Applies to: Exchange Server 2007 SP3, Exchange Server
2007 SP2, Exchange Server 2007 SP1
Topic Last Modified: 2008-07-03
Microsoft Exchange Server 2007 Unified Messaging and Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 can be deployed together to provide voice messaging, Instant Messaging (IM), enhanced user presence, audio-video conferencing, and an integrated e-mail and messaging experience for users in your organization. This topic discusses how to configure Exchange 2007 Unified Messaging and Communications Server 2007 to support these features.
For more information about Communications Server 2007 and to download the reference and Help documentation for Communications Server 2007, see Office Communications Server and Client Documentation Rollup.
 Deploying Exchange Unified
Messaging and Communications Server 2007
Deploying Exchange Unified
Messaging and Communications Server 2007
Exchange 2007 Unified Messaging combines voice messaging and e-mail messaging into a single messaging infrastructure. Communications Server 2007 Enterprise Voice takes advantage of the Unified Messaging infrastructure to provide voice mail, subscriber access, call notification, and auto attendant services.
Before you can implement these services or features, you must do the following:
- Install Communications Server 2007 in the same
Active Directory directory service topology as the Unified
Messaging servers.
- Deploy the following Exchange 2007 server roles:
- Unified Messaging server role The
Unified Messaging server connects Exchange 2007 with
Communications Server 2007.
- Hub Transport server role The Hub
Transport server routes e-mail messages from the Unified Messaging
server to user mailboxes.
- Client Access server role The Client
Access server hosts client protocols, such as Post Office Protocol
3 (POP3), Internet Message Access Protocol 4 (IMAP4), Secure
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTPS),
Outlook Anywhere (formerly known as RPC over HTTP), the
Availability service, and the Autodiscover service. The Client
Access server also hosts Exchange Web services.
- Mailbox server role The Mailbox server
hosts user mailboxes.
For more information about the server roles that are included in Exchange 2007, see Overview. For more information about how to install each server role that is included in Exchange 2007, see New Installation.
- Unified Messaging server role The
Unified Messaging server connects Exchange 2007 with
Communications Server 2007.
- Install Exchange 2007 Service Pack 1 (SP1) on the
computers that have the Unified Messaging server role
installed.
- Install and configure Communications Server 2007 in your
organization, as follows:
- Install Communications Server 2007 on servers in your
organization.
- Install a valid certificate that is valid and signed by a
certification authority on the Communications Server 2007
servers.
- Make sure that the certificate that you installed on the
Communications Server 2007 servers is trusted by the Unified
Messaging servers.
- Confirm that at least one Communications Server 2007 pool
object is created during installation.
- Install Communications Server 2007 on servers in your
organization.
Certificate Configuration Recommendations
You must have a certificate that is trusted by both the computers that are running Microsoft Exchange and Office Communications Server 2007. In an environment that has Office Communications Server 2007 and Exchange 2007 Unified Messaging, use the following guidelines for deploying a trusted certificate:
- Import a certificate that is valid and signed by a
certification authority (CA). This should be a trusted third-party
commercial certificate or a public key infrastructure (PKI)
certificate and should be imported on the Communications Server
2007 computers and the Exchange servers that have the Unified
Messaging and Client Access server roles installed.
- The most simple certificate deployment scenario is to import
the same third-party commercial or PKI certificate to each
Exchange 2007 server that has the following server roles
installed: Unified Messaging, Client Access, and Hub
Transport. Also install this trusted certificate on each
computer that is running Office Communications Server 2007. This
will help simplify your certificate deployment and reduce the
administrative overhead associated with deploying certificates.
However, you must obtain a trusted certificate that supports
Subject Alternative Names (SANs).
 Note:
Note:If you are using a SIP secured or Secured dial plan, a trusted certificate is required between the Unified Messaging servers and the IP gateways or if a direct SIP connection is used. If you are using a SIP secured or Secured dial plan, you can use the same trusted certificate that is used between Communication Server 2007 computers and the Unified Messaging, Client Access, and Hub Transport servers. - Although you can install the Unified Messaging server role and
other Exchange 2007 server roles on the same computer, when
you are deploying Communications Server 2007 we recommend that you
install the Unified Messaging server role on a computer that will
not be running other Exchange 2007 server roles. If another
server role is installed on the same computer as the Unified
Messaging server role, the Microsoft Exchange Unified
Messaging service may select the incorrect certificate and be
unable to use mutual TLS to encrypt traffic. This occurs because of
limitations with subject alternative names found in
certificates
For example, if you install the Unified Messaging server role first, and then later install the Client Access server role on the same server, the Microsoft Exchange Unified Messaging service will use the certificate that is created by the Client Access server role instead of the certificate that was created when the Unified Messaging server role was installed. This is because the Microsoft Exchange Unified Messaging service looks for the certificate in the Trusted Root Store that has the most time left before it will expire.
- Because the trusted certificate uses mutual TLS to establish an
encrypted channel with Communications Server 2007, Client Access,
Hub Transport, and Unified Messaging servers, the name on the
certificate that is used during mutual TLS negotiation must match
the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the server that presents
the certificate.
 Note:
Note:If no PKI, commercial certificate, or self-signed certificate is located in the Trust Root Certification Authorities store on the Unified Messaging server, the Microsoft Exchange Unified Messaging service will create another self-signed certificate and use it for mutual TLS.
 Deployment Path
Deployment Path
After you have installed the required server roles in your Exchange 2007 organization, there is a recommended sequence of steps that you must perform on the Exchange UM environment and in your Communications Server 2007 environment to correctly deploy Enterprise Voice and Exchange 2007 Unified Messaging. Exchange 2007 Unified Messaging is used to provide call answering, Outlook Voice Access, and auto attendant services. Communications Server 2007 enables more advanced features that are found in Enterprise Voice services. The following figure illustrates the recommended deployment path for implementing Enterprise Voice services found with Exchange 2007 Unified Messaging and Communications Server 2007.
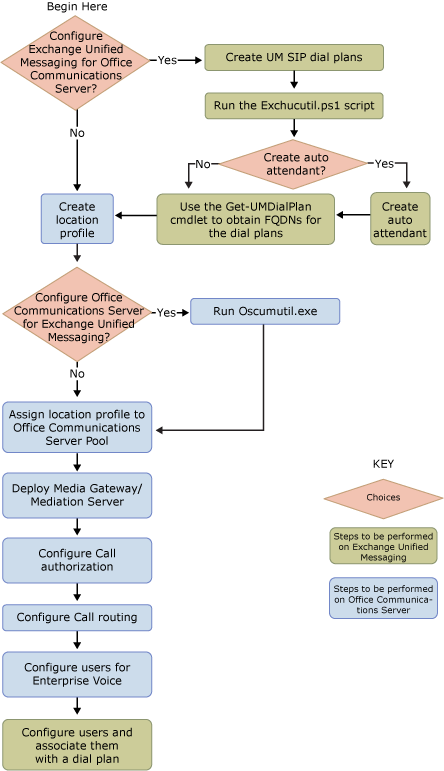
For more information about Communications Server 2007 and to download the reference and Help documentation for Communications Server 2007, see Office Communications Server and Client Documentation Rollup.
There are several steps that you must complete to configure Exchange 2007 Unified Messaging to work with Enterprise Voice in Communications Server 2007. You must do the following:
- Create one or more Exchange 2007 Unified Messaging
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) URI dial plans that each map
to a corresponding Communications Server 2007 location profile. An
Enterprise Voice location profile must be created for
each Exchange UM dial plan. The location profile name has to
match the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) of the UM dial
plans. The Unified Messaging dial plan FQDN is used as the
name of its corresponding location profile. Use the
Get-UMDialPlan cmdlet to obtain the FQDN of a SIP
URI dial plan, and then create its corresponding location profile.
For more information about how to create a SIP URI dial plan, see
How to Create a
Unified Messaging SIP URI Dial Plan.
- Install a certificate on the Unified Messaging servers that is
valid and signed by a certification authority, and then restart the
Microsoft Exchange Unified Messaging service on each
Unified Messaging server.
- To encrypt the VoIP traffic, configure the SIP URI dial plan as
SIP secured or Secured. For more information about
how to configure the security settings on a UM dial plan, see
How to Configure
Security on a Unified Messaging Dial Plan. For more information
about VoIP security and configuring MTLS, see Understanding Unified
Messaging VoIP Security.
Although a Unified Messaging dial plan can be configured as SIP Secured or Secured, we recommend that you configure the dial plan as Secured to enable Microsoft Office Communicator Phone Edition devices to work correctly. This is recommended because of the default encryption level settings that are configured in Communications Server 2007. An Office Communicator Phone Edition device will only work if the encryption settings are configured as they are in the following table. This table shows the relationship between the encryption settings for both Communications Server 2007 and Unified Messaging dial plans.
Encryption settings for Office Communicator Phone Edition
Communications Server 2007 Unified Messaging dial plan Encryption Required (default)
Secured
Encryption Optional
SIP Secured/Secured
No Encryption
SIP Secured
- Add the servers that are running the Unified Messaging server
role to the SIP dial plan. To enable the server to answer incoming
calls, you must add the Unified Messaging server to a dial plan.
For more information about how to add a Unified Messaging server to
a dial plan, see How to Add a Unified
Messaging Server to a Dial Plan.
- Create a SIP address for the users who will be using Enterprise
Voice. For more information about how to create a SIP address for a
UM-enabled user, see How to Add, Remove, or
Modify a SIP Address for a UM-Enabled User.
 Important:
Important:Users who are associated with a SIP URI dial plan cannot receive incoming faxes. This is because incoming voice and fax calls are routed through a Mediation Server and faxing is not supported when you are using a Mediation Server. - Open the Exchange Management Shell and run the exchucutil.ps1
script that is located in the <Exchange Installation
folder>\Exchange Server\Script folder. The exchucutil.ps1 script
does the following:
- Grants Office Communications Server permission to read
Exchange UM Active Directory objects, specifically, the SIP
URI dial plan objects that were created in the previous
task. For more information about how to configure permissions
on Active Directory objects, see How to Use ADSI Edit to Apply Permissions.
- Creates a UM IP gateway object in Active Directory for
each Communications Server pool or for each server that is running
Communications Server 2007 Standard Edition that hosts users who
are enabled for Enterprise Voice. For more information about how to
create a UM IP gateway, see How to Create a New
Unified Messaging IP Gateway.
- Creates an Exchange UM hunt group for each gateway. The hunt
group pilot identifier will be the name of the dial plan that is
associated with the corresponding gateway. The hunt group
must specify the Exchange 2007 Unified Messaging SIP dial
plan that is used with the UM IP gateway. For more information
about how to create a Unified Messaging hunt group, see How to Create a New
Unified Messaging Hunt Group.
- Grants Office Communications Server permission to read
Exchange UM Active Directory objects, specifically, the SIP
URI dial plan objects that were created in the previous
task. For more information about how to configure permissions
on Active Directory objects, see How to Use ADSI Edit to Apply Permissions.
You must also complete the following tasks to configure Communications Server 2007 to work with Exchange 2007 Unified Messaging:
- Create location profiles. The location profile name has to
match the FQDN of the corresponding UM dial plans.
- Assign location profiles to Communications Server 2007
pools.
- Deploy and configure media gateways and Mediation Servers.
- Define telephone usages, voice policies, and outbound call
routes.
- Configure the users for Enterprise Voice services.
- Run the ocsumutil.exe command that creates the contact
objects for subscriber access and for the auto attendant. It also
validates that there is a location profile name whose name matches
the FQDN of the Exchange UM dial plan.
 Note:
Note:When you install Communications Server 2007, the msRTC-SIPLine attribute is added to Active Directory. If you have not installed Communications Server 2007 in your environment, this attribute is not added to Active Directory and caller ID name resolution across dial plans in a single forest and in cross-forest scenarios will not work correctly unless you configure Unified Messaging proxy addresses for users who are not UM-enabled.
For more information about how to perform the tasks that must be completed for Communications Server 2007, see Office Communications Server and Client Documentation Rollup.
After you have configured the Communications Server 2007 and the Unified Messaging servers, you must enable the user to use Communications Server 2007 and install Office Communicator 2007 on the user's client computer.
 For More Information
For More Information
For more information about how to plan an Exchange 2007 Unified Messaging and Communications Server 2007 deployment, see Planning an Exchange 2007 Unified Messaging and Office Communications 2007 Server Deployment.

