The
Microsoft.Lync.Model
.
.
::
.
.
LyncClient
class is the basis for all Microsoft Lync 2010 API
functionality. This class exposes a static method,
LyncClient
.
.
::
.
.
GetClient
, that you call to get an instance of the
Microsoft.Lync.Model
.
.
::
.
.
LyncClient
class before initiating any further Lync 2010 API logic. All
subsequent application logic uses this class instance for Lync 2010
API features.
The
Microsoft.Lync.Model
.
.
::
.
.
LyncClient
instance uses the endpoint established by a running instance
of Microsoft Lync 2010. When you sign in, sign out, start or accept
a conversation, add contacts or custom groups, you are actually
performing these actions using the Lync 2010 endpoint. As your
custom application performs these actions, you see these actions
mirrored in Lync 2010.
 Important
Important
|
|
For the call to the
LyncClient
.
.
::
.
.
GetClient
method to succeed, Lync 2010 must be running on the local
computer.
|
 Signing in and out of Lync
Server
Signing in and out of Lync
Server
The
Microsoft.Lync.Model
.
.
::
.
.
LyncClient
class lets you verify that your local user is signed in to
Lync Server 2010. If not signed in then you call the
LyncClient
.
.
::
.
.
BeginSignIn
method to sign the local user in. If the local user is
already signed in to Lync Server 2010, calling this method raises
an exception. You should read the
Client
.
.
::
.
.
State
property to discover the sign-in state before attempting to
sign in.
You can also sign the user out of Lync Server 2010 using the
Microsoft.Lync.Model
.
.
::
.
.
LyncClient
instance. A call to the
LyncClient
.
.
::
.
.
BeginSignOut
method raises an exception if the user not signed in to Lync
Server 2010.
The sign-in/sign-out process is asynchronous and requires that
you handle events raised by the
Microsoft.Lync.Model
.
.
::
.
.
LyncClient
instance when you have called either of the previous
methods. For information about asynchronous programming in Lync
2010 API, see
Asynchronous
Programming
.
 Classes Exposed by the LyncClient
Class
Classes Exposed by the LyncClient
Class
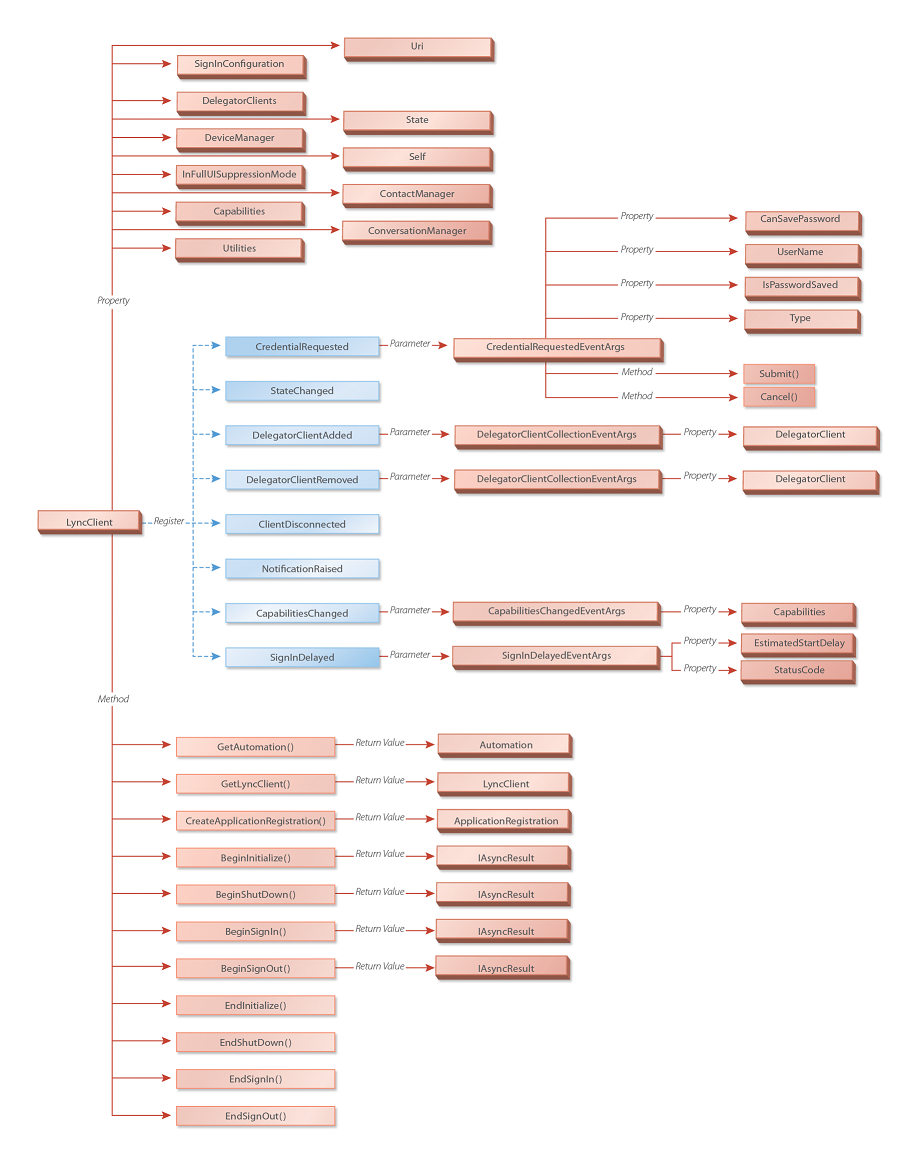
The following figure illustrates the classes you obtain from the
Microsoft.Lync.Model
.
.
::
.
.
LyncClient
class. Note that these client classes expose member methods
and classes for more specific functionality.
Conversation Manager
To start a new conversation with another user or join a
conference, you get an instance of the
Microsoft.Lync.Model.Conversation
.
.
::
.
.
ConversationManager
class from your
Microsoft.Lync.Model
.
.
::
.
.
LyncClient
instance. The conversation manager exposes a collection of
current conversations as well as a collection of properties
describing previous conversations. You obtain the voice mails
manager class from the conversation manager so that you can access
the Outlook voicemail system for retrieving voice mail.
Contacts and Groups Manager
The contacts and groups manager class (
Microsoft.Lync.Model.Conversation
.
.
::
.
.
ConversationManager
) gives you access to the local user's contact list. Through
this class, you can:
-
Enumerate the contact list and the group list.
-
Add and remove contacts and distribution groups from the contact
list.
-
Add and remove contacts from custom groups.
-
Add, remove, and rename custom groups.
-
Enumerate the contacts in a distribution group.
Self
The
Microsoft.Lync.Model
.
.
::
.
.
Self
class allows you to:
-
Publish a set of the local user's telephone numbers for other
users to use.
-
Set inbound call routing rules to control which phone to ring
for an inbound call.
-
Set many user options for customization.
Delegator Client
The
Microsoft.Lync.Model
.
.
::
.
.
DelegatorClient
class allows your user to assign a team member such as an
administrative assistant to the responsibility of answering
incoming telephone calls on your user's behalf.
Utilities
The
Microsoft.Lync.Model
.
.
::
.
.
Utilities
class provides features such as email sending, meeting
scheduling, a device-tuning wizard, adding contacts to Outlook, and
accessing previous conversations stored in Microsoft Outlook.
Device Manager
The
Microsoft.Lync.Model.Device
.
.
::
.
.
DeviceManager
class lets you discover the device for audio and video
transmissions and play an audio file on a specified playback
device.
 In this Section
In this Section
 See Also
See Also
Other Resources
API Overview
The Automation Interface
 Signing in and out of Lync
Server
Signing in and out of Lync
Server
 Classes Exposed by the LyncClient
Class
Classes Exposed by the LyncClient
Class
