Topic Last Modified: 2006-12-05
The Microsoft® Exchange Server Analyzer Tool queries the Win32_NetworkAdapterConfiguration Microsoft Windows® Management Instrumentation (WMI) class to obtain the DNSServerSearchOrder attribute for remote servers that the server that is running Exchange Server tries to send messages to. This attribute is an array of server IP addresses that are used to query for Domain Name System (DNS) servers.
The Exchange Server Analyzer also queries the Microsoft Active Directory® directory service to determine the value for the msExchSMTPExternalDNSServers attribute in the protocolCfgSMTPServer class for the Exchange 2000 Server and Exchange Server 2003 server objects. The protocolCfgSMTPServer class contains the settings for a Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) virtual server. If the msExchSMTPExternalDNSServers attribute is set, the SMTP virtual server uses an external DNS server.
Finally, the Exchange Server Analyzer uses the following Exchange Management Shell cmdlet to query for the values of the ExternalDNSServers and InternalDNSServers properties of any target Exchange 2007 Transport server roles. The ExternalDNSServers property specifies the list of external DNS servers that the server queries when it resolves a remote domain. The InternalDNSServers property specifies the list of DNS servers that should be used to resolve a local domain name for the target server.
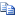 Copy Code Copy Code |
|
|---|---|
get-TransportServer -Identity %ExchangeServerName% -DomainController %DomainControllerName% |
|
The Exchange Server Analyzer displays an error if the following conditions are true:
- The Exchange Server Analyzer is unable to successfully retrieve
the value of the DNSServerSearchOrder attribute.
Alternatively, the attribute contains no data.
- The msExchSMTPExternalDNSServers attribute for the
Exchange 2000 Server and Exchange Server 2003 server
objects is not set.
- The values of the ExternalDNSServers and
InternalDNSServers properties for the target
Exchange 2007 Transport server roles contain no data.
This error indicates that the Exchange Server Analyzer cannot identify any DNS servers that are used by the target Exchange server. In addition, mail flow may be adversely affected by this condition.
Possible causes of this condition may include the following:
- DNS is configured incorrectly on the target server.
- WMI is failing or cannot be accessed.
To resolve this issue:
- Review the DNS configuration on the target server.
- Verify that the Exchange WMI can be accessed.
-
Make sure that the Exchange server has been started and is connected to the network.
-
Use the PING command to see whether the Exchange server is reachable.
-
If there is a firewall, check to see whether remote procedure call (RPC) ports are blocked.
-
Examine the permissions for the account under which the Exchange Server Analyzer is running. The account under which the Exchange Server Analyzer is running must have local Administrator permissions on each Exchange server that it scans.
Alternatively, you can grant specific WMI permission to the account under which the Exchange Server Analyzer runs:
- On the Exchange server, open the Computer Management
Microsoft Management Console (MMC) tree.
- Under Services and Applications, right-click WMI
Control, and then click Properties.
- On the WMI Controls Property page, click the
Security tab, and then expand Root.
- Select the CIMV2 folder, and then click
Security.
- On the Security for ROOT\CIMV2 page, add the account
under which the Exchange Server Analyzer runs.
- On the Exchange server, open the Computer Management
Microsoft Management Console (MMC) tree.
-
Select the account that you added in step 4. In Permissions for Selected_Account, under the Allow column, select both Remote Enable and Read Security, and then click OK.
For more information about how to configure DNS to work with Exchange Server, see Microsoft Knowledge Base article 322856, "How to configure DNS to use with Exchange Server" (http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=3052&kbid=322856).
For more information about network connectivity problems, see Microsoft Knowledge Base article 325487, "How to troubleshoot network connectivity problems" (http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=3052&kbid=325487).
For more information about Exchange Server Analyzer connectivity problems, see "Microsoft Exchange Server Best Practices Analyzer Tool Troubleshooting Connectivity Problems" (http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=56285).
For more information about port requirements, see Knowledge Base article 832017, "Service overview and network port requirements for the Windows Server system" (http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=3052&kbid=832017).

