Office Communications Server supports the following three scenarios or workloads: instant messaging (IM) and presence, conferencing (including Web conferencing, desktop sharing, audio/video conferencing), and Enterprise Voice, which encompasses telephony. This section describes all of the architectural components of an Office Communications Server 2007 R2 Standard Edition server or Enterprise pool. Collectively, these components support all three workloads.
This section focuses on the services that run on the core Office
Communications Server roles, the components within those services,
and relationships between them. This section does not cover network
architecture or deployment architecture, which complement component
architecture. For details about those aspects of architecture, see
the
While this section describes components in the context of an Enterprise pool, it also applies to most aspects of a Standard Edition server. All server components (that is, services, database, and so on) described in this section run together on a single instance of a Standard Edition server. This is a typical configuration for simple or relatively small deployments (that is, up to a few thousand users) where high availability is not a requirement.
Conceptually, a pool consists of one or more Front End Servers and one or more databases on the Back-End Database Server with a single SQL Server. In a pool, all persistent states are stored in the database on the Back-End Database Server, so that when a Front End Server component fails, failover can be quick. Figure 1 shows a sample Enterprise pool.
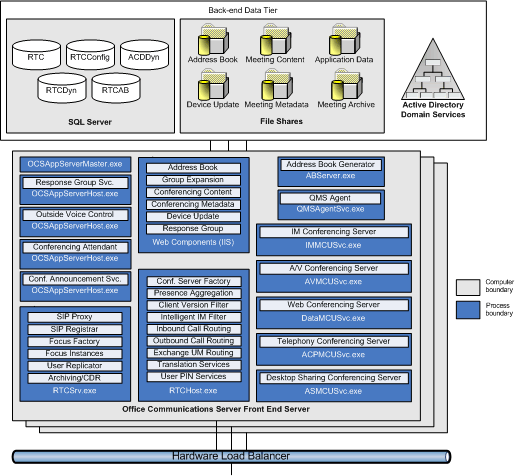
Figure 1 illustrates the components of Front End Servers and the Back-End Database Server. There is a hardware load balancer for the Front End Servers, which are required for an Enterprise pool that has more than one Enterprise Edition server. (If your pool consists of only one Front End Server, which is connected to a separate Back-End Database Server running SQL Server, a load balancer is not required.) All Front End Servers in a consolidated configuration pool are homogeneous and identical to each other. Therefore, all relevant Office Communications Server services and applications are installed on all Front End Servers in this type of a pool.
On each Office Communications Server 2007 R2 Front End Server, the main components can be classified as follows:
-
Common infrastructure components.These components are
required for the operation of any Office Communications Server
workload, and provide a foundation for conferencing and voice
components. The common infrastructure components include:
-
RTCSrv.This is the main Office Communications Server service
that runs the Office Communications Server Session Initiation
Protocol (SIP) stack, performs presence functions, performs
directory replication functions and interfaces with the database,
hosts application interfaces, and has modules to capture archiving
and call detail recording (CDR) data.
-
Back-end database.This is a SQL persistent store with
information on user identities and capabilities that are replicated
from Active Directory, user contact lists, and dynamic presence and
conferencing data.
-
RTCHost.This process hosts several Office Communications
Server applications for presence, conferencing, and Enterprise
Voice that are required for core functioning of these scenarios.
-
OCS Application interfaces.These interfaces enable the
applications on RTCHost (as well as third-party applications built
on the same API) to interface with the main server process RTCSrv
(for example, to inspect the SIP stream).
-
Web Components infrastructure.This infrastructure, which is
built on Microsoft Internet Information Server (IIS), hosts various
HTTP components required for presence, conferencing, and Enterprise
Voice functions.
-
UCAS infrastructure.The Unified Communications Application
Services (UCAS) infrastructure enables Office Communications Server
to host robust, scalable, middle-tier server endpoint applications.
Several UCAS applications for Enterprise Voice are hosted by this
infrastructure.
-
RTCSrv.This is the main Office Communications Server service
that runs the Office Communications Server Session Initiation
Protocol (SIP) stack, performs presence functions, performs
directory replication functions and interfaces with the database,
hosts application interfaces, and has modules to capture archiving
and call detail recording (CDR) data.
-
Conferencing components.These components include various
conferencing-specific components hosted by the common
infrastructure discussed previously (for example, an RTCHost
application, several web components), as well as a set of
conferencing servers which perform mixing functions for IM
conferencing, Web conferencing, desktop sharing conferencing, and
audio/video conferencing.
-
Voice components.These are the additional Office
Communications Server components required for enterprise telephony
functions. These components include RTCHost applications for
inbound telephony routing, outbound telephony routing, and phone
number normalization, as well as UCAS applications for dial-in
conferencing, response groups (that is, similar to Automatic Call
Distribution for Voice), and Outside Voice Control (which extends
enterprise telephony functionality to cellular phones).
Each of these classes of components is described in the topics that follow.








 See Also
See Also