Topic Last Modified: 2011-03-24
Use the following Firewall and Port table to determine firewall requirements and which ports to open. Then, review the network address translation (NAT) terminology because NAT can be implemented in many different ways. For a detailed example of firewall port settings, see the reference architectures in Topologies for External User Access.
A/V Firewall and Port Requirements
| Federation with | Feature | TCP/443 | UDP/3478 | RTP/UDP 50.000-59,999K | RTP/TCP 50,000-59,999K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Windows Live Messenger 2011 |
Point to Point Audio/Video (A/V) |
Open inbound |
Open inbound Open outbound |
Do not open in either direction |
Open outbound |
|
Lync Server 2010 |
Lync Server 2010 |
Open inbound |
Open inbound Open outbound |
Do not open in either direction |
Open outbound |
|
Lync Server 2010 |
Application sharing/desktop sharing |
Open inbound |
Open inbound Open outbound |
Do not open in either direction |
Open outbound |
|
Lync Server 2010 |
File transfer |
Open inbound |
Open inbound Open outbound |
Do not open in either direction |
Open outbound |
|
Office Communications Server 2007 R2 |
A/V |
Open inbound |
Open inbound Open outbound |
Do not open in either direction |
Open outbound |
|
Office Communications Server 2007 R2 |
Desktop sharing |
Open inbound |
Open inbound Open outbound |
Do not open in either direction |
Open outbound |
|
Office Communications Server 2007 R2 |
File transfer |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Office Communications Server 2007 |
A/V |
Open inbound |
Open inbound |
Open inbound Open outbound |
Open inbound Open outbound |
|
Office Communications Server 2007 |
Desktop sharing |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Office Communications Server 2007 |
File transfer |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
 Note: Note: |
|---|
| (inbound) refers to RTP/TCP and RTP/UDP traffic from the
Internet to the A/V Edge external interface. (outbound) refers to RTP/TCP and RTP/UDP traffic from the A/V Edge external interface to the Internet. |
 External A/V Firewall Port
Requirements for External User Access
External A/V Firewall Port
Requirements for External User Access
The firewall port requirements for external (and internal) SIP and conferencing (PowerPoint presentations, whiteboarding and polling) interfaces are consistent, regardless of the version your federation partner is running.
The same is not true for the Audio/Video Edge external interface. In most cases, the A/V Edge service requires that external firewall rules allow RTP/TCP and RTP/UDP traffic in the 50,000 through 59,999 port range to flow in one or both directions. For example, opening this port range is required to support certain federation scenarios and the preceding table provides the details for each scenario. The table assumes that Lync Server 2010 is the primary federation partner and it is being configured to communicate with one of the four federation partner types listed.
 Note: Note: |
|---|
| Regarding the 50,000-59,999 port range, the best practice for Lync Server 2010 is to open it outbound, to "Any" for RDP/TCP for the A/V Edge external interface if corporate policy allows. |
 NAT Requirements for External
User Access
NAT Requirements for External
User Access
NAT is typically a routing function, but newer devices such as firewalls, and even hardware load balancers can be configured for NAT. Rather than focusing on which device is performing NAT, this topic describes the required NAT behavior instead.
Microsoft Lync Server 2010 communications software does not support NAT for traffic to or from the Edge internal interface, but for the Edge external interface, the following NAT behavior is required. This documentation uses the acronyms ChangeDST and ChangeSRC in tables and drawings to define the following required behavior:
- ChangeDST The process of changing the
destination IP address on packets destined for the network that is
using NAT. This is also known as transparency, port forwarding,
destination NAT mode, or half-NAT mode.
- ChangeSRC the process of changing the
source IP address on packets leaving the network that is using NAT.
This is also known as proxy, secure NAT, stateful NAT, source NAT
or full-NAT mode.
Regardless of the naming convention used, the NAT behavior required for the external interface of the Edge Server is as follows:
- For traffic from the Internet to the Edge external
interface:
- Change the destination IP address of the incoming packet from
the Edge external interface public IP address to the translated IP
address of the Edge external interface.
- Leave the source IP address intact so that there is a return
route for the traffic.
- Change the destination IP address of the incoming packet from
the Edge external interface public IP address to the translated IP
address of the Edge external interface.
- For traffic from the Edge external interface to the
Internet:
- Change the source IP address of the packet leaving the Edge
external interface, from the translated IP address to the public IP
address of the Edge external interface so that the internal Edge IP
address is not exposed and because it is a non-routable IP
address.
- Leave the destination IP address intact on the outgoing
packets.
- Change the source IP address of the packet leaving the Edge
external interface, from the translated IP address to the public IP
address of the Edge external interface so that the internal Edge IP
address is not exposed and because it is a non-routable IP
address.
The following figure shows the distinction between changing the destination IP address (ChangeDST) for inbound traffic and changing the source IP Address (ChangeSRC) for outbound traffic using the A/V edge as an example.
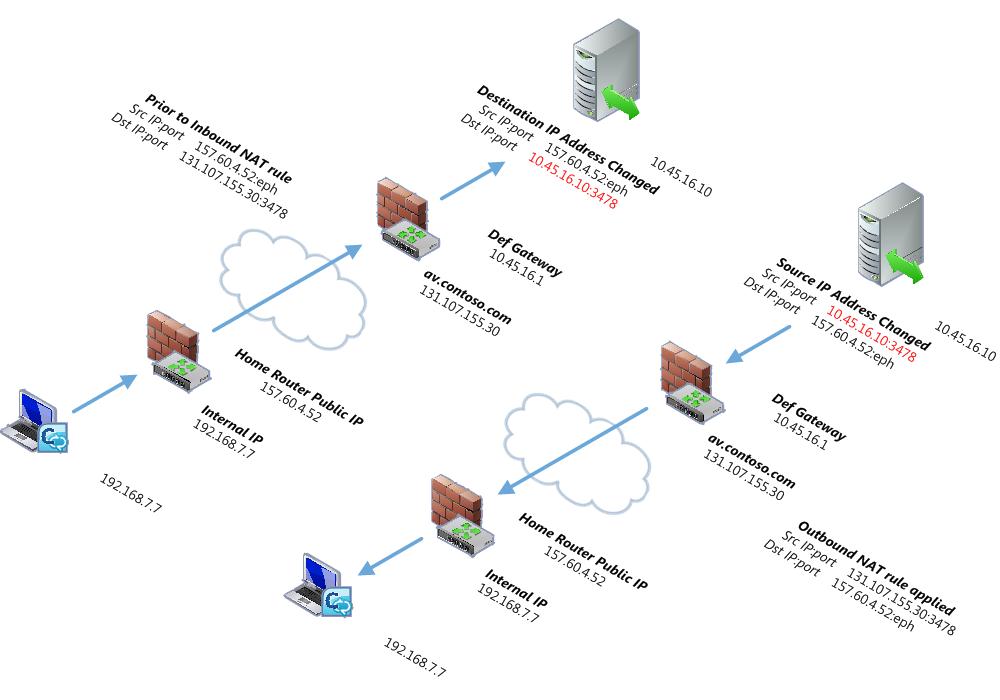
The key points are:
- For traffic incoming to the A/V Edge, the source IP address and
port do not change but the destination IP address changes from
63.123.155.30 to the translated IP address of 10.45.16.10.
- For traffic outbound from the A/V Edge back to the workstation,
the source IP address changes from that of the workstation’s public
IP address to that of the A/V Edge’s public IP address. And the
destination IP remains the workstation’s public IP address. After
the packet leaves the first NAT device outbound, the rule on the
NAT device changes the source IP address from the A/V Edge’s
external interface IP address (10.45.16.10) to its public IP
address (63.123.155.30).

