Applies to: Exchange Server 2010 SP3, Exchange Server 2010 SP2
Topic Last Modified: 2010-01-20
Because organizations tend to group their management tasks around a core set of server roles, Exchange 2010 maps Exchange Server management to this same approach.
A server role is a unit that logically groups the required features and components needed to perform a specific function in the messaging environment. The requirement of a server role is that it is a server that could be run as an atomic unit of scalability. A server role is composed of a group of features.
Server roles, the primary unit of deployment, enable administrators to easily choose which features are installed on an Exchange server. Logically grouping features in server roles offers the following advantages:
- Reduces attack surface on an Exchange server.
- Allows you to install and configure an Exchange server the way
you intend to use it.
- Offers the ability to fully customize a server to support your
business goals and needs.
The following figure illustrates a domain with each server role deployed.
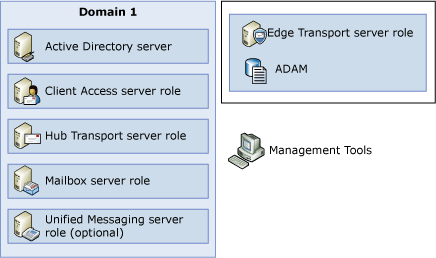
Exchange 2010 includes the following server roles:
- Mailbox Server This server hosts
mailboxes and public folders. For more information about the
Exchange 2010 Mailbox server role, see Overview of the Mailbox
Server Role.
- Client Access Server This is the server
that hosts the client protocols, such as Post Office
Protocol 3 (POP3), Internet Message Access Protocol 4
(IMAP4), Secure Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTPS), Outlook
Anywhere, Availability service, and Autodiscover service. The
Client Access Server also hosts Web services. For more information
about the Exchange 2010 Client Access server role, see Client Access.
- Unified Messaging Server This is the
server that connects a Private Branch eXchange (PBX) system to
Exchange 2010. For more information about the Exchange 2010 Unified
Messaging server role, see Unified
Messaging.
- Hub Transport Server This is the mail
routing server that routes mail within the Exchange organization.
For more information about the Exchange 2010 Hub Transport server
role, see Transport and
Overview of the
Hub Transport Server Role.
- Edge Transport Server This is the mail
routing server that typically sits at the perimeter of the topology
and routes mail in to and out of the Exchange organization. For
more information about the Exchange 2010 Edge Transport server
role, see Transport and
Overview of the
Edge Transport Server Role.

