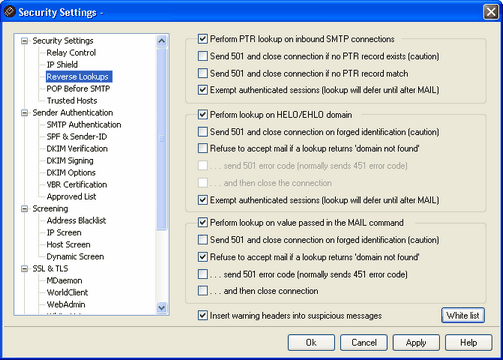
With the options on this screen, MDaemon can be configured to do a reverse lookup on the domain passed in the HELO/EHLO and MAIL commands. When performing the lookups MDaemon will attempt to acquire all of the MX and A record IP addresses for the given domain. Then the IP of the server making the connection is compared to this list in an attempt to determine whether the sender might be using a forged identity.
Oftentimes the sending mail server's IP address will not match any known MX or A records for a given domain and yet still be delivering the mail legitimately. The purpose of the Reverse Lookup process is therefore not to exclude mail but to include as much information as possible in the log files, and to provide the means whereby the postmasters can act according to their own local policies regarding these suspicious messages. To that end, an option exists that makes it possible for a special header to be inserted into all messages that do not pass a reverse lookup. The content filter system can then be used to determine the fate of messages containing the header.
You can also perform reverse lookups on pointer records (PTR) of incoming IP addresses. When using this option the connection can be aborted or a warning header inserted into the message if the incoming IP address does not match any PTR record.
Finally, it is generally agreed that accepting mail from sources that identify themselves by using a domain that does not exist should be optional. Therefore, a switch exists that makes it possible for you to refuse messages for which the reverse lookup process returns a "domain not found" message from the DNS server. In such cases, MDaemon will return a 451 error code, refuse to accept the message, and then allow the SMTP session to progress. However, should you wish to return a 501 error code, close the socket connection, or do both, other switches are provided for those purposes.
Trusted IP addresses and localhost (127.0.0.1) are always exempt from reverse lookups.
Perform PTR lookup on inbound SMTP connections
Enable this option if you want MDaemon to perform pointer record lookups on all inbound SMTP connections.
...send 501 and close connection if no PTR record exists (caution)
If this box is checked then MDaemon will send a 501 error code (syntax error in parameters or arguments) and close the connection if no PTR record exists for the domain.
...send 501 and close connection if no PTR record match
If this box is checked then MDaemon will send a 501 error code (syntax error in parameters or arguments) and close the connection if the result of a pointer record lookup fails to match.
Exempt authenticated sessions (lookup will defer until after MAIL)
Click this option if you wish to defer the PTR lookup on inbound SMTP connections until after the SMTP MAIL command in order to see whether or not the connection will use authentication.
Perform lookup on HELO/EHLO domain
Click this box if you want a lookup to be performed on the domain name that is reported during the HELO/EHLO portion of the session. The HELO/EHLO command is used by the client (sending machine) to identify itself to the server. The domain name passed by the client in this command is used by the server to populate the from portion of the Received header.
Perform lookup on value passed in the MAIL command
Enabling this switch will cause a lookup to be performed on the domain name that is passed during the MAIL command portion of the mail transaction. The address passed in the MAIL command is supposed to be the reverse-path for the message, and is usually the mailbox from which the message is originating. Sometimes, however, it is the address to which error messages should be directed instead.
...send 501 and close connection on forged identification (caution)
Click this check box if you want a 501 error code to be sent and then the connection closed when the result of a lookup appears to be a forged identification.
|
|
When the result of a reverse lookup states that the server is using a forged identification, this result may frequently be incorrect. It is very common for mail servers to identify themselves with values that do not match their IP addresses. This can be due to ISP limitations and restrictions and other legitimate reasons. For this reason, you should exercise caution before enabling this option. It is likely that using this option could result in your server refusing some legitimate messages. |
Refuse to accept mail if a lookup returns 'domain not found'
When a lookup results in "domain not found", enabling this option will cause the message to be refused with a 451 error code (Requested action aborted: local error in processing) and then the session will be allowed to progress normally to its conclusion.
...send 501 error code (normally sends 451 error code)
Enable this checkbox if you want the error code that is sent in response to a "domain not found" result to be 501 (syntax error in parameters or arguments) instead of 451.
...and then close the connection
Click this checkbox if you want the connection to be closed immediately instead of allowed to progress when "domain not found" is the result of the reverse lookup.
Exempt authenticated sessions (lookup will defer until after MAIL)
Click this option if you wish to defer the lookup until after the SMTP MAIL command in order to see whether or not the connection will use authentication.
Insert warning headers into suspicious messages
Click this checkbox if you want a header to be inserted into messages that are considered suspicious due to the results of the reverse lookup. You can edit the name and content of the header by adding the following MDaemon.ini key:
[Special]
LookupWarningHeader=X-Lookup-Warning: text
If you edit this value, MDaemon will allow you to make the "X-Lookup-Warning: text" portion anything that you want, but be certain that your alterations conform to RFC regulations regarding mail headers.
White list
Click this button to open the Reverse Lookup White List dialog. On it you can designate IP addresses, domains, and hosts that you wish to be exempt from reverse lookups.