Applies to: Exchange Server 2007 SP3, Exchange Server
2007 SP2, Exchange Server 2007 SP1
Topic Last Modified: 2008-06-18
Microsoft Exchange Server 2007 Unified Messaging uses information about the calling and called parties to perform a name lookup. This lookup makes it possible for the caller's name to be sent with missed call notifications or when a caller leaves a voice message for a UM-enabled user. This topic discusses how the calling party information is used to try to resolve the name of the caller.
 Caller ID
Caller ID
Caller ID is a service that is provided by telephone companies that can tell the person who is receiving a call the telephone number and sometimes the name of the person who is calling and other information about the call. This information is sent over a serial cable by using call signaling. When a call is received by a PBX or IP PBX from a telephone company, the call includes calling identification information such as the following:
- The calling party's number.
- The called party's number.
- Status codes that indicate such things as the following:
- Ring-no-answer (The phone rang but the called party didn't
answer)
- The state or condition of the telephone line
- Line busy (The call connected but the line is busy)
- Call forward always (The incoming call is always forwarded to
another number)
- Ring-no-answer (The phone rang but the called party didn't
answer)
- The line or port number that is being used for the call.
For more information about calling and called party identification and the telephony interfaces that are used with Exchange 2007 Unified Messaging, see Understanding PBX and IP PBX Configurations.
 Name Lookup Process
Overview
Name Lookup Process
Overview
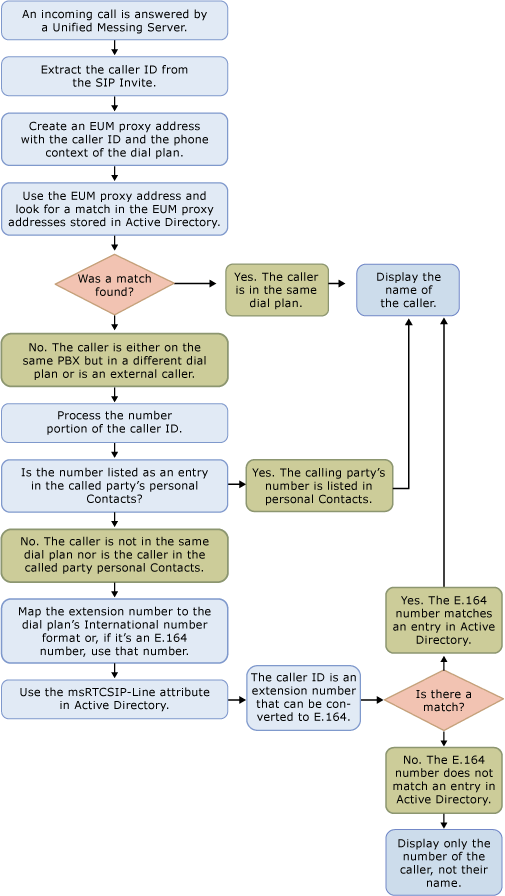
Exchange 2007 Unified Messaging uses two data sources to receive information about the calling party and to map it to the name of the caller: Active Directory and personal Contacts. When the name lookup process is successful, the name of the calling party will be inserted into voice mail messages and missed call notifications if they have been enabled for the called party. When an incoming call is received, the calling party information is passed to a Unified Messaging server. The Unified Messaging server tries to perform the name lookup by doing the following:
- If the caller's identity is already known because they are
already logged on to their mailbox and placed the call by using
Outlook Voice Access, Office Communicator 2007, or Office
Communicator Phone Edition, Unified Messaging server uses the name
that is provided.
- If the caller's identity is not known:
- The Unified Messaging server uses the E.164 number or extension
to search the EUM proxy addresses that are configured and stored in
Active Directory to find a match. If the number contains an at sign
(@), the Unified Messaging server searches the SIP proxy addresses
that are configured and stored in Active Directory.
- If the number has not been resolved by using one of the methods
above, the Unified Messaging server searches the personal Contacts
of the called party for the name of the calling party.
- If the number is not resolved to the name of the caller by
using one of the methods above and the Exchange environment
includes Office Communications Server 2007, the
msRTCSIP-Line attribute is used. The msRTCSIP-Line
attribute is added as part of the Active Directory schema
extensions that are installed by Office Communications Server 2007.
A number in the E.164 format is required. However, if the number is
not in the correct format, the International number format property
on the called party's dial plan will be used to extend the number
into the correct E.164 format.
- The Unified Messaging server uses the E.164 number or extension
to search the EUM proxy addresses that are configured and stored in
Active Directory to find a match. If the number contains an at sign
(@), the Unified Messaging server searches the SIP proxy addresses
that are configured and stored in Active Directory.
- If these methods do not successfully locate the name of the
calling party, the telephone number or extension will be inserted
into the voice message for the called party. If missed call
notifications are enabled for the called party, the telephone
number or extension will also be included in the missed call
notification message that is sent to them.
 Caution:
Caution:Telephone numbers that can be configured on the Telephones tab in Active Directory are not used by Unified Messaging to perform name lookups.
The following figure shows the steps that are performed by a Unified Messaging server when it tries to perform a name lookup from the calling party information that is provided.
 For More Information
For More Information
For more information about Exchange 2007 Unified Messaging and Office Communications Server 2007, see Planning an Exchange 2007 Unified Messaging and Office Communications 2007 Server Deployment.

