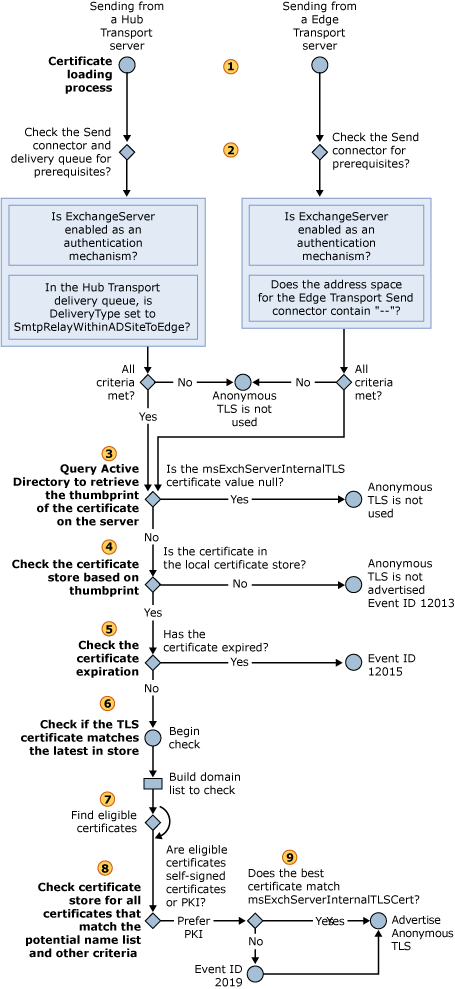
This topic describes the selection process for outbound anonymous TLS certificates. All the steps are performed on the sending server. The following figure shows the steps of this process.
 Note: Note: |
|---|
| During the initial loading of the certificate, the outbound certificate selection process is different for the Edge Transport server role and the Hub Transport server role. The following figure shows the starting point for each server role. |
 Sending from a Hub Transport
Server
Sending from a Hub Transport
Server
- When the SMTP session is established from a Hub Transport
server or Edge Transport server, Microsoft Exchange calls a
process to load the certificates.
- The certificate loading process depends on whether the SMTP
session is initiated from a Hub Transport server or an Edge
Transport server.
On a Hub Transport server The following checks are made:
- The Send connector to which the session is connected is checked
to see whether the SmartHostAuthMechanism property is
configured for
ExchangeServer. You can set the SmartHostAuthMechanism property on the Send connector by using the Set-SendConnector cmdlet. You can also set the SmartHostAuthMechanism property toExchangeServerby selecting Exchange Server Authentication on the Configure Smart Host Authentication Settings page of a given Send connector. To open the Configure Smart Host Authentication Settings page, click Change on the Network tab of the Send connector properties page.
- The DeliveryType property of the message is checked to
determine whether it is set to a value of
SmtpRelayWithinAdSitetoEdge. You can view the DeliveryType property by running the Get-Queue cmdlet with the format list argument (| FL).
Both of these conditions must be met. IfExchangeServeris not enabled as an authentication mechanism, or if the DeliveryType property is not set toSmtpRelayWithinAdSitetoEdge, the sending Hub Transport server does not use anonymous TLS and no certificate is loaded. If both conditions are met, the certificate selection process continues to step 3.
- The Send connector to which the session is connected is checked
to see whether the SmartHostAuthMechanism property is
configured for
ExchangeServer. As noted earlier in this topic, you can set the SmartHostAuthMechanism property on the Send connector by using the Set-SendConnector cmdlet. You can also set the SmartHostAuthMechanism property toExchangeServerby selecting Exchange Server Authentication on the Configure Smart Host Authentication Settings page of a given Send connector. To open the Configure Smart Host Authentication Settings page, click Change on the Network tab of the Send connector properties page.
- The Send connector to which the session is connected is checked
to determine whether the SmartHost address space property
contains “- -“.
Both of these conditions must be met. IfExchangeServeris not enabled as an authentication mechanism and the address space does not contain “- -“, the sending Edge Transport server does not use anonymous TLS and no certificate is loaded. If both conditions are met, the certificate selection process continues to step 3.
- The Send connector to which the session is connected is checked
to see whether the SmartHostAuthMechanism property is
configured for
- Microsoft Exchange queries the Active Directory
directory service to retrieve the thumbprint of the certificate on
the server. The msExchServerInternalTLSCert attribute on the
server object stores the certificate thumbprint.
If the msExchServerInternalTLSCert attribute cannot be read or if the value isnull, Microsoft Exchange does not advertise X-ANONYMOUSTLS in the SMTP session and no certificate is loaded.
 Note:
Note:If the msExchServerInternalTLSCert attribute cannot be read or if the value is nullduring startup of the Microsoft Exchange Transport service, instead of during the SMTP session, Event ID 12012 is logged in the Application log. - If a thumbprint is found, the certificate selection process
searches the local computer certificate store for a certificate
that matches the thumbprint. If the certificate is not found, the
server does not advertise X-ANONYMOUSTLS, no certificate is loaded,
and Event ID 12013 is logged in the Application log.
- After a certificate is loaded from the certificate store, it is
checked to see whether it has expired. The Valid to field on
the certificate is compared to the current date and time. If the
certificate has expired, Event ID 12015 is logged in the
Application log. But the certificate selection process does not
fail and continues with the remaining checks.
- The certificate is checked to see whether it is the latest in
the local computer’s certificate store. As part of this check, a
domain list is built for potential certificate domains. The domain
list is based on the following computer configuration:
- Fully qualified domain name (FQDN), such as
mail.contoso.com
- Host name, such as EdgeServer01
- Physical FQDN, such as EdgeServer01.contoso.com
- Physical host name, such as EdgeServer01
 Note:
Note:If the server is configured as a cluster or for a computer that is running Microsoft Windows Load Balancing, the following registry key is checked instead of the DnsFullyQualifiedDomainName setting: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\WLBS\Parameters\Interface\{GUID}\ClusterName - Fully qualified domain name (FQDN), such as
mail.contoso.com
- After the domain list is built, the certificate selection
process performs a search to find all certificates in the
certificate store that have a matching FQDN. From this list, the
certificate selection process identifies a list of eligible
certificates. Eligible certificates must meet the following
criteria:
- The certificate is an X.509 version 3 or a later version
certificate.
- The certificate has an associated private key.
- The Subject or Subject Alternate Name fields contain the FQDN
that was retrieved in step 6.
- The certificate is enabled for Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)/TLS
use. Specifically, the SMTP service has been enabled for this
certificate by using the Enable-ExchangeCertificate
cmdlet.
- The certificate is an X.509 version 3 or a later version
certificate.
- From the eligible certificates, the best certificate is
selected based on the following sequence:
- Sort eligible certificates by most recent Valid from
date. Valid from is a Version 1 field on the
certificate.
- The first valid public key infrastructure (PKI) certificate
that is found in this list is used.
- If no valid PKI certificates are found, the first self-signed
certificate is used.
- Sort eligible certificates by most recent Valid from
date. Valid from is a Version 1 field on the
certificate.
- After the best certificate has been determined, another check
is made to determine whether its thumbprint matches the certificate
that is stored in msExchServerInternalTLSCert attribute. If
the certificate matches, the certificate is used for
X-AnonymousTLS. If it does not match, Event ID 1037 is
logged in the Application log. However, this does not cause
X-AnonymousTLS to fail.
 For More Information
For More Information
For more information about how certificates are selected for other TLS scenarios, see the following topics:

