Applies to: Exchange Server 2013
Topic Last Modified: 2012-10-14
You can configure a hierarchical address book (HAB), which is a feature in Microsoft Exchange Server 2013 and Microsoft Outlook 2010 or later. With a HAB, users can browse recipients in their Exchange organization by using an organizational hierarchy. To learn more about HABs, see Hierarchical Address Books.
What do you need to know before you begin?
- Estimated time to complete: 1 hour.
- You need to be assigned permissions before you can perform this
procedure or procedures. To see what permissions you need, see the
"Distribution groups" entry in the Recipients
Permissions topic.
- You can’t use the Exchange Administration Center (EAC) to
perform this procedure. You must use the Shell.
- Before you get started, read the topic Hierarchical Address
Books. You should understand if a HAB is appropriate for your
Exchange organization.
- Understand how organizational units (OUs), groups, users, and
contacts are currently configured in your Exchange
organization.
- Understand the cmdlets and associated parameters in the
following table, which are required to configure a HAB.
Cmdlet Parameter HierarchicalAddressBookRoot
IsHierarchicalGroup
SeniorityIndex
PhoneticDisplayName
SeniorityIndex
PhoneticDisplayName
SeniorityIndex
PhoneticDisplayName
- For information about keyboard shortcuts that may apply to the
procedures in this topic, see Keyboard Shortcuts in
the Exchange Admin Center.
 Tip: Tip: |
|---|
| Having problems? Ask for help in the Exchange forums. Visit the forums at: Exchange Server, Exchange Online, or Exchange Online Protection |
What do you want to do?
Use the Shell to enable a HAB
 Note: Note: |
|---|
| Although you can't use the EAC to enable a HAB, after it’s enabled you can use the EAC to manage the membership of the groups in the organizational hierarchy. |
For this example, an OU called HAB will be created for the HAB. The name of the domain for the Exchange 2013 organization is Contoso-dom, and Contoso,Ltd will be the name of the top-level organization in the hierarchy (the root organization). Subordinate groups named Corporate Office, Product Support Organization, and Sales & Marketing Organization will be created as child organizations under Contoso,Ltd. Additionally, the groups Human Resources, Accounting Group, and Administration Group will be created as child organizations under Corporate Office.
For detailed information about creating distribution groups, see Manage Distribution Groups.
- Create an OU named HAB in the Contoso organization. You can use
Active Directory Users and Computers or type the following at a
command prompt.
 Note:
Note:Alternatively, you can use an existing OU in your Exchange forest.  Copy Code
Copy Codedsadd ou "OU=HAB,DC=Contoso-dom,DC=Contoso,DC=com"
 Note:
Note:For details, see Create a New Organizational Unit. - Create the root distribution group Contoso,Ltd for the HAB.
 Note:
Note:For the purposes of this topic, the Shell example is provided. However, you can also use the EAC to create a distribution group. For details, see Manage Distribution Groups.  Copy Code
Copy CodeNew-DistributionGroup -Name "Contoso,Ltd" -DisplayName "Contoso,Ltd" -Alias "ContosoRoot" -OrganizationalUnit "Contoso-dom.Contoso.com/HAB" -SamAccountName "ContosoRoot" -Type "Distribution"
- Designate Contoso,Ltd as the root organization for the HAB.
 Copy Code
Copy CodeSet-OrganizationConfig -HierarchicalAddressBookRoot "Contoso,Ltd"
- Create distribution groups for the other tiers in the HAB. For
this example, you would create the following groups: Corporate
Office, Product Support Organization, Sales & Marketing
Organization, Human Resources, Accounting Group, and Administration
Group. This example creates the distribution group Corporate
Office.
 Note:
Note:For the purposes of this topic, the Shell example is provided. However, you can also use the EAC to create distribution groups. For details, see Manage Distribution Groups.  Copy Code
Copy CodeNew-DistributionGroup -Name "Corporate Office" -DisplayName "Corporate Office" -Alias "CorporateOffice" -OrganizationalUnit "Contoso-dom.Contoso.com/HAB" -SamAccountName "CorporateOffice" -Type "Distribution"
- Designate each of the groups as members of the HAB. For this
example, you would designate the following groups as being
hierarchical groups: Contoso,Ltd, Corporate Office, Product Support
Organization, Sales & Marketing Organization, Human Resources,
Accounting Group, and Administration Group. This example designates
the distribution group Contoso,Ltd as a member of the HAB.
 Copy Code
Copy CodeSet-Group -Identity "Contoso,Ltd" -IsHierarchicalGroup $true
- Add each of the subordinate groups as members of the root
organization. For this example, distribution groups Corporate
Office, Product Support Organization, and Sales & Marketing
Organization, are added as members of the root organization
Contoso,Ltd in the HAB. This example adds the Corporate Office
distribution group as a member of the Contoso,Ltd root distribution
group.
 Note:
Note:This example uses the alias of the distribution groups.  Copy Code
Copy CodeAdd-DistributionGroupMember -Identity "ContosoRoot" -Member "CorporateOffice"
- Add each of the groups that are subordinate to the distribution
group Corporate Office as members of the group. For this example,
distribution groups Human Resources, Accounting Group, and
Administration Group, are added as members of the distribution
group Corporate Office. This example adds the Human Resources
distribution group as a member of the Corporate Office distribution
group.
 Note:
Note:This example uses the alias of the distribution groups and assumes the Human Resources distribution group alias is HumanResources.  Copy Code
Copy CodeAdd-DistributionGroupMember -Identity "CorporateOffice" -Member "HumanResources"
- Add users to the groups in the HAB. For this example, David
Hamilton (SMTP address DHamilton@contoso.com) is an existing user
in the OU Contoso-dom.Contoso.com/Users and will be added to the
group Corporate Office. Repeat this step to add other users to
groups in the HAB.
 Copy Code
Copy CodeAdd-DistributionGroupMember -Identity "CorporateOffice" -Member "DHamilton"
- Set the SeniorityIndex parameter for groups in the HAB.
For this example, the Corporate Office group contains three child
groups: Human Resources, Accounting Group, and Administration
Group. Instead of having the groups listed in ascending
alphabetical order, which is the default, the preferred sorting
will be Human Resources (SeniorityIndex = 100), Accounting
Group (SeniorityIndex = 50), and then Administration Group
(SeniorityIndex = 25). This example sets the
SeniorityIndex parameter for the Human Resources group to
100.
 Copy Code
Copy CodeSet-Group -Identity "Human Resources" -SeniorityIndex 100
 Note:
Note:The SeniorityIndex parameter is a numerical value used to sort groups or users in descending numerical order in a HAB. If the SeniorityIndex parameter isn't set or is equal for two or more users, the HAB sorting order uses the PhoneticDisplayName parameter value to list the users in ascending alphabetical order. If the PhoneticDisplayName value isn't set, the HAB sorting order defaults to the DisplayName parameter value and lists the users in ascending alphabetical order. - Set the SeniorityIndex parameter for users in the HAB
groups. For this example, the Corporate Office group contains three
users: Amy Alberts, David Hamilton, and Rajesh M. Patel. Instead of
having the users listed in ascending alphabetical order by default,
the preferred sorting will be David Hamilton (SeniorityIndex
= 100), Rajesh M. Patel (SeniorityIndex = 50), and then Amy
Alberts (SeniorityIndex = 25). This example sets the
SeniorityIndex parameter for the user David Hamilton to
100.
 Copy Code
Copy CodeSet-User -Identity "DHamilton@contoso.com" -SeniorityIndex 100
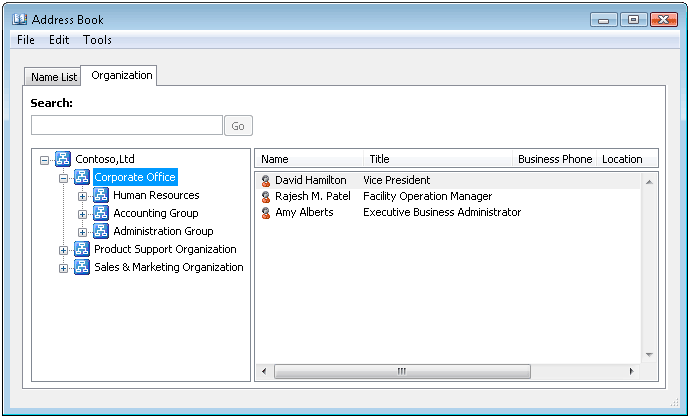
After completing the preceding steps, the HAB will be visible in Outlook. To view the HAB, open Outlook and click Address Book. The HAB is displayed on the Organization tab, similar to the following figure.
After the HAB is created, you can use the EAC to manage the membership of the groups in the organizational hierarchy. However, you must use the Shell to modify the SeniorityIndex parameter for any new groups or users.
For detailed syntax and parameter information, see the following:
Use the Shell to disable a hierarchical address book
This example disables the root organization used for the HAB.
 Copy Code Copy Code |
|
|---|---|
Set-OrganizationConfig -HierarchicalAddressBookRoot $null |
|
 Note: Note: |
|---|
| This command doesn't delete the root organization or child groups used in the HAB structure or reset the SeniorityIndex values for groups or users. It only prevents the HAB from being displayed in Outlook. To enable the HAB with the same configuration settings again, you only need to enable the root organization again. |
For detailed syntax and parameter information, see Set-OrganizationConfig.

