This figure shows the data flow between participating components when an intranet client creates and joins a conference.
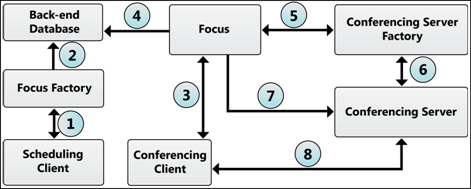
This is a description of the data flow between conferencing components when an intranet client creates and joins a conference:
-
Step 1.The scheduling client communicates with the Focus
Factory using Domain Name System (DNS) lookup or the manually
configured server address. The scheduling client sends information
required for creating a meeting, such as the conference ID,
participant list, user role information, and expiration date in a
SERVICE request.
-
Step 2.The Focus Factory creates a conference record in the
conferencing database on the Back-End Database Server. The Focus
Factory also creates and returns a SIP URI that represents the
conference to the client.
-
Step 3.The conferencing client connects to the Focus and
establishes two dialogs with it, an INVITE dialog to join a
conference and carry additional command traffic from the client to
the Focus and a SUBSCRIBE/NOTIFY dialog to get conference state
change notifications.
-
Step 4.The Focus connects to the Back-End Database Server to
retrieve the conference record and to query the conferencing
database to verify that the client joining the meeting is valid.
Policy checks are also performed at this time.
-
Step 5.The Focus requests information from the Conferencing
Server Factory about how to contact a conferencing server.
-
Step 6.The Conferencing Server Factory finds the
conferencing server of the type requested by the Focus and then
tries to provision a conference on that conferencing server, in
order to allocate resources for the conference. If provisioning
succeeds, the Conferencing Server Factory returns to the Focus an
HTTP URL that allows the Focus to establish a control link with the
conferencing server.
-
Step 7.The Focus communicates with the conferencing server
to issue commands that begin or end the conference, change the
participant list, or otherwise change the conference state.
-
Step 8.The conferencing client communicates with the
conferencing server. If the server is an A/V Conferencing Server,
the signaling protocol is SIP and the media is transported over
RTP/RTCP. If the server is a Web Conferencing Server, both
signaling and media are sent using the PSOM protocol. If the server
is an Application Sharing Server, the signaling protocol is SIP and
the media is transported over RDP encapsulated within RTP.








 See Also
See Also