Applies to: Exchange Server 2007 SP3, Exchange Server
2007 SP2, Exchange Server 2007 SP1, Exchange Server 2007
Topic Last Modified: 2007-09-24
This topic describes the options for deploying a Microsoft Exchange Server 2007 Edge Transport server role in your existing Exchange Server topology. In addition, the topic explains what to consider when you configure a server that is running Microsoft Internet Security and Acceleration (ISA) Server 2006 as a firewall between your Edge Transport server and Hub Transport server.
Designed to minimize the attack surface, the Edge Transport server handles all Internet-facing mail flow, which provides Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) relay and smart host services for the Exchange organization. Additional layers of message protection and security are provided by a series of agents that run on the Edge Transport server and act on messages as they are processed by the message transport components. These agents support the features that provide protection against viruses and spam and apply transport rules to control message flow.
 Supported Deployments
Supported Deployments
The following deployments are supported:
- Deploy an Exchange 2007 Edge Transport server into an
existing Exchange Server 2003 environment. For more
information, see How to Deploy an Edge
Transport Server in an Existing Exchange Server 2003
Organization.
- Recommended topology: Deploy an Exchange 2007 Edge
Transport server in an Exchange 2007 organization in a
perimeter network, which is also known as the boundary network or
screened subnet, as part of a workgroup or domain. For more
information, see How to Perform a Custom
Installation Using Exchange Server 2007 Setup.
- Deploy an Exchange 2007 Edge Transport server as a member
of the Exchange 2007 organization that has the
Active Directory directory service.
- Deploy more than one Exchange 2007 Edge Transport server
in an Exchange 2007 organization in the perimeter network of a
domain or workgroup.
The recommended option is to deploy the Edge Transport server role outside the Exchange organization in an organization's perimeter network. The Edge Transport server can be deployed as a stand-alone server or as a member of a perimeter Active Directory domain.
For more information about how to deploy an Edge Transport server in an Exchange 2007 organization in a perimeter network, see the following topics:
- Edge
Transport Server Role: Overview
- Planning for
Edge Transport Servers
- Planning for
Edge Transport Server Features
- Subscribing
the Edge Transport Server to the Exchange Organization
- Preparing to
Run the Microsoft Exchange EdgeSync Service
- Configuring
Edge Transport Rules to Manage Viruses
The following table lists the advantages of the different types of Edge Transport server deployment.
| Edge Transport server deployment | Advantage |
|---|---|
|
As part of a domain |
Less secure, easy to manage |
|
As a stand-alone server |
More secure, more difficult to manage |
|
As part of a workgroup |
More secure, more difficult to manage |
|
As a special perimeter forest |
More secure and easy to manage but requires more hardware support (recommended for large enterprises) |
 Note: Note: |
|---|
| You don't have to deploy the Edge Transport server role to deploy Exchange 2007. You can have a single computer that is running the core server roles, such as the Mailbox, Client Access, and Hub Transport server roles, accepting Internet e-mail for your domain and running anti-spam and antivirus programs on that computer. |
When you install an Edge Transport server, you enable anti-spam functionality on that server. When you add an Edge Transport server to your Exchange 2007 perimeter network, you must subscribe the Edge Transport server to an Active Directory site by using the Edge Subscription process if either of the following conditions is true:
- You plan to use the anti-spam features, recipient lookup, or
safelist aggregation,
- You plan to deploy Domain Security with a partner
organization.
When you deploy more than one Edge Transport server in an Exchange 2007 organization in the perimeter network of a domain or workgroup, you can load-balance SMTP traffic among all Edge Transport servers by defining more than one MX resource record with the same priority in the Domain Name System (DNS) database for your mail domain. Deploying more than one Edge Transport server also provides fault tolerance.
The following table compares features that are available for the different deployment options for Edge Transport servers in an Exchange 2007 organization.
Deployment options for Edge Transport servers
| Edge Transport server is not deployed | Edge Transport server is deployed in an Active Directory forest that services the Exchange organization | Recommended: Edge Transport server role is deployed in the perimeter workgroup or perimeter domain | Comments or description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Minimum number of servers |
1 |
2 |
2 |
The Edge Transport server role cannot be installed on the same computer as the other server roles. In the single-server scenario, anti-spam agents are manually deployed on the Hub Transport server role. The Edge Transport server role is not installed. |
|
Network isolation |
No |
No |
Yes |
Spam and malware are rejected before they enter the network only if the Edge Transport server role is deployed at the perimeter network. |
|
Anti-spam agents installed by default |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
If the Edge Transport server role is not deployed, an administrator can enable anti-spam agents on the Hub Transport server role by running an Exchange Management Shell command. For more information, see How to Enable Anti-Spam Functionality on a Hub Transport Server. |
|
Anti-spam user interface |
Anti-spam user interface is not visible by default. It is enabled after anti-spam agents are deployed manually. |
Visible by default |
Visible by default |
The Exchange Management Console provides a user interface for configuring the following:
|
|
Internet e-mail processing |
Internet e-mail processing is enabled only after you set the Internet usage type on the Receive connector, and create a new Send connector with the Internet usage type. |
Yes |
Yes |
For more information, see How to Configure Connectors for Internet Mail Flow. |
|
Connection Filtering |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Connection filtering provides IP Block lists and IP Allow lists to protect against spam. For more information, see Connection Filtering. |
|
Sender Filtering |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Sender reputation is dynamically analyzed and updated over time. For more information, see Sender Filtering. |
|
Recipient Filtering |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Recipients are validated by using the global address list (GAL). For more information, see Recipient Filtering. |
|
Microsoft Exchange EdgeSync service |
Not applicable |
Yes |
Yes |
Microsoft Office Outlook Safe Senders lists and the GAL are pushed in encrypted format to the network perimeter. |
|
Sender ID |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Sender ID is checked when e-mail is received and included in spam rating. For more information, see Sender ID. |
|
Content Filtering (Intelligent Mail Filtering) |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Regular Microsoft SmartScreen updates help counter spam and phishing threats. For more information, see How to Configure Anti-Spam Automatic Updates. |
|
Spam confidence level |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
A spam confidence level (SCL) rating is assigned to a message, based on several factors. For more information, see Adjusting the Spam Confidence Level Threshold. |
|
Anti-spam stamp |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Messages are stamped with details of spam assessment. For more information, see Anti-Spam Stamps. |
|
Back pressure and tarpitting |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Back pressure and tarpitting protect against denial of service and directory harvest attacks. For more information, see the Understanding Back Pressure and the "Tarpitting Functionality" section of Recipient Filtering. |
|
Two-tiered spam quarantine |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
An administrator can access the spam quarantine folder and release a message to its recipient. For more information, see Spam Quarantine. |
|
Attachment Filtering |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Attachments are removed based on size, content, or file type. For more information, see Attachment Filtering. |
|
Forefront Security for Exchange Server |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
For more information, see Protecting Your Microsoft Exchange Organization with Microsoft Forefront Security for Exchange Server. |
Network Adapter Configuration in the Perimeter Network
Depending on the network adapter (also known as NIC) configuration or firewall configuration in your perimeter network topology, you can deploy an Edge Transport server as a multi-homed bastion host configuration or as a single-homed, or screened subnet, configuration as shown in the following figure.
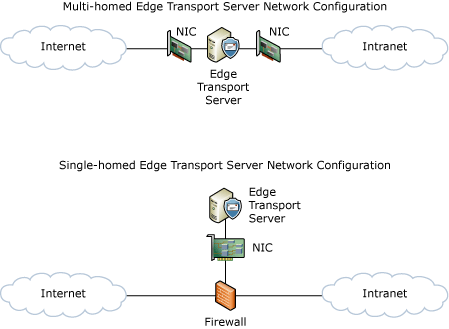
In a multi-homed configuration, a host is connected to two or more networks or has two or more network addresses. In a single-homed configuration, there is a single firewall with three network adapters or NICs. This is generally known as a triple-homed firewall.
In both the multi-homed configuration and the single-homed configuration, you can have one or more IP addresses to configure Send connectors and Receive connectors accordingly on your Edge Transport servers and Hub Transport servers. For more information about how to configure connectors, see Managing Connectors.
 What to Consider When You Deploy
an Edge Transport Server Together with
ISA Server 2006
What to Consider When You Deploy
an Edge Transport Server Together with
ISA Server 2006
You can configure an Edge Transport server or Hub Transport server together with Microsoft Internet Security and Acceleration (ISA) Server 2006 to protect your corporate network and applications. For more information about how to configure an ISA Server 2006 firewall between your Hub Transport servers and Edge Transport servers, see Using ISA Server 2006 with Exchange 2007.
When you configure ISA Server 2006 in your Exchange organization with Edge Transport servers and Hub Transport servers, if you want to allow SMTP or SMTPS (secure SMTP) traffic to flow between Edge Transport servers and Hub Transport servers, follow these guidelines:
- If SMTP traffic from the Edge Transport server to the Hub
Transport server is being filtered through the server that is
running ISA Server 2006, disable the SMTP filter on that
server.
- If SMTPS traffic from the Edge Transport server to the Hub
Transport server is being filtered through the server that is
running ISA Server 2006, disable the SMTP filter for this
option on that server too.
Or, if you don't want to disable SMTP or SMTPS filtering on the server that is running ISA Server 2006, you can add SMTP verb commands, such as X-ANONYMOUSTLS and X-EXPS, which are unique to Exchange 2007, to the SMTP filter add-in on ISA Server 2006.
For more information about how to disable SMTP or SMTPS filtering on ISA Server 2006 or how to add SMTP verb commands to ISA Server 2006, see Messages Queue on an Edge Transport Server with 500 5.1.1 Unrecognized Command Error.
 For More Information
For More Information
For more information, see the following topics:
- Planning for
Anti-Spam and Antivirus Features
- Planning
Antivirus Deployment
- Planning for
Coexistence
- How to
Deploy an Edge Transport Server in an Existing Exchange Server 2003
Organization
- New
Anti-Spam and Antivirus Functionality
- Managing
Anti-Spam and Antivirus Features
- Overview of
Transport Rules
- Deployment
Options for Hub Transport Servers
- How to
Configure Internet Mail Flow Directly Through a Hub Transport
Server

