Topic Last Modified: 2012-09-21
Media bypass refers to removing the Mediation Server from the media path whenever possible for calls whose signaling traverses the Mediation Server.
Media bypass can improve voice quality by reducing latency, needless translation, possibility of packet loss, and the number of points of potential failure. Scalability can be improved, because elimination of media processing for bypassed calls reduces the load on the Mediation Server. This reduction in load complements the ability of the Mediation Server to control multiple gateways.
Where a branch site without a Mediation Server is connected to a central site by one or more WAN links with constrained bandwidth, media bypass lowers the bandwidth requirement by allowing media from a client at a branch site to flow directly to its local gateway without first having to flow across the WAN link to a Mediation Server at the central site and back.
By relieving the Mediation Server from media processing, media bypass may also reduce the number of Mediation Servers that an Enterprise Voice infrastructure requires.
The following figure shows basic media and signaling pathways in topologies with and without media bypass.
Media and signaling pathways with and without media bypass
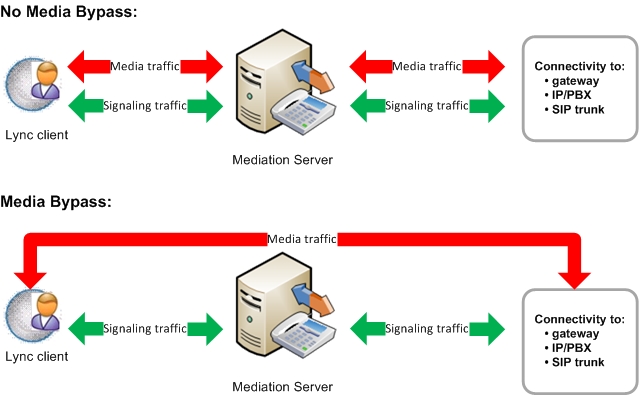
As a general rule, enable media bypass wherever possible.
 See Also
See Also

