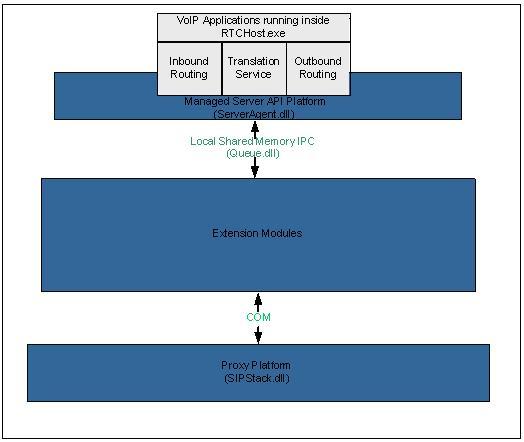
The core voice components of Office Communications Server 2007 R2 are the Inbound Routing application, the Translation Service, and the Outbound Routing application that run inside the RTCHost.exe process on each Front End Server. The Inbound Routing application determines how incoming calls to the server should be routed, based on settings configured on the client. The Translation Service uses administrator-specified phone number normalization rules to translate a dialed number into an E.164 format that can be consumed by other components in the system, such as the private branch exchange (PBX) or public switched telephone network (PSTN) gateway. The Outbound Routing application uses call authorization rules to route each call to the appropriate media gateway.
The following figure shows the architecture of the core components: Translation Service, Inbound Routing, and Outbound Routing.
 Inbound Routing
Inbound Routing
The Inbound Routing application determines how incoming calls to the server should be routed. If an Enterprise Voice client specifies settings for handling missed calls, the Inbound Routing application acts accordingly. For example, if a client is configured for call forwarding, the Inbound Routing application can forward incoming calls either to a specified number or to an Exchange Server 2007 Unified Messaging server that can answer the call.
 Translation Service
Translation Service
The Translation Service applies administrator-specified phone number normalization rules to translate a dialed number into an E.164 format that can be more easily consumed by a PBX or PSTN gateway. Enterprise Voice in Office Communications Server 2007 R2 employs the Translation Service to normalize phone numbers into a single format. Normalized phone numbers assist the server with reverse number lookup, outbound call routing, and call authorization rules.
Reverse number lookup is a process whereby a user's phone number is mapped to the appropriate SIP Uniform Resource Identifier (URI). By performing reverse number lookup, the server can route calls to all endpoints associated with a particular user’s SIP URI. Reverse number lookup also enables advanced call handling features, such as call forwarding.
After a dialed number is normalized by the Translation Service, the Outbound Routing application can apply call authorization rules to route the call.
 Outbound Routing
Outbound Routing
The Outbound Routing application uses call authorization rules configured by the administrator to route each call to the appropriate media gateway. Call authorization rules in Office Communications Server 2007 R2 are similar to traditional telephony "class of service" options. If the Outbound Routing application determines that a caller is not authorized to dial a particular number (for example, numbers outside the organization or international numbers), the Outbound Routing application can inform the caller that the call cannot be completed.







 See Also
See Also