The interface for connecting Office Communications Server environment to the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) trunk of the service provider is made on the external side of a Mediation Server. The following list contains the supported topologies that you can use to enable this connection to your service provider’s SIP trunk:
-
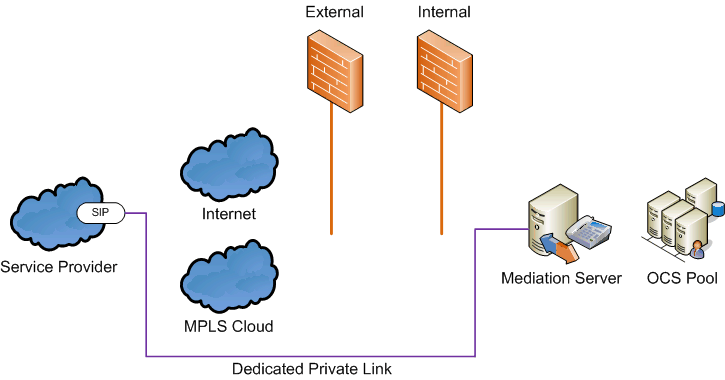
Private connection.In this configuration, the mediation
server connects to the SIP trunk using a private network connection
to the service provider. For instance, this could be a dedicated
MPLS T1 connection installed for the purpose of SIP trunking.
-
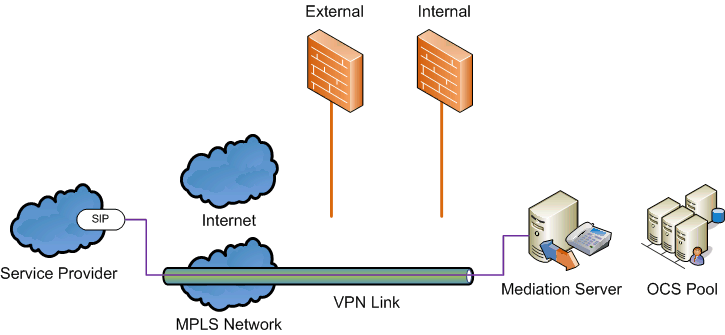
VPN connection.In this configuration, the mediation server
connects to the SIP trunk using a virtual private network (VPN)
connection to the service provider. This could run over a general
Internet connection or an existing MPLS wide area network (WAN)
connection. Unlike the private connection option, these
multi-purpose connections are usually shared and used for multiple
scenarios. The purpose for the VPN connection is to create an
isolated, secure channel on which the SIP trunked calls are
carried.
-
Public Connection.In this configuration, the Mediation
Server connects to the SIP trunk by using a direct Internet
connection. Unlike the private and VPN options, this topology does
not leverage an isolated link to the SIP trunk.









 See Also
See Also