Applies to: Exchange Server 2007 SP3, Exchange Server
2007 SP2, Exchange Server 2007 SP1, Exchange Server 2007
Topic Last Modified: 2006-09-20
You can classify your Microsoft Exchange organization in the following three ways:
- Logical topology
-
A logical topology refers to the Active Directory directory service forest structure. For more information about logical topologies, see Logical Topologies.
- Physical topology
-
The physical topology refers to the physical sites and computers in your Exchange organization. For more information about physical topologies, see Physical Topologies.
- Exchange organization topology
-
The Exchange organization topology refers to the Exchange server roles and how you position them within the physical and logical topologies. Your Exchange organization should fit into one of the following predefined Exchange organization topologies:
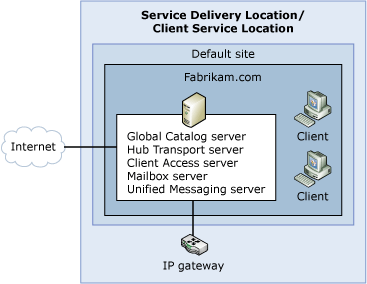
- Simple Exchange organization
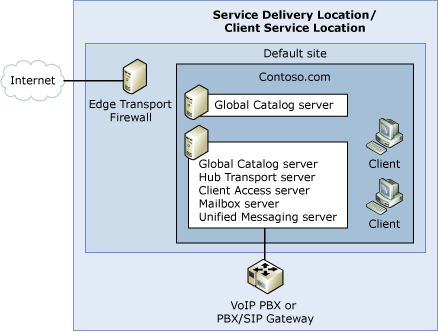
- Standard Exchange organization
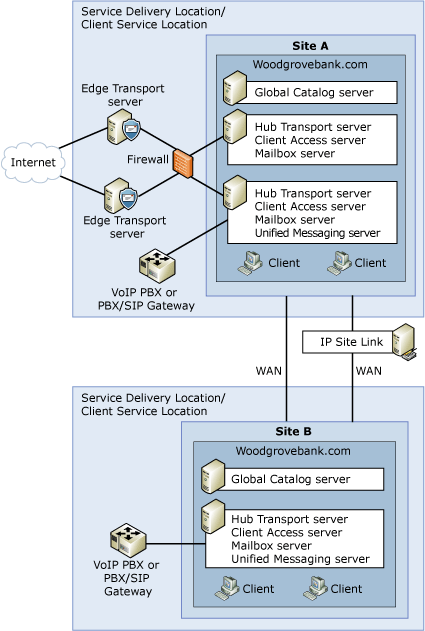
- Large Exchange organization
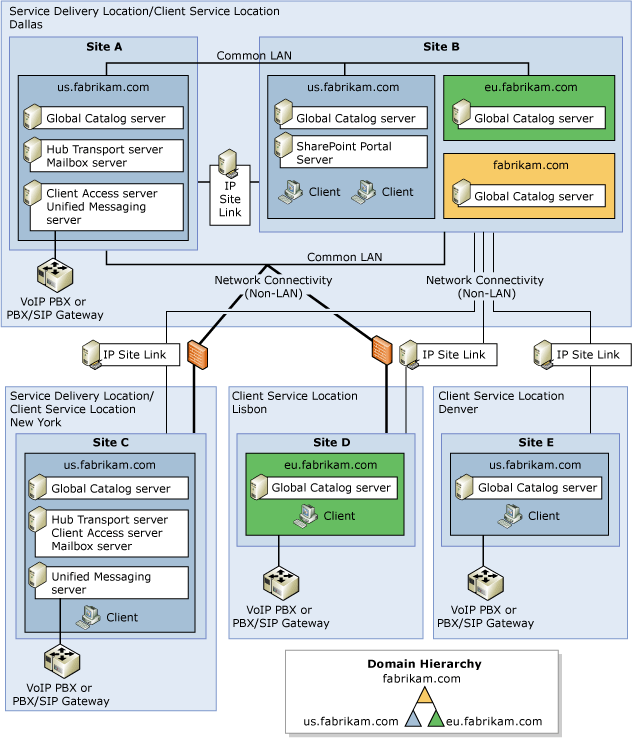
- Complex Exchange organization
For more information about Exchange topologies, see the following topics:
- Simple Exchange organization
 Examples of Exchange
Organization Topologies
Examples of Exchange
Organization Topologies
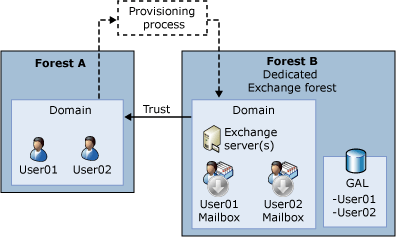
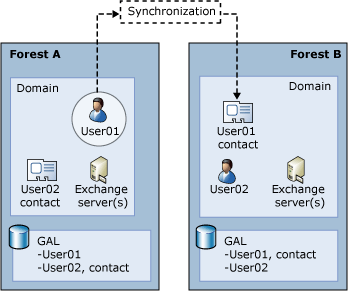
The following figures show examples of the four predefined Exchange organization topologies.