Applies to: Exchange Server 2007 SP3, Exchange Server
2007 SP2, Exchange Server 2007 SP1, Exchange Server 2007
Topic Last Modified: 2007-01-30
In Microsoft Exchange Server 2007, recipients (which include users, resources, contacts, and groups) are any mail-enabled object in the Active Directory directory service to which Exchange can deliver or route messages. For a recipient to send or receive e-mail messages, the recipient must have an e-mail address. E-mail address policies generate the primary and secondary e-mail addresses for your recipients so they can receive and send e-mail.
By default, Exchange contains an e-mail address policy for every mail-enabled user. This default policy specifies the recipient's alias as the local part of the e-mail address and uses the default accepted domain. The local part of an e-mail address is the name that appears before the at sign (@). However, you can change how your recipients' e-mail addresses will display. For example, you can specify that your recipients' e-mail addresses display as firstname.lastname@contoso.com.
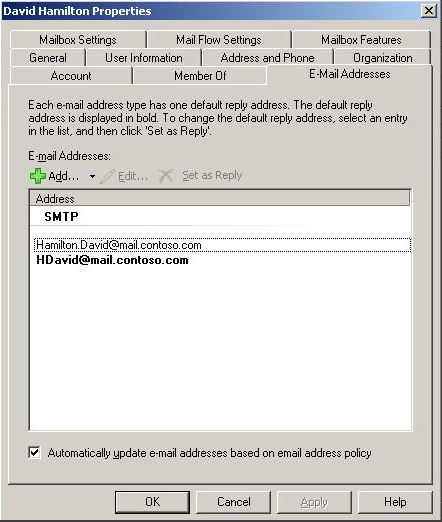
Furthermore, if you want to specify additional e-mail addresses for all recipients or just a subset, you can modify the default policy or create additional policies. For example, Figure 1 illustrates a configuration in which the recipient David Hamilton can receive e-mail messages that are addressed to hdavid@mail.contoso.com and hamilton.david@mail.contoso.com.
 Improvements in Exchange
2007
Improvements in Exchange
2007
Exchange Server 2003 used recipient policies to generate e-mail addresses for recipients in the organization. However, after the e-mail address policy was created, it was applied only to new recipients in the organization. Therefore, to improve the management of e-mail address policies, Exchange 2007 applies the policy to all recipients that match the recipient filtering criteria.
The following are additional improvements that Exchange 2007 e-mail address policies provide over Exchange 2003 recipient policies:
- In Exchange 2007, the recipient policy
functionality is divided into two features: e-mail address
policies and accepted domains.
 Note:
Note:A detailed discussion about accepted domains is outside the scope of this topic. For information about accepted domains, see Managing Accepted Domains. - Exchange 2007 has eliminated the asynchronous
behavior of the Exchange 2003 Recipient Update Service in
favor of a more predictable, synchronous provisioning process. When
you run the Update-EmailAddressPolicy cmdlet in
the Exchange Management Shell, the recipient object is updated
with the e-mail address policy. For detailed syntax and parameter
information, see Update-EmailAddressPolicy.
- In Exchange 2007, each time a recipient object is modified
and saved, Exchange 2007 enforces the correct application
of the e-mail address criteria and settings. When an e-mail address
policy is modified and saved, all associated recipients are updated
with the change. In addition, if a recipient object is
modified, that recipient's e-mail address policy membership is
re-evaluated and enforced.
 For More Information
For More Information
For information about managing e-mail address policies, see Managing E-Mail Address Policies.
For more information about accepted domains, see Managing Accepted Domains.

