Applies to: Exchange Server 2007 SP3, Exchange Server
2007 SP2, Exchange Server 2007 SP1, Exchange Server 2007
Topic Last Modified: 2006-11-27
In Microsoft Exchange Server 2007 Unified Messaging (UM), callers can use dual tone multi-frequency (DTMF), also referred to as touch-tone, and voice inputs to interact with the system. The method callers can use depends on how the UM dial plans and auto attendants are configured.
The DTMF interface enables callers to use the telephone keypad to locate users and navigate the UM menu system when they call a subscriber access number that is configured on a dial plan or when they call a telephone number that is configured on an auto attendant. This topic discusses the DTMF interface and how it is used by callers to locate users and to navigate the Exchange 2007 Unified Messaging menu system.
For more information about how voice inputs are used in Unified Messaging, see Understanding Automatic Speech Recognition Directory Lookups.
 DTMF Overview
DTMF Overview
DTMF requires a caller to press a key on the telephone keypad that corresponds to a Unified Messaging menu option or to input a user's name by using the letters on the keys to spell the user's name or e-mail alias. Callers might use DTMF because Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) has not been enabled or because they tried to use voice commands and failed. In either case, DTMF inputs are used to navigate menus and search for users.
By default, in Exchange 2007 Unified Messaging, DTMF inputs are used on dial plans and are the default caller interface for UM auto attendants.
 Note: Note: |
|---|
| Only auto attendants that are configured to use English can be speech-enabled. |
DTMF inputs may be used by callers for:
- Dial plan subscriber access by using Outlook Voice Access.
- Dial plan directory lookups and searches to locate users.
- Auto attendants that are not speech-enabled.
- Auto attendants that are speech-enabled that do or do not have
a DTMF fallback auto attendant configured.
- DTMF fallback auto attendants (not speech-enabled).
 UM Dial Plans and Dial by
Name
UM Dial Plans and Dial by
Name
When you create a UM dial plan, you can configure the primary and secondary input method that callers will use to look up names when they search for a user or want to contact a user. These settings are located on the dial plan's Settings tab and are called Dial by name primary method and Dial by name secondary method. The following options are available for the Dial by name primary method and the Dial by name secondary method:
- Last First
- First Last
- SMTP Address
Additionally, None is an available option on the Dial by name secondary method.
By default, Last First is selected for the Dial by name primary method and SMTP Address is selected as the Dial by name secondary method. Therefore, when a caller dials in to the subscriber access number that is configured on the UM dial plan, the dial plan's welcome message will be played and the operator will say something like, "Welcome to Contoso Outlook Voice Access. To access your mailbox, enter your extension. To contact someone, press the # key." After the caller has pressed the # key, the system will respond with "Spell the name of the person you are calling, last name first, or to spell their e-mail alias, press the # key twice." In this scenario, depending on how your dial plan is configured, the system then prompts the caller to enter the user's last name first and then the user's first name (Last First) or to spell their e-mail alias, excluding the domain name.
For example, if the user's e-mail alias is tsmith@contoso.com, the caller would enter tsmith. If you want to change this configuration because the default setting does not meet your needs, you can change it to enable callers to enter the users e-mail alias first or the user's first name followed by their last name. In this case, you would configure the Dial by name primary method with the SMTP Address setting and configure the Dial by name secondary method with the First Last setting. The settings for the dial by name methods will also apply to any UM auto attendants that are associated with the dial plan. For callers to be able to enter the name of the user by using DTMF inputs or the keys on the telephone keypad, a DTMF map and values for the user must exist within the Active Directory directory service.
For more information about how to change the dial by name primary and secondary methods on a Unified Messaging dial plan, see How to Change the Dial by Name Primary Method on a Unified Messaging Dial Plan and How to Change the Dial by Name Secondary Method on a Unified Messaging Dial Plan.
 DTMF Maps
DTMF Maps
In an Exchange 2007 organization, an attribute named msExchUMDtmfMap is associated with each user that is created in Active Directory. This attribute is used by Unified Messaging to map the user's first name, last name, and e-mail alias to a set of numbers. This mapping is referred to as a DTMF map. A DTMF map enables a caller to enter the digits on the telephone keypad that correspond to the letters of the user's name or e-mail alias. This attribute contains the values that are needed to create a DTMF map for the user's first name followed by their last name, for the user's last name followed by their first name, and for the user's e-mail alias.
Table 1 shows the DTMF map values that would be stored in Active Directory on the msExchUMDtmfMap attribute for a UM-enabled user named Tony Smith with an alias of tsmith@contoso.com.
Table 1 DTMF values that are stored in Active Directory for a UM-enabled user named Tony Smith
| Active Directory entry | User's name |
|---|---|
|
tonysmith |
|
smithtony |
|
tsmith |
- Names and e-mail aliases may contain other non-alphabetic
characters such as commas, hyphens, underscores, or periods.
Characters such as these will not be used in a DTMF map for a user.
For example, if the e-mail alias for Tony Smith is
tony-smith@contoso.com, the DTMF map value would be 866976484 and
the hyphen would not be included. However, if a user's e-mail alias
contains a number or numbers, for example,
tonysmith123@contoso.com, the numbers would be used in the DTMF map
that is created. The DTMF map for tonysmith123 would be
866976484123.
A DTMF map must exist for a user for callers to be able to enter the user's name or e-mail alias. However, in some cases, not all users will have a DTMF map associated with their user account.
 DTMF Maps for Users Who Are Not
Enabled for UM
DTMF Maps for Users Who Are Not
Enabled for UM
Users, including mailbox-enabled users, are not enabled for Unified Messaging by default. Therefore, the msExchUMDtmfMap attribute is not populated with the values that are needed for a DTMF map for those users. Figure 1 illustrates the properties of a user for which the msExchUMDtmfMap attribute has not been populated.
Figure 1 msExchUMDtmfMap attribute without values
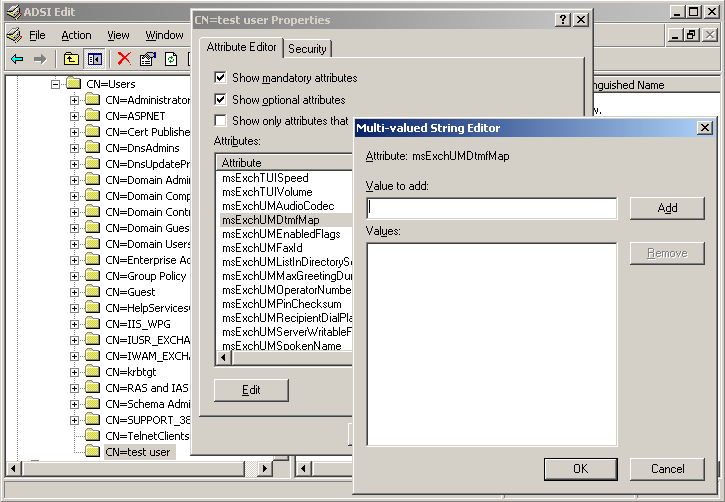
Because the users shown in the previous diagram do not have DTMF map values defined for their user accounts, callers will be unable to contact them when they press a telephone key from a UM auto attendant menu or perform a directory search. Also, UM-enabled users will be unable to send messages or transfer calls to users who do not have a DTMF map unless they can use ASR. To enable callers to transfer calls or contact non UM-enabled users by using the telephone keypad, you must create the necessary values for the DTMF map for users. To create the values for a DTMF map for users who are not enabled for Unified Messaging, you can run the galgrammargenerator.exe -u command. This command updates the DTMF maps for all users within your Microsoft Exchange. The galgrammargenerator.exe command updates or creates DTMF maps for all non UM-enabled users. You can use the Set-User cmdlet with the -CreateDtmfMap parameter to create and update a single user's DTMF map or update a DTMF map for a user if the name of the user was changed after a DTMF map was already created. Optionally, you can create an Exchange Management Shell script by using this cmdlet to update the DTMF map values for multiple users.
For more information about the Set-User Exchange Management Shell cmdlet, see Set-User.
For more information about galgrammargenerator.exe, see Understanding Automatic Speech Recognition Directory Lookups.
 DTMF Maps for Users Who Are
Enabled for UM
DTMF Maps for Users Who Are
Enabled for UM
A DTMF map is created for each UM-enabled user so that callers can contact them. By default, a DTMF map is created for users when they are enabled for Unified Messaging. This makes it possible for calls to be transferred to a UM-enabled user from external callers, non users who are not enabled for UM, and other UM-enabled users who use the telephone keypad to spell the user's name or e-mail alias. Figure 2 illustrates the properties on a user account where the msExchUMDtmfMap attribute has been populated with DTMF map values.
Figure 2 msExchUMDtmfMap attribute with values
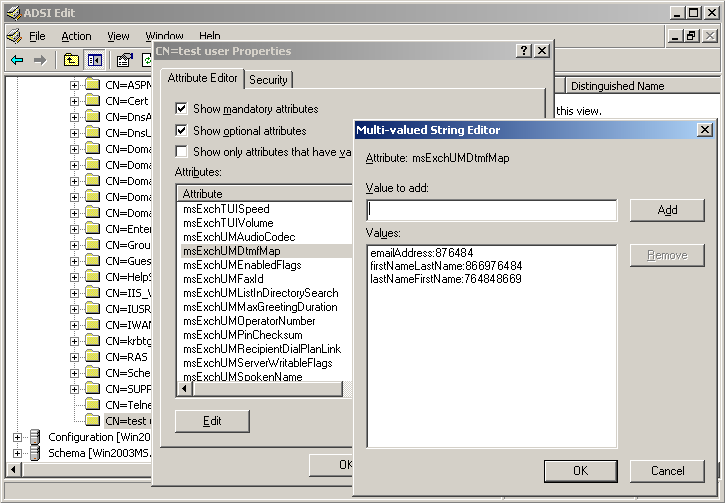
After the DTMF map values have been created for a UM-enabled user, callers can use the directory search feature. Callers use directory search when they use the telephone keypad to in the following situations:
- To identify or search for a user when they call in to the
subscriber access number
- To locate or transfer calls to a UM-enabled user when they call
in to a UM auto attendant.
For more information about how to enable a user for Unified Messaging, see How to Enable a User for Unified Messaging.
Sometimes a user's first name, last name, or e-mail alias changes after they have been enabled for Unified Messaging. The user's DTMF map values will not be updated automatically in Active Directory. If a caller enters the user's new last name or e-mail alias and the user's DTMF map has not been updated to reflect the change to the name or e-mail alias, the caller will be unable to locate the user in the directory, send a message to the user, or transfer calls to the user. If you have to update a user's DTMF map after they have been enabled for Unified Messaging, you can use the Set-User cmdlet with the -CreateDtmfMap parameter. You can also create an Exchange Management Shell script by using this cmdlet if you want to update the DTMF maps for multiple UM-enabled users.
 Note: Note: |
|---|
| You can also use the galgrammargenerator.exe -u command to update the DTMF map for UM-enabled users. However, if you use the galgrammargenerator.exe -u command, it will update or create DTMF maps for all users. |
 Caution: Caution: |
|---|
| We do not recommended that you manually change the DTMF values for users by using a tool such as ADSI Edit because it might result in inconsistent configurations or other errors. We recommend that you only use galgrammargenerator.exe or the Set-User cmdlet to create or update DTMF maps for users. |
 For More Information
For More Information
- For more information about Unified Messaging dial plans, see
Understanding
Unified Messaging Dial Plans.
- For more information about how to manage Unified Messaging dial
plans, see Managing Unified
Messaging Dial Plans.
- For more information about ADSI Edit, see Adsiedit Overview.

